How to automate note taking with ai offers a transformative approach to capturing and organizing information efficiently. By leveraging advanced artificial intelligence technologies, users can save time, reduce manual effort, and enhance the accuracy of their notes across various contexts.
This overview explores the core concepts, technologies, setup procedures, and practical applications of AI-powered note automation, providing insights into how this innovative solution can streamline workflows and improve information management in diverse environments.
Overview of AI-powered note taking automation
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has revolutionized various aspects of productivity, and note taking is no exception. AI-powered note taking automation involves leveraging advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques to capture, organize, and summarize information efficiently. This technological integration aims to minimize manual effort, reduce errors, and enhance the overall quality of notes, especially in fast-paced or complex environments such as academic lectures, business meetings, or research activities.
The primary benefit of automating note taking with AI lies in its ability to process large volumes of spoken or written content rapidly and accurately, providing users with structured, searchable, and contextually relevant notes. This not only saves time but also allows individuals to focus on critical thinking and decision-making rather than tedious transcription tasks. Additionally, AI tools can adapt to various note-taking styles, integrate multimedia content, and generate summaries or highlights, making the process more dynamic and accessible across multiple devices and platforms.
Key features and functionalities of AI note taking tools
To comprehend the capabilities of AI-powered note taking solutions, it is essential to identify the core features that distinguish them from traditional methods. Modern tools typically include a combination of speech recognition, natural language processing, and contextual understanding to deliver high-quality outputs.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Speech Recognition | Converts spoken language into text with high accuracy, enabling real-time transcription during meetings or lectures. |
| Natural Language Processing (NLP) | Analyzes and interprets the transcribed content, allowing for context-aware organization, tagging, and summarization. |
| Automatic Summarization | Generates concise summaries of lengthy conversations or documents, highlighting key points and action items. |
| Extraction | Identifies and tags significant terms or phrases, facilitating easy search and categorization. |
| Integration Capabilities | Syncs with calendar apps, cloud storage, and collaboration platforms to streamline workflows and share notes seamlessly. |
| Search and Retrieval | Enables rapid access to specific information within large collections of notes through natural language queries. |
| Multimedia Support | Allows embedding images, audio, and video recordings, enriching the note content and context. |
Compared to manual note taking, which relies heavily on human memory, handwriting, or typing, AI automation offers consistency, speed, and the ability to process complex data sets. Manual notes are often subject to biases, omissions, and varying levels of detail, whereas AI tools aim for comprehensive and uniform capture. Furthermore, automated notes can be easily edited, searched, and organized, providing a significant advantage in environments where information is rapidly evolving or voluminous.
Core technologies enabling AI note automation
Advancements in artificial intelligence have significantly transformed the landscape of automated note-taking, enabling systems to accurately interpret, process, and organize information conveyed through speech or text. These core technologies form the backbone of AI-powered note automation, ensuring efficiency, accuracy, and scalability in various applications such as meetings, lectures, and research.
The primary AI techniques involved include natural language processing (NLP), machine learning (ML), speech recognition, and data integration algorithms. Together, these technologies allow systems to understand linguistic nuances, classify and extract relevant information, and convert unstructured data into well-organized notes. By leveraging these capabilities, AI-driven note-taking platforms can adapt to diverse contexts and user preferences, enhancing productivity and knowledge management.
Natural Language Processing and Machine Learning Techniques
Natural language processing (NLP) encompasses a set of computational techniques that enable machines to interpret, analyze, and generate human language. In note automation, NLP models facilitate tasks such as sentiment analysis, entity recognition, summarization, and contextual understanding, which are essential for extracting meaningful information from speech or text inputs.
Machine learning (ML), particularly deep learning models, underpin many NLP applications by training algorithms on large datasets to recognize patterns and improve over time. Techniques such as supervised learning are used for classification tasks, while unsupervised and semi-supervised learning support clustering and topic modeling. Reinforcement learning can also optimize note summarization based on user feedback.
Transformers, a recent innovation in NLP, have revolutionized text understanding by enabling models like BERT and GPT to process context more effectively, leading to more accurate note generation.
Popular Algorithms and Models
Efficiency in converting speech and text into organized notes relies on specific algorithms and models tailored to linguistic complexity and domain requirements. These models are trained to recognize relevant content, discard noise, and produce concise summaries that align with user expectations.
- Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs): Designed to handle sequential data, RNNs are useful for speech recognition and language modeling tasks where context over sequences influences outcomes.
- Transformer Models: Models like BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) and GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) excel in understanding context, generating summaries, and performing question-answering tasks essential for note automation.
- Hidden Markov Models (HMMs): Historically significant in speech recognition, HMMs model temporal sequences and are still used in some hybrid systems for phoneme detection.
- Sequence-to-Sequence (Seq2Seq) Models: Employed in text summarization and translation, these models convert lengthy input sequences into shorter, coherent notes.
These algorithms are integrated within platforms to enhance the accuracy and reliability of automated note-taking, especially in dynamic and noisy environments such as live meetings or lectures.
AI Tools and Platforms Supporting Note Automation
Several tools and platforms have been developed to leverage these core AI technologies, offering diverse capabilities for automatic note generation, transcription, and organization. Below is a table summarizing some of the most prominent options, their key capabilities, and supported functionalities:
| Tool/Platform | Core Capabilities | Supported Features | Integration & Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Otter.ai | Speech transcription, real-time note-taking | Audio-to-text conversion, extraction, sharing, and collaborative editing | Web, iOS, Android, integrations with Zoom, Dropbox |
| Microsoft OneNote with Dictate | Voice-to-text, note organization, AI-assisted suggestions | Speech recognition, handwriting conversion, multimedia embedding | Windows, Mac, mobile apps, Microsoft 365 integration |
| Notion AI | Automated content generation, summarization, organization | Text summarization, task creation, content suggestions | Web, desktop, integrations with Slack, Zapier |
| Rev.ai | Speech-to-text services with high accuracy | Real-time transcription, custom vocabulary, speaker diarization | API-based, adaptable to various workflows |
Setting up an AI-based note taking system
Establishing an effective AI-powered note-taking system requires careful planning and integration into existing workflows. This process involves selecting appropriate tools, configuring hardware and software components, and designing a seamless flow from input to organized notes. A systematic setup ensures the AI system functions accurately, efficiently, and aligns with users’ specific needs, ultimately enhancing productivity and information management.
Implementing an AI-based note taking setup involves multiple stages, from initial tool selection to final deployment. It is essential to understand the technical requirements, integration procedures, and workflow design to achieve optimal performance. This structured approach guarantees that the AI system complements existing tools like note apps, voice recorders, and project management platforms, creating a cohesive ecosystem for automated note generation.
Integrating AI tools into existing workflows
Successful integration of AI note-taking tools into current workflows hinges on a clear understanding of the user environment and identifying points of automation. The following step-by-step procedures facilitate a smooth transition:
- Assess Current Workflow: Map out existing note-taking processes, identifying key touchpoints such as meetings, lectures, and brainstorming sessions.
- Select Appropriate AI Tools: Choose AI-powered applications that align with specific needs, such as speech-to-text transcription, smart summarization, or contextual tagging. Popular options include Otter.ai, Notion AI, or custom solutions via APIs like OpenAI’s GPT models.
- Configure Hardware Requirements: Ensure hardware compatibility, including a reliable microphone for voice input, a camera if visual notes are involved, and sufficient processing power for local AI processing, if applicable.
- Install and Set Up Software: Download, install, and configure the selected AI tools. This may include creating accounts, connecting APIs, and setting preferences for note formatting, storage location, and synchronization with existing platforms.
- Integrate with Existing Applications: Connect AI tools with current note-taking apps, calendar systems, or communication platforms to enable automated data flow. Use APIs or plugins to facilitate seamless integration.
- Customize and Test Workflows: Tailor the system to specific use cases, establishing rules for input capture, note organization, and action triggers. Perform test runs to verify accuracy and system responsiveness.
- Train Users and Document Procedures: Provide training on system usage, troubleshooting, and best practices to ensure consistent operation and user confidence.
This structured approach ensures that AI-powered note-taking integrates smoothly within existing operational frameworks, reducing disruptions and maximizing efficiency.
Hardware and software requirements for optimal performance
To guarantee the effectiveness and reliability of an AI-based note-taking system, specific hardware and software components are essential. These requirements vary depending on the complexity of AI functionalities and the volume of data processed.
- Hardware Requirements:
- Processing Power: A modern multi-core CPU with at least 8GB RAM to handle real-time transcription and AI processing tasks efficiently.
- Microphone: High-quality, noise-canceling microphones increase speech recognition accuracy, especially in noisy environments such as crowded offices or public spaces.
- Storage: Adequate SSD storage to quickly save large audio files, processed data, and generated notes while maintaining fast access speeds.
- Connectivity: Stable high-speed internet connection for cloud-based AI services, API integrations, and synchronization of notes across devices.
- Software Requirements:
- Operating System Compatibility: Compatibility with Windows, macOS, or Linux, depending on user preference and existing infrastructure.
- AI and Speech Recognition Tools: Cloud-based APIs like OpenAI, Google Speech-to-Text, or Microsoft Azure Speech Services, which require proper API keys and authentication setup.
- Note-Taking Applications: Compatibility with popular platforms such as Notion, Evernote, or custom dashboards that support API integration.
- Security and Privacy Software: Encryption tools, firewalls, and VPNs to safeguard sensitive information captured during note-taking sessions.
Ensuring these hardware and software components are in place and properly configured is vital for achieving accurate, fast, and secure AI-enabled note automation.
Flowchart illustrating the setup process from input to note generation
The setup process begins with capturing input, such as voice or visual data, and proceeds through processing, transcription, organization, and storage. The following flowchart describes each step in this sequence:
Input Capture → Data Processing & Transcription → Natural Language Understanding → Note Structuring & Tagging → Storage & Synchronization
In detail, the flow is as follows:
| Stage | Description | Key Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Input Capture | The system receives raw data, such as audio, video, or text input. | Activate microphones, upload files, or connect external data sources. |
| Data Processing & Transcription | The AI engine transcribes speech to text or extracts relevant visual information. | Utilize speech-to-text APIs, preprocess data for noise reduction, and ensure accurate transcription. |
| Natural Language Understanding | The system interprets the transcribed content, identifies key themes, and extracts intent. | Apply NLP models for summarization, extraction, or sentiment analysis. |
| Note Structuring & Tagging | The AI organizes information into structured notes, adds tags, and categorizes data. | Implement rules for formatting, assign tags based on content, and set priorities. |
| Storage & Synchronization | The final notes are saved in designated platforms, synchronized across devices, and made accessible for review. | Store in cloud-based or local repositories, enable automatic sync, and set access permissions. |
This flowchart serves as a visual blueprint for establishing an efficient, end-to-end AI note-taking system, ensuring all components interact seamlessly from input to final note generation.
Methods for capturing input data
Effective note-taking automation relies heavily on accurately capturing input data from diverse sources. As different environments and situations demand varied data collection methods, understanding these input streams is crucial for building a robust AI-powered note-taking system. This section explores the primary sources of input data, techniques for converting multimedia recordings into text, and procedures to organize these data feeds to ensure high-quality note generation.Capturing input data involves gathering information from multiple channels, each with unique characteristics and challenges.
The primary sources include voice recordings, text documents, and images, all of which can be processed to extract meaningful notes. Properly integrating these sources ensures comprehensive coverage of the information being recorded, facilitating accurate and contextually relevant notes.
Input sources for AI note-taking systems
Utilizing various input sources allows AI systems to adapt to different environments and user preferences. The main sources include:
- Voice: Voice input encompasses spoken words captured via microphones during meetings, lectures, or personal dictations. These sources are often the most natural form of data input, especially in real-time scenarios.
- Text: Digital documents, emails, chat logs, and other written content serve as valuable input streams. They provide structured and detailed information that can be directly processed by AI algorithms.
- Images and Visual Data: Photographs, scanned handwritten notes, diagrams, and slides contribute visual information that can be converted into textual data through image processing techniques.
Techniques for converting audio and video recordings into text
Transforming audio and video data into usable text is fundamental for effective note automation. Several advanced techniques are employed to accomplish this:
- Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR): This technology converts spoken language into text by analyzing audio waveforms. Modern ASR systems leverage deep learning models trained on vast speech datasets, enabling high accuracy even in noisy environments. Examples include Google’s Speech-to-Text API and open-source solutions like Mozilla DeepSpeech.
- Video Transcription: Video recordings are segmented into smaller audio clips, which are then processed with ASR. Additional context can be extracted by analyzing visual cues—such as speaker identification or slide content—using computer vision techniques to enhance transcription quality.
- Noise Reduction and Signal Processing: Preprocessing audio signals involves filtering background noise and enhancing speech clarity. Techniques such as spectral subtraction and beamforming improve the accuracy of subsequent transcription processes.
Implementing these techniques ensures that spoken content from various sources is reliably converted into text, facilitating seamless note generation.
Organizing data feeds for accurate note generation
After capturing and converting data, organizing these inputs systematically is essential to produce coherent and contextually accurate notes. Key procedures include:
- Timestamping and Metadata Tagging: Assigning timestamps and relevant metadata to each data segment helps maintain chronological order and context, especially when dealing with multiple input sources simultaneously.
- Categorization and Labeling: Organizing data based on topics, speakers, or content type improves retrieval and relevance during note synthesis. For example, tagging sections of a meeting recording with speaker identities or agenda items enhances clarity.
- Data Validation and Cleaning: Ensuring the accuracy and consistency of the input data involves filtering out noise, correcting transcription errors, and removing irrelevant content. This step is crucial to prevent inaccuracies in final notes.
- Integration with Data Management Systems: Using databases or cloud storage solutions enables efficient data retrieval and synchronization. Structuring data feeds with standardized formats ensures scalability and interoperability across various AI modules.
Proper organization of input data ensures that AI systems can efficiently process, analyze, and generate notes that are both accurate and contextually relevant, ultimately enhancing productivity and information retention.
Automating Note Formatting and Organization

Efficient note-taking automation extends beyond capturing raw data; it involves structuring and organizing notes in a clear, accessible manner. Automating this process enhances readability, facilitates rapid retrieval, and ensures consistency across various notes. Leveraging AI tools enables the automatic application of formatting standards, categorization, and structured presentation, transforming scattered information into a coherent knowledge base.Effective note formatting and organization are critical for maximizing the utility of automated note-taking systems.
Proper structuring includes the use of hierarchical headings, bullet points, numbered lists, and tables to categorize information logically. Additionally, implementing tagging and categorization methods ensures that notes are easily retrievable, even as the volume of data grows. This section explores methods for structuring notes, sample HTML table structures for organized presentation, and techniques for tagging and categorizing notes for efficient data management.
Structuring Notes with Headings, Bullet Points, and Tables
Structured notes facilitate quick scanning and comprehension. Headings delineate major topics and s, providing a clear hierarchy within each note. Bullet points and numbered lists help break down complex information into digestible units, making the content more accessible. Tables serve as a powerful tool for presenting comparative data, summaries, or multi-dimensional information in a compact format.Automated systems can analyze the content to identify key topics and generate corresponding HTML elements dynamically.
For example, an AI algorithm can recognize sections within a transcript and insert appropriate
tags for subheadings, while bullet points can be generated to list key points or action items. Tables can be constructed by identifying related data points and organizing them into rows and columns, enhancing clarity and data organization.
Sample HTML Table Structures for Organized Note Presentation
Tables can be designed with up to four columns to accommodate diverse types of information, such as categories, descriptions, dates, and statuses. Here are simple templates illustrating structured presentation:
Table 1: Basic 3-Column Table Structure
Category Description Status Meeting Notes Discuss project milestones and deadlines. Completed Research Data Summary of recent survey findings. In Progress
Table 2: Four-Column Table for Task Management
Task Assigned To Due Date Priority Draft Project Report Jane Doe 2024-05-15 High Update Website Content John Smith 2024-05-20 Medium
These templates can be dynamically generated by AI based on the content and context, ensuring an organized and professional appearance for all notes.
Tagging and Categorizing Notes for Easy Retrieval
Effective retrieval of notes hinges on systematic tagging and categorization. Tags act as metadata that classify notes based on topics, projects, importance, or other relevant criteria. AI-powered note systems can automatically assign tags by analyzing the text for s, entities, or contextual clues, reducing manual effort and ensuring consistent categorization.Categories or folders can be created based on broader themes such as “Research,” “Meetings,” “Personal,” or specific projects.
Combining hierarchical folder structures with granular tags allows for multi-dimensional organization. For example, a note related to a marketing campaign can be tagged with “Marketing,” “Q2 Goals,” and “Social Media,” making it easily retrievable regardless of the user’s navigation path.Automated tagging also enables advanced search capabilities, such as filtering notes by date, category, or tags, significantly speeding up information retrieval.
Furthermore, machine learning models can learn from user behavior to suggest or automatically assign the most relevant tags, enhancing the overall organization and usability of the note-taking system.
Enhancing Note Accuracy and Relevance

Maintaining high precision and contextual relevance in AI-assisted note-taking is essential for ensuring that notes serve as reliable resources for future reference. Employing targeted strategies for training AI models, refining note outputs, and customizing templates based on various scenarios can significantly improve the overall effectiveness of automated note-taking systems. These enhancements help users obtain clearer, more accurate, and situation-specific notes, thereby boosting productivity and comprehension.
Achieving these improvements involves deploying advanced techniques to optimize the AI’s understanding of context, filtering out inaccuracies, and tailoring note formats to suit particular content types or user needs.
Strategies for Training AI Models to Improve Contextual Understanding
Effective training is fundamental for enhancing the AI’s ability to produce contextually relevant notes. Incorporating diverse and well-curated datasets that mirror real-world scenarios ensures the AI learns nuanced language patterns and domain-specific terminology. Using supervised learning methods, where human reviewers validate and correct AI outputs, helps adjust the model’s understanding of context over time.Transfer learning also plays a vital role by leveraging pre-trained models and fine-tuning them on specialized datasets relevant to the user’s niche, such as academic lectures, business meetings, or technical discussions.
This approach enables the AI to develop a deeper grasp of context, idiomatic expressions, and subject-specific jargon, ultimately resulting in more accurate note summaries.
Filtering and Refining Notes to Eliminate Errors
Once the AI generates notes, implementing robust filtering processes is critical to identify and correct inaccuracies. This can include automated validation techniques that cross-reference notes with authoritative sources or previous records to verify facts and figures. Additionally, employing natural language understanding tools allows the system to detect inconsistencies, redundant information, or ambiguous phrasing.User feedback mechanisms further enhance note quality by allowing individuals to flag errors or suggest corrections.
Integrating these corrections into the system’s learning loop ensures ongoing refinement. Regular audits and manual reviews, especially in high-stakes environments like medical or legal note-taking, also contribute to maintaining high standards of accuracy and relevance.
Comparing Methods for Customizing Note Templates Based on Different Scenarios
Adapting note templates to specific scenarios enhances clarity and appropriateness, making notes more actionable. Customization methods include creating predefined templates for various contexts, such as lectures, project meetings, or client consultations, each with tailored sections and prompts.Scenario-specific templates might feature dedicated areas for action items, key decisions, or follow-up questions, ensuring relevant information is systematically captured. Dynamic template generation, driven by metadata such as meeting type or subject matter, allows the system to automatically select or modify templates based on context.
This flexibility ensures notes are not only accurate but also structured in a way that aligns with user workflows and scenario requirements.By leveraging these strategies, AI-powered note-taking systems can significantly enhance the precision, relevance, and usability of captured information, transforming raw data into meaningful knowledge assets.
Use Cases and Practical Applications of AI-Powered Note Taking Automation
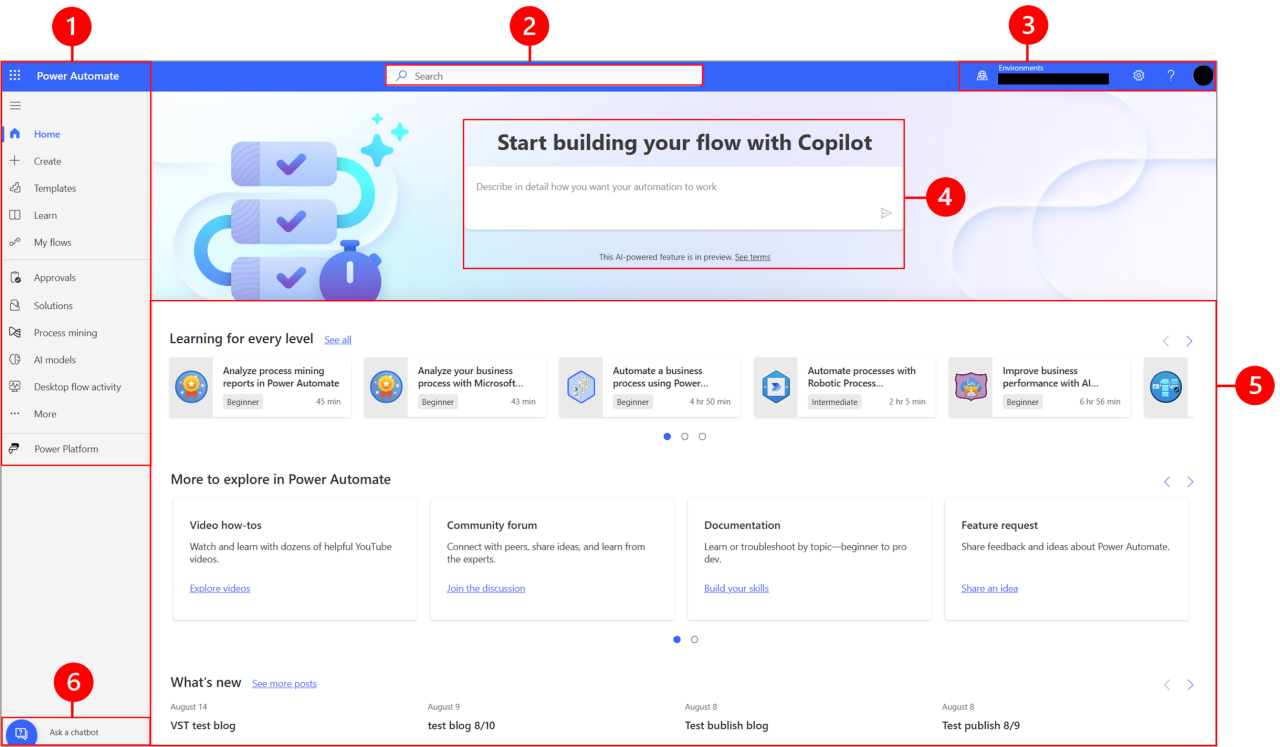
AI-driven note taking automation has revolutionized how individuals and organizations capture, organize, and utilize information across diverse environments. Its adaptability and efficiency make it invaluable in settings ranging from corporate meetings to academic lectures and fieldwork. By integrating AI technologies into daily workflows, users can enhance productivity, accuracy, and knowledge retention, leading to more informed decision-making and streamlined operations.
These applications demonstrate AI’s versatility in automating routine note-taking tasks, allowing users to focus on analysis, strategy, and engagement instead of manual transcription. Below are specific environments where AI-powered note automation is particularly impactful, along with real-world examples and case studies illustrating successful implementations.
Environments Utilizing AI-Powered Note Taking Automation
- Meetings and Conferences: AI tools can transcribe conversations in real-time, identify speakers, and extract key points, enabling participants to have accurate records without manual effort.
- Educational Lectures and Seminars: Automated note systems capture spoken content, organize it into structured formats, and even generate summaries, assisting students and educators alike.
- Fieldwork and On-Site Data Collection: In industries such as environmental research, archaeology, and journalism, AI automates the recording of observations, photos, and audio, ensuring comprehensive documentation even in challenging environments.
- Legal and Healthcare Settings: AI note-taking applications facilitate the transcription of consultations, legal proceedings, and medical examinations, maintaining detailed and accurate records essential for compliance and analysis.
Examples of Automated Note Taking Workflows Across Industries
Across various sectors, automated note taking workflows have been tailored to meet specific needs, often incorporating integration with other enterprise systems, cloud storage, and analytics platforms.
- Corporate Sector: During meetings, AI transcription tools record discussions, categorize action items, and generate follow-up summaries. These notes are then automatically uploaded to project management platforms, ensuring seamless continuity and accountability.
- Educational Institutions: Lecture capture systems utilize speech recognition to produce real-time transcripts, which are linked with digital textbooks and note apps. Students can access synchronized notes and highlights post-lecture, enhancing comprehension and revision.
- Field Research: Researchers employ AI-enabled mobile apps to record observations through voice or photo inputs, with algorithms automatically extracting relevant data points, tagging locations, and organizing entries into databases for later analysis.
- Legal and Medical Practices: Automated transcription services convert spoken testimonies and consultations into structured, searchable records, reducing administrative burdens and ensuring accurate documentation for future reference.
Case Study Summaries of Successful Implementations
Case Study 1: Corporate Meeting OptimizationA multinational technology firm implemented an AI-powered transcription and note organization tool during quarterly meetings. The system accurately captured spoken discussions, identified key decisions, and generated action item summaries. Post-meeting, these notes were integrated into the company’s task management software, reducing follow-up time by 40% and improving team accountability.
Case Study 2: Academic Lecture SupportA university adopted an AI-driven lecture capture platform that provided real-time transcriptions and automated note summaries for students. The platform’s ability to organize content according to curriculum modules facilitated better review sessions and improved student engagement, especially for students with learning differences. Academic performance metrics showed a measurable increase in comprehension and retention.
Case Study 3: Field Data Collection EfficiencyAn environmental research organization deployed AI-enabled mobile devices for on-site data collection. The system automatically transcribed voice notes, annotated photos with location data, and organized observations into a centralized database. This automation shortened data processing time from weeks to days and enhanced data accuracy, leading to more timely environmental reports.
Challenges and considerations
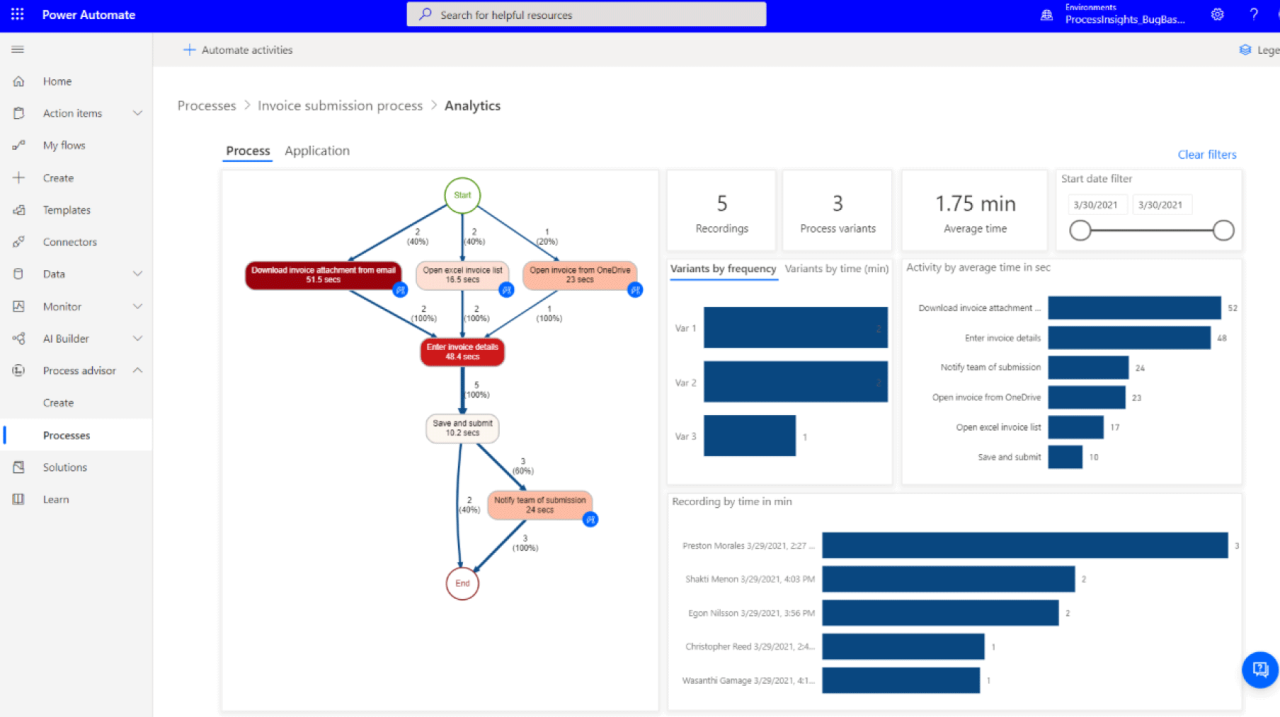
Automating note-taking with AI offers significant advantages in efficiency and accuracy; however, it also presents a range of challenges that organizations and individuals must carefully navigate. Understanding these obstacles, alongside considerations surrounding privacy, security, and data management, is essential for successful implementation and sustainable operation of AI-powered note-taking systems. Addressing these factors proactively ensures that technological benefits do not come at the expense of sensitive information or operational integrity.While AI-driven note automation continues to evolve rapidly, it faces technical, ethical, and operational hurdles.
These include issues related to data quality, system reliability, user acceptance, and compliance with legal standards. Recognizing and mitigating these challenges helps optimize the benefits of automation while safeguarding organizational and personal interests.
Common obstacles in automating note taking with AI
Implementing AI-based note-taking solutions is often hindered by several technical and practical barriers. These include:
- Data quality and variability: AI models depend heavily on high-quality, consistent input data. Variability in language, accents, terminology, and formatting can reduce accuracy and cause misinterpretations.
- Limited contextual understanding: While AI can process language efficiently, capturing nuanced context, sarcasm, or complex concepts remains challenging, which may lead to incomplete or inaccurate notes.
- Integration complexities: Seamlessly integrating AI tools with existing workflows, applications, and data sources can require significant technical effort and customization.
- User adoption: Resistance to change, lack of trust in AI-generated notes, or unfamiliarity with new tools can impede widespread acceptance and effective utilization.
- Resource constraints: Developing, training, and maintaining sophisticated AI models demand substantial investment in hardware, expertise, and ongoing updates.
Privacy, security, and data management issues
As AI note-taking systems process potentially sensitive information, protecting privacy and ensuring data security are paramount. The inclusion of personal, confidential, or proprietary information raises concerns about unauthorized access and misuse.Organizations need to address several key considerations:
- Data confidentiality: Ensuring that sensitive information is encrypted both at rest and during transmission helps prevent unauthorized access. Access controls and user authentication protocols are essential.
- Compliance with legal standards: Adherence to regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or other regional data protection laws is critical. This involves obtaining necessary consents and establishing transparent data handling policies.
- Data lifecycle management: Clear policies should govern how long data is retained, how it is stored, and procedures for secure deletion to minimize risks of data breaches or misuse.
- Bias and fairness: AI models trained on biased data may produce unfair or discriminatory outputs. Regular audits and updates are necessary to mitigate such risks.
- Audit trails and accountability: Maintaining detailed logs of data access and processing activities helps in tracking issues and demonstrating compliance during audits.
Recommendations for mitigating potential risks during implementation
To ensure a secure, compliant, and effective deployment of AI-powered note-taking systems, organizations should adopt a strategic approach that includes:
- Rigorous data governance: Establish comprehensive policies for data collection, storage, processing, and sharing. Regularly audit data sources and model outputs for accuracy and fairness.
- Security best practices: Implement multi-factor authentication, encryption, and intrusion detection systems. Conduct vulnerability assessments periodically to identify and address security gaps.
- Transparency and user education: Clearly communicate how data is used and protected. Provide training to users on system capabilities, limitations, and security protocols to foster trust and proper usage.
- Continuous monitoring and improvement: Monitor system performance, privacy compliance, and security metrics regularly. Incorporate user feedback and audit findings to refine AI models and policies.
- Legal and ethical compliance: Consult with legal experts when designing policies and ensure adherence to relevant laws and ethical standards, especially when handling sensitive information.
Adopting these measures minimizes risks and enhances the reliability and integrity of AI-powered note-taking solutions. By addressing challenges thoughtfully and proactively, organizations can harness the transformative potential of AI while safeguarding their data and maintaining user trust.
Future Trends in AI Note Taking Automation
As artificial intelligence continues to evolve rapidly, the future of AI-powered note taking automation promises to be even more sophisticated, intuitive, and integrative. Emerging technologies are poised to redefine how users capture, organize, and utilize their notes across diverse digital environments. Staying abreast of these developments allows organizations and individuals to leverage cutting-edge tools that enhance productivity, accuracy, and contextual relevance in note management.
Anticipating future innovations involves examining technological breakthroughs, integration possibilities with existing digital platforms, and potential feature enhancements. These advancements aim to streamline workflows, improve user experience, and facilitate seamless data synchronization across multiple applications and devices, ultimately transforming the landscape of digital note-taking.
Emerging Technologies and Innovations in the Field
The trajectory of AI note taking is heavily influenced by breakthroughs in several technological domains. Notably, advancements in natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning (ML) continue to improve the precision and contextual understanding of AI systems. Future models are expected to grasp nuanced human expressions, idioms, and domain-specific terminologies with greater accuracy, thereby enhancing note relevance and clarity.
Additionally, the integration of multimodal AI technologies that combine text, voice, images, and even video inputs will significantly expand the ways users can capture information. For instance, voice-activated note entry will become more accurate and context-aware, enabling hands-free operation in dynamic environments such as meetings or fieldwork. Real-time data analysis and summarization algorithms will also evolve, offering concise overviews of lengthy audio or video recordings, making information retrieval more efficient.
Potential Integrations with Digital Tools and Platforms
The future of AI note taking automation is closely linked to its ability to seamlessly integrate with a broad ecosystem of digital tools. These include calendar applications, project management platforms, cloud storage solutions, and communication channels like email and messaging apps. Such integrations will facilitate automatic note synchronization, context-aware suggestions, and cross-platform data consistency.
For example, AI-powered note systems might automatically extract action items from meeting transcripts in platforms like Microsoft Teams or Zoom, and then synchronize these tasks directly with project management tools such as Asana or Trello. Integration with enterprise systems could also enable secure, compliant data handling, making AI note taking an integral part of organizational workflows.
Furthermore, the development of open APIs and standardized data formats will encourage third-party developers to create customized plugins and extensions, expanding the functionality and adaptability of AI note taking solutions across various industries and use cases.
Upcoming Features and Improvements for Enhanced Automation Efficiency
As the field advances, several innovative features are expected to significantly improve automation efficiency and user experience. These include:
- Contextual Personalization: AI systems will adapt to individual user preferences, learning terminologies, preferred formats, and organizational styles to deliver highly tailored note-taking experiences.
- Intelligent Content Categorization: Enhanced algorithms will automatically classify notes into relevant categories or tags, reducing manual effort and improving discoverability.
- Semantic Search Capabilities: Improved search functionalities will enable users to find notes based on concepts and context rather than mere s, saving time and increasing productivity.
- Proactive Summarization and Insights: AI will generate summaries and highlight key points from extensive notes or recordings proactively, facilitating quick comprehension and decision-making.
- Enhanced Data Security and Privacy: Future offerings will incorporate more robust encryption, user-controlled access, and compliance features to address growing concerns around data privacy in automated note systems.
These innovations will collectively foster more efficient, accurate, and user-centric AI note-taking solutions, empowering users to manage information more effectively in increasingly complex digital environments.
Closing Summary
In summary, understanding how to automate note taking with ai opens new horizons for productivity and organization. As technology continues to evolve, integrating AI tools into your routines can lead to more efficient, accurate, and accessible note management, revolutionizing the way you capture and utilize information.