Effective management of references is a crucial aspect of thesis writing, ensuring academic integrity and streamlining the research process. As the volume of sources grows, traditional manual methods can become overwhelming and prone to errors. Incorporating artificial intelligence into reference organization offers a transformative solution, enhancing efficiency and accuracy throughout the scholarly journey. This approach not only simplifies the collection and classification of sources but also ensures consistency in citation formatting and seamless updates, ultimately empowering researchers to focus more on the intellectual content of their work.
Overview of reference management in thesis writing
Effective reference management is a cornerstone of scholarly writing, ensuring that all sources are accurately documented and easily accessible throughout the research process. Proper organization of references not only maintains academic integrity by giving appropriate credit to original authors but also streamlines the workflow, allowing researchers to focus more on analysis and synthesis rather than administrative tasks. In thesis writing, where multiple sources spanning various formats and disciplines are involved, systematic management of citations becomes indispensable to produce a coherent and credible document.
Managing an extensive array of sources manually can present numerous challenges. These include the risk of misplaced or duplicated references, inconsistent citation styles, and the significant time commitment required for searching, formatting, and updating references. As the volume of references grows, maintaining accuracy and consistency becomes increasingly difficult, often leading to frustration and potential errors that may undermine the credibility of the thesis.
Consequently, researchers need efficient methods to organize and cite their sources reliably and swiftly.
Traditional versus AI-assisted reference organization methods
The traditional approach to reference management typically involves manual recording and organization of sources using tools like spreadsheets, index cards, or basic word processor functions. While straightforward, this method is labor-intensive and prone to human error, especially when dealing with numerous references. Manual systems require meticulous attention to detail to ensure proper citation formatting, which can become overwhelming as the number of sources increases.
AI-assisted reference organization introduces advanced tools and software that automate many aspects of the process. These systems can automatically extract citation details from digital sources, suggest proper citation styles, and organize references into structured databases. For example, AI-powered reference managers like Zotero or EndNote employ algorithms that can detect duplicates, update references based on new information, and integrate seamlessly with word processing applications.
Such intelligent tools significantly reduce the workload, enhance accuracy, and facilitate real-time updates, making the process more efficient and less error-prone. They also support collaborative efforts, enabling multiple users to share and manage references effortlessly. Overall, AI-assisted methods represent a substantial upgrade over traditional manual techniques, aligning with the needs of modern academic research for reliability and efficiency.
Tools and technologies for AI-assisted reference management
In the landscape of thesis writing, the integration of AI-powered tools has revolutionized the way researchers and students manage their references. These advanced technologies not only streamline the process of organizing citations but also enhance accuracy and efficiency, allowing writers to focus more on content development rather than manual referencing tasks. AI-assisted reference management tools leverage machine learning algorithms to automate citation formatting, detect duplicate entries, and suggest relevant sources based on contextual analysis, thereby elevating the overall quality and reliability of scholarly work.
Understanding the capabilities, advantages, and limitations of these tools is essential for selecting the most suitable option for individual research needs. The following overview highlights prominent AI-driven reference management software, emphasizing their core features, integration capabilities, and compatibility with various writing platforms and citation styles.
AI-powered reference management software options
| Tool | Features | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zotero |
|
|
|
| EndNote |
|
|
|
| Mendeley |
|
|
|
| RefMed |
|
|
|
Many of these tools feature seamless integration with popular writing platforms such as Microsoft Word, Google Docs, and LaTeX editors, enabling users to insert citations and generate bibliographies effortlessly. Compatibility with multiple citation styles, including APA, MLA, Chicago, and custom formats, further enhances flexibility. AI capabilities across these platforms facilitate automatic detection and correction of citation errors, suggestion of relevant sources, and organization of references based on thematic or chronological criteria, contributing significantly to the coherence and professionalism of thesis documents.
Methods for collecting and inputting references using AI
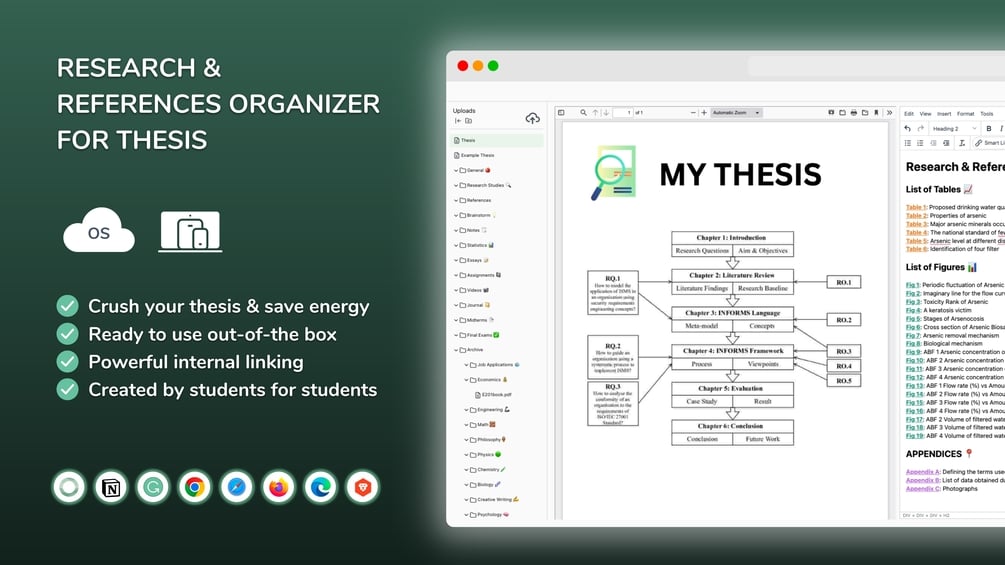
Effective management of references is a cornerstone of high-quality thesis writing, and leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) can significantly streamline this process. Incorporating AI-driven techniques allows researchers to efficiently gather, organize, and input bibliographic data from diverse sources, reducing manual effort and minimizing errors. This section explores practical methods for collecting and inputting references using AI tools, emphasizing automated data extraction, batch processing, and structured workflows.AI methodologies for collecting and inputting references enhance the accuracy and speed of compiling bibliographies.
These techniques utilize advanced algorithms and machine learning models to automatically retrieve, parse, and categorize reference data from a wide range of online sources, including digital libraries, journal repositories, and academic databases. By integrating these methods into the research workflow, scholars can ensure their references are comprehensive, correctly formatted, and readily accessible for citation management and literature review purposes.
Importing references from digital databases and online sources
The cornerstone of AI-assisted reference collection lies in seamlessly importing citations from various digital repositories and online platforms. Modern reference management software, integrated with AI capabilities, can connect directly with databases such as PubMed, Google Scholar, Scopus, and Web of Science. These integrations typically involve APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that allow for direct querying and retrieval of bibliographic records.To utilize these features, researchers initiate a search within the database interface, often aided by AI-powered search filters that can refine and prioritize results based on relevance, publication date, or relevance.
Once the desired references are identified, the software can automatically import the citation details—including authors, titles, publication dates, volume and issue numbers, and digital object identifiers (DOIs)—into the reference library. This process eliminates manual data entry, reduces typographical errors, and accelerates the compilation process.
Automated extraction of metadata and bibliographic information
AI-driven tools excel in automatically extracting comprehensive metadata from digital sources, ensuring that each reference contains complete and accurate information. These tools typically employ natural language processing (NLP) and pattern recognition algorithms to parse PDF files, web pages, or digital documents and identify key bibliographic components.For example, when a researcher downloads a PDF of a journal article, AI software can scan the document to extract metadata such as the title, authorship, journal name, publication year, and s.
Additionally, AI algorithms can recognize patterns like citation formats, DOI links, and page numbers. This automated extraction guarantees consistency across references and minimizes the risk of missing critical data, which is essential for precise citation and bibliography generation.
“AI-based metadata extraction not only accelerates reference collection but also enhances the accuracy and completeness of bibliographic records, supporting rigorous academic standards.”
Designing an organized workflow for batch importing and categorizing references
Developing a systematic workflow for batch importing and categorizing references maximizes efficiency and keeps the research library organized. An effective process involves several key steps:
- Collect multiple references from digital databases or files in formats like RIS, BibTeX, or EndNote XML, which are compatible with most reference management tools.
- Use AI-enabled import functions to automatically parse and categorize references based on predefined criteria, such as subject area, publication type, or relevance.
- Implement tagging and assignment features within the software, facilitated by AI suggestions based on the content of each reference, to enable easy retrieval and grouping.
- Establish rules for automatic deduplication, ensuring that duplicate entries are identified and merged without manual intervention, thereby maintaining a clean library.
- Regularly review and refine categorization criteria, leveraging AI insights to adapt to evolving research themes or new sources.
This organized workflow ensures that references are not only imported efficiently but also systematically categorized, making subsequent citation, review, and analysis more manageable. By combining AI capabilities with structured processes, researchers can maintain a comprehensive, accurate, and accessible bibliographic database throughout their thesis journey.
Structuring References with AI Algorithms
Effective organization of references is a cornerstone of a well-crafted thesis. Leveraging AI algorithms enhances this process by automating classification and formatting, thereby saving time and increasing accuracy. AI-driven structuring not only streamlines the management of large reference datasets but also ensures consistency across citation styles, which is vital for academic credibility and compliance with institutional guidelines. Incorporating AI into reference structuring facilitates a more efficient workflow, allowing researchers to focus on analysis and writing rather than manual sorting and formatting tasks.AI algorithms can significantly improve the organization of references by classifying them based on various criteria such as type, relevance, or topic.
This capability allows for tailored retrieval and better thematic coherence within the thesis. Moreover, customizable AI settings enable users to adapt classification parameters to specific project needs, ensuring that the system aligns with particular research scopes and citation requirements. Additionally, AI-assisted tools can automatically generate citation entries in multiple formats—such as APA, MLA, Chicago, or IEEE—adapting dynamically to the context of the thesis and the target publication or institution’s standards.
Classifying References by Type, Relevance, or Topic
AI algorithms utilize machine learning and natural language processing techniques to analyze reference data, enabling precise classification based on predefined criteria. These systems can distinguish between journal articles, books, conference papers, theses, and other source types with high accuracy by examining metadata and content cues. Relevance classification involves analyzing the thematic content of references in relation to the thesis topic.
AI models trained on domain-specific corpora can assess the contextual importance of each reference, ranking or grouping them accordingly. For example, in a thesis on renewable energy, AI can prioritize recent peer-reviewed articles over less relevant historical texts, ensuring the researcher focuses on the most impactful sources.Topic classification employs algorithms to group references into thematic clusters. These can be visualized as digital folders or tags, making it easier for the researcher to navigate extensive bibliographies.
For instance, references related to solar power technology can be categorized separately from those focusing on policy implications, facilitating targeted review and citation.
Customizing AI Settings for Thesis Needs
Personalizing AI algorithms enhances their effectiveness and ensures they serve the specific requirements of a thesis project. Customization involves setting parameters such as classification criteria, relevance thresholds, and preferred citation styles. The process begins with selecting the reference types or topics most pertinent to the research. Users can train AI models by providing sample references, allowing the system to learn and adapt to the specific language and metadata conventions of their field.
Adjusting relevance sensitivity helps to fine-tune how strictly references are filtered or prioritized, balancing comprehensiveness with specificity.Implementing these custom settings typically involves navigating the AI tool’s user interface, accessing preference panels, and inputting domain-specific s or categories. For example, a thesis on biomedical engineering might require AI algorithms to focus on recent journal articles within the last five years, excluding older or less relevant sources.
Automatic Generation of Citation Entries in Various Formats
Automation of citation formatting is a significant advantage of AI-assisted reference management, reducing manual effort and minimizing errors in conforming to style guides. Once references are classified and inputted into the system, AI tools can generate properly formatted citation entries that adhere to the chosen style, whether APA, MLA, Chicago, or others.The process involves mapping reference metadata—author names, publication dates, titles, journal names, volume, issue, pages, URLs, etc.—to the syntax rules of each style.
AI algorithms utilize built-in style templates or rule-based engines that automatically adapt citation entries accordingly. For example, in the APA style, the system will format an article as: Author(s). (Year). Title. Journal Name, Volume(Issue), pages.
DOI or URL.This automation extends to in-text citations, reference lists, and bibliographies, ensuring consistency and saving considerable time during the writing process. Advanced AI tools also provide real-time updates if citation details are modified, maintaining synchronization across all reference entries and in-text citations. These systems can further integrate with word processors, allowing seamless insertion and updating of references within the thesis document.
Organizing References within a Thesis Document
Embedding and organizing references effectively within a thesis is crucial for maintaining academic integrity, ensuring clarity for readers, and facilitating smooth editing processes. Utilizing AI tools for managing references can significantly enhance accuracy and efficiency throughout the writing journey. Proper integration of citations not only supports the credibility of the research but also streamlines the process of updating references as the thesis evolves.
AI-assisted reference organization involves strategic embedding of citations directly into the manuscript, maintaining consistency across various sections, and adapting to different citation styles. Implementing systematic procedures for managing references helps prevent discrepancies, ensures uniformity, and simplifies updates—especially when dealing with extensive bibliographies or multiple referencing styles.
Strategies for Embedding References Using AI Tools
AI tools facilitate seamless integration of references into the manuscript by automating citation insertion during the writing process. These tools can detect when a reference is needed, suggest appropriate citations based on context, and insert formatted citations according to the selected style. Integrating references with AI also allows real-time synchronization with reference databases, reducing manual errors and saving time.
For example, when drafting a paragraph discussing recent advances in machine learning, an AI tool can automatically suggest and embed relevant citations from a linked reference library. Furthermore, AI can assist in ensuring that citations are placed accurately within the text, such as within parentheses or as part of a narrative, depending on the chosen citation style.
Illustrative Citation Styles and Their Applications
Different academic disciplines and journals require specific citation styles, each with unique formatting rules. To visualize this, the following table summarizes common styles, their typical application, and key formatting features:
| Style | Application | In-Text Citation Format | Reference List Format |
|---|---|---|---|
| APA | Social sciences, Psychology, Education | (Author, Year) | Author, A. A., & Author, B. B. (Year). Title of work. Publisher. |
| MLA | Humanities, Literature, Arts | (Author 123) | Author Last Name, First Name. Title of Book. Publisher, Year. |
| Chicago | History, Business, Fine Arts | Footnotes or Author-Date | Author Last Name, First Name. Year. Title of Work. Publisher. |
| IEEE | Engineering, Computer Science | [Number] | Numbered list: Author(s), “Title,” Journal/Conference, vol., no., pages, Year. |
Procedures for Maintaining Consistency and Updating References
The integrity of the referencing system within a thesis hinges on consistent formatting and timely updates, especially as new references are added or existing ones are modified. AI-powered reference management tools facilitate these processes through automated synchronization, version control, and style enforcement.
Implementing a centralized reference database enables tracking all sources in a structured manner. When a change occurs, AI tools can propagate updates throughout the manuscript, ensuring all citations are current and formatted uniformly. Regularly reviewing reference entries, utilizing built-in validation features, and setting up style templates further enhance consistency. For example, if a student switches from APA to Chicago style midway, AI can reformat all the citations and bibliography entries accordingly, avoiding manual rework and potential errors.
Periodic audits using AI checks ensure that all references conform with institutional or publication-specific guidelines. Moreover, integrating reference management software with word processors allows dynamic updating of citations, making the process of maintaining consistency and accuracy an integral part of thesis writing.
Automating Reference Updates and Maintenance
Efficient management of references in a thesis requires continuous updates and maintenance to ensure accuracy, relevance, and consistency. Leveraging AI technologies to automate these processes not only reduces manual effort but also enhances the integrity of the scholarly work. This section explores methods for AI to detect and incorporate new sources or corrections, procedures for synchronizing reference lists across multiple chapters, and the use of AI alerts to identify outdated or duplicate references, ensuring a seamless and up-to-date bibliography throughout the thesis writing process.
Methods for AI to Detect and Incorporate New Sources or Corrections
Maintaining an accurate and comprehensive reference list is vital as new research emerges and existing sources evolve. AI-driven systems can continuously monitor relevant databases, repositories, and journals for new publications or updates to existing references. These systems use natural language processing (NLP) algorithms to analyze metadata, abstracts, or full texts, identifying citations that fit the thesis’s scope.Such AI tools can automate the identification and extraction of bibliographic information from new publications, simplifying the process of incorporating the latest sources.
When discrepancies or errors are detected in references—such as incorrect author names, publication dates, or titles—AI algorithms can compare existing entries against authoritative databases like CrossRef, PubMed, or Google Scholar. If inconsistencies are found, the AI can suggest corrections or automatically update the references, subject to user approval.This proactive updating ensures that the reference list remains current, accurate, and comprehensive, reflecting the most recent developments in the field without requiring extensive manual oversight.
Procedures for Synchronizing Reference Lists Across Multiple Chapters or Sections
In multi-chapter theses, maintaining consistency in references across various sections is crucial to avoid duplication or conflicting citations. AI-powered reference management systems employ synchronization procedures that dynamically link citation data across all parts of the document.These procedures involve establishing a centralized repository of references that is accessible and editable by the AI system. When a reference is added or modified in one chapter, the AI automatically propagates these changes to other sections that cite the same source.
This synchronization is typically achieved through unique identifiers, such as Digital Object Identifiers (DOIs) or persistent keys, ensuring that each reference remains uniform throughout the thesis.Moreover, AI can perform periodic consistency checks, flagging any discrepancies or orphaned references—those cited but not listed or vice versa—and recommend corrections. This approach minimizes manual reconciliation efforts and guarantees that the reference list is coherent and synchronized across all chapters.
Leveraging AI Alerts for Outdated or Duplicate References
AI systems can be configured to continuously analyze the reference database for potential issues that compromise the quality of the bibliography. Using pattern recognition and database cross-referencing, AI alerts can highlight outdated references, such as sources that have been retracted, superseded by newer research, or have updated versions.These alerts help authors promptly replace or update references, maintaining the scholarly rigor of the thesis.
Additionally, AI can detect duplicate references by comparing bibliographic data, and identify instances where the same source has been cited multiple times with slight variations in formatting or metadata. Such duplicates can be consolidated to streamline the reference list and avoid confusion.AI-driven notification mechanisms can proactively inform authors of these issues via dashboard alerts, email notifications, or in-application prompts. By integrating these alerts into the writing workflow, authors can address reference anomalies efficiently, ensuring the bibliography remains accurate, up-to-date, and free of redundancies.
Ensuring accuracy and compliance with citation standards
Maintaining precision in references is fundamental to the integrity and credibility of a thesis. Employing AI-driven techniques to verify the completeness and correctness of references enhances the reliability of scholarly work while streamlining the citation management process. Such automation supports researchers in adhering strictly to established citation standards across various disciplines and style guides, thereby reducing unintentional errors and increasing efficiency.AI techniques for verifying reference completeness and correctness incorporate advanced algorithms capable of cross-referencing citation data with authoritative databases, such as CrossRef, PubMed, or Google Scholar.
These algorithms can identify missing information—such as author names, publication years, journal titles, or DOI numbers—and suggest corrections where discrepancies are detected. Machine learning models trained on vast datasets can also recognize patterns of common citation errors and alert users to potential inaccuracies before submission.To ensure compliance with specific citation standards like APA, MLA, or Chicago, AI tools utilize rule-based formatting engines that automatically adjust reference entries to match the required style guidelines.
These engines consider nuances such as punctuation, italicization, order of elements, and capitalization rules. For example, when formatting an APA reference, the AI system will ensure the author’s name appears in last name, initials format, the publication year is enclosed in parentheses, and the journal title is italicized, maintaining consistency throughout the bibliography.Generating reports or summaries of reference accuracy provides valuable insights into the overall quality of the reference list.
AI-powered reporting tools can compile detailed summaries highlighting the number of references verified, identified errors, and suggestions for correction. These reports can include visual dashboards that display error patterns, such as frequent missing DOIs or inconsistent author name formats, enabling researchers to quickly identify and address issues prior to final submission.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Automated completeness check | Verifies that all essential reference components are present, such as author, year, title, source, and identifiers like DOI or ISBN. |
| Consistency validation | Ensures uniform application of citation rules across the entire reference list, detecting anomalies or deviations from style guidelines. |
| Error reporting | Provides detailed lists of detected issues, with suggestions for correction according to the selected citation style. |
| Style-specific formatting | Automatically formats references to adhere to specific style guides, minimizing manual formatting efforts. |
| Summary dashboards | Visual reports that display the accuracy level, common errors, and progress over the reference verification process. |
Implementing AI techniques in reference verification not only reduces manual workload but also significantly enhances the accuracy, consistency, and compliance of scholarly references, thereby strengthening the overall quality of thesis documentation.
Enhancing Referencing Workflows with AI-Generated Suggestions
Integrating AI-generated recommendations into the thesis referencing process can significantly streamline research efforts, enhance the relevance of cited sources, and improve overall accuracy. By leveraging advanced algorithms capable of analyzing thesis content, researchers can receive tailored suggestions for pertinent literature, thereby enriching their scholarly work while saving valuable time. This approach not only complements traditional reference management methods but also elevates the efficiency and precision of source selection within academic writing.
In practical terms, AI-powered suggestion systems analyze key themes, s, and contextual cues from the thesis draft to identify academic articles, books, and other credible sources that align with the research focus. These recommendations can be dynamically updated as the thesis evolves, providing continuous support throughout the writing process. When employed effectively, AI suggestions serve as a valuable tool for broadening literature reviews, filling research gaps, and ensuring a comprehensive and up-to-date bibliography.
Methods for AI to Recommend Relevant Sources Based on Thesis Content
AI recommendation systems utilize a combination of natural language processing (NLP), semantic analysis, and machine learning algorithms to interpret the thesis content and suggest relevant references. These methods include:
- Extraction and Topic Modeling: AI tools extract key phrases and conceptual themes from the thesis draft, then match these with extensive academic databases to identify pertinent sources.
- Semantic Similarity Analysis: Using embedding models such as BERT or Word2Vec, AI evaluates the semantic closeness between thesis sections and potential references, ensuring recommendations are contextually relevant.
- Citation Network Analysis: AI examines existing citation networks within digital repositories to identify influential and related works that have shaped similar research topics.
- Content-Based Filtering: Based on the thesis content, AI filters sources by relevance, publication recency, and credibility, prioritizing high-quality references that align with the research scope.
These approaches enable AI to generate a prioritized list of suggested references that are both pertinent and authoritative, tailored to the specific needs of the thesis writer.
Evaluating and Selecting Suggested References
Effective integration of AI recommendations requires careful evaluation of suggested sources to ensure their relevance and credibility. The process involves:
- Assessing Relevance: Examine the title, abstract, and s of each suggested source to determine alignment with the thesis themes. AI tools may offer snippets or summaries to facilitate quick assessment.
- Checking Credibility and Impact: Review citation counts, publication venues, and author profiles. Reputable sources from peer-reviewed journals or established publishers should be prioritized.
- Cross-Referencing Citations: Verify whether the suggested references are cited by other authoritative works in the field, indicating their influence and reliability.
- Contextual Integration: Determine how well each source complements existing references and whether it fills identified gaps or offers new perspectives.
In practice, the selection process involves a combination of automated ranking provided by AI and manual review by the researcher to ensure depth, accuracy, and relevance.
Tips for Seamless Integration of AI Suggestions into the Writing Process
To maximize the benefits of AI-generated recommendations, consider the following strategies:
- Regularly Update AI Recommendations: Incorporate ongoing suggestions as the thesis develops, ensuring the bibliography remains current and comprehensive.
- Use AI-Generated Annotations: Leverage AI tools that provide summaries or key points of suggested sources to facilitate quick evaluation.
- Maintain a Critical Perspective: While AI suggestions are valuable, always review sources manually for relevance, credibility, and alignment with research objectives.
- Integrate Suggestions into Reference Management Software: Use compatible platforms that allow direct import of AI-recommended references, streamlining citation insertion and formatting.
- Balance Automation with Manual Input: Incorporate AI suggestions as a supplement rather than a replacement for rigorous literature review practices, ensuring scholarly integrity.
By following these tips, thesis writers can efficiently incorporate AI-driven reference suggestions, enriching their bibliographies while maintaining high standards of academic rigor and accuracy.
Visualizing Reference Networks and Relationships
Effective visualization of reference networks provides a powerful means to understand and interpret the complex web of citations and scholarly influence within a thesis. AI-driven tools can generate detailed visual maps that illustrate how sources are interconnected, highlighting key nodes of influence and thematic clusters. These visualizations not only facilitate a clearer comprehension of the scholarly landscape but also enhance the presentation quality of the thesis by offering intuitive, visual representations of research connections.
Automated visualization leverages AI algorithms to analyze citation data, identify relationship patterns, and produce diagrams that depict the network of references. These diagrams can vary from simple node-link diagrams to more sophisticated clusters or heatmaps, depending on the depth of analysis. Integrating these visual maps into thesis presentations can effectively communicate the scope, influence, and interdisciplinary nature of the research, making complex citation relationships accessible and engaging for audiences.
Creating Citation Relationship Maps with AI
AI can analyze vast bibliometric data to identify citation patterns and influence pathways among scholarly sources. By processing citation databases, AI algorithms detect how sources cite each other, revealing influential works, emerging research clusters, and interdisciplinary connections. The generated maps typically represent each source as a node, with links indicating citation relationships, enabling researchers to visualize the flow of knowledge and identify seminal works within their field.
Advanced AI tools incorporate features such as dynamic zooming, filtering by publication date or relevance, and color-coding based on thematic categories. These features allow researchers to explore the network from different perspectives, such as chronological development or thematic connections, providing a comprehensive understanding of the research landscape.
Designing Diagrams to Display Source Connections and Influence
Designing effective citation maps involves clarity, simplicity, and meaningful representation of relationships. When creating diagrams, it is crucial to focus on the most significant connections to avoid clutter and enhance interpretability. Consistent use of colors, node sizes, and edge thicknesses can encode additional information such as citation frequency, source impact, or thematic relevance.
Diagrams should be organized hierarchically or clustered based on research themes or chronological order to facilitate understanding of the development and influence of ideas over time. Balancing detail with visual clarity ensures that the map serves as a useful analytical and presentation tool, guiding viewers through the scholarly influences that underpin the thesis.
Incorporating Visualizations into Thesis Presentations
Incorporating citation network visualizations into thesis presentations enhances the communication of research context and influence dynamics. Researchers can embed static images or interactive diagrams within slides, allowing audiences to grasp complex relationships quickly. Interactive visualizations enable viewers to explore the network in real-time, such as clicking on nodes to view source details or filtering relationships by specific criteria.
To maximize impact, visualizations should be introduced with clear explanations of their significance, highlighting key nodes, clusters, or influence pathways. Using animations or step-by-step unveilings can help audiences follow the evolution of the citation network and appreciate the scholarly landscape underpinning the research. When well-integrated, these visual tools make the thesis more engaging, demonstrating a deep understanding of the interconnectedness of sources and research influence.
Ethical considerations and best practices

As the integration of AI into reference management becomes increasingly prevalent in thesis writing, it is essential to address the ethical considerations that underpin responsible use. Ensuring that AI tools are employed ethically not only maintains academic integrity but also fosters trust, transparency, and accountability throughout the research process. Adhering to best practices mitigates potential risks associated with reliance on automated systems and promotes a balanced approach that combines technological efficiency with human oversight.
Employing AI in managing references requires careful attention to ethical principles such as transparency, fairness, and accuracy. It is imperative to recognize the limitations of AI algorithms and to ensure that their use complements, rather than replaces, critical scholarly judgment. Establishing clear guidelines for responsible AI deployment safeguards against issues like unintentional bias, misattribution, and the propagation of outdated or incorrect information.
Ultimately, maintaining ethical standards in reference management upholds the credibility of the research and aligns with the broader ethical framework of academic scholarship.
Responsible use of AI in managing academic references
Responsible utilization of AI involves understanding the capabilities and limitations of automated reference management tools. Researchers should view AI as an aid that enhances efficiency but not as an infallible source of truth. Ensuring ethical use entails regular manual checks, verifying the accuracy of AI-generated references, and being vigilant about potential biases embedded within algorithms.
- Employ AI tools as supplementary aids rather than sole authorities for reference curation.
- Be aware of the source data feeding AI systems, as biased or incomplete datasets can influence outcomes.
- Maintain a critical perspective by cross-referencing AI suggestions with original sources or authoritative databases.
- Document AI intervention steps transparently within the research process to uphold accountability.
Guidelines for transparency and avoiding over-reliance on automation
Transparency in AI-assisted reference management fosters trust and reproducibility in research. Clear guidelines help prevent over-reliance on automation, which can lead to complacency and overlooked errors. Researchers should develop and adhere to protocols that explicitly define the scope of AI use, the verification process, and documentation standards.
- Disclose the extent of AI involvement in reference collection, organization, and validation within the thesis methodology.
- Implement systematic manual reviews of AI-generated references to ensure correctness and completeness.
- Establish periodic audits of automated processes to detect any deviations or inaccuracies.
- Encourage peer review of reference lists to identify potential oversights originating from automation.
Strategies for manual verification to complement AI-generated organization
Despite the advanced capabilities of AI tools, manual verification remains a crucial step to ensure accuracy and scholarly integrity. Combining AI efficiency with human oversight minimizes errors and enhances the quality of references. Effective strategies include systematic cross-checking, utilizing authoritative databases, and conducting peer reviews.
- Compare AI-organized references against original sources or official bibliographic records for accuracy.
- Confirm that citation details such as authorship, publication year, and titles are correctly transcribed.
- Update references manually if discrepancies or outdated information are identified by AI tools.
- Engage colleagues or mentors in reviewing reference lists to catch potential oversights and validate correctness.
- Maintain a detailed log of manual verification steps for transparency and future reference.
Effective ethical reference management balances AI automation with diligent human oversight, ensuring integrity, transparency, and scholarly rigor in thesis writing.
Final Conclusion
In summary, leveraging AI tools for organizing references in a thesis can significantly improve accuracy, save time, and maintain compliance with various citation standards. By embracing these innovative technologies, researchers can enhance their workflow, produce more reliable bibliographies, and present their findings with greater confidence. As the landscape of academic writing evolves, integrating AI-driven reference management becomes an invaluable practice for modern scholars seeking efficiency and precision in their research endeavors.