Learning how to automate research workflows with AI opens new horizons for scholars and professionals seeking to improve accuracy and productivity in their projects. By integrating advanced artificial intelligence tools, researchers can streamline complex tasks, reduce manual effort, and accelerate data processing. This approach not only optimizes resource utilization but also enables a focus on insightful analysis rather than repetitive activities.
Implementing AI-driven automation involves understanding key technologies such as natural language processing, machine learning, and data mining. These components collectively create a robust ecosystem that simplifies literature reviews, data collection, and analysis. As a result, researchers can achieve more precise outcomes with less time investment, making their workflows more efficient and reliable.
Overview of Automating Research Workflows with AI

In the rapidly evolving landscape of academic and industry research, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) tools has become a transformative force. Automating research workflows with AI involves leveraging advanced algorithms and machine learning models to streamline, enhance, and expedite various research tasks. This approach not only accelerates the pace of discovery but also reduces the potential for human error, ultimately leading to more accurate and reliable outcomes.
By embedding AI into research processes, organizations and individual researchers can achieve significant improvements in efficiency. Tasks such as data collection, literature review, data analysis, hypothesis generation, and report writing are increasingly being automated through AI-driven solutions. These tools enable researchers to handle large volumes of data swiftly, identify relevant patterns, and generate insights that might be overlooked through manual methods.
Moreover, AI facilitates a more systematic and reproducible approach to research, which is crucial for maintaining scientific integrity.
Comparison Between Manual Research Methods and AI-Powered Automation
Manual research methods traditionally involve painstakingly gathering data, reviewing literature, coding qualitative data, and manually analyzing results. While these approaches have been foundational, they are often time-consuming, labor-intensive, and susceptible to human biases or oversights. Researchers might spend days or weeks just organizing and synthesizing information, which can delay critical decision-making processes.
In contrast, AI-powered automation transforms this workflow by employing computational tools designed to perform repetitive and complex tasks with high speed and precision. For instance, natural language processing (NLP) algorithms can rapidly scan thousands of research articles to extract relevant information, identify emerging trends, and summarize key findings in minutes. Machine learning models can analyze vast datasets to uncover patterns or predict outcomes with a level of accuracy that surpasses manual analysis.
Furthermore, AI systems can assist in designing experiments, optimizing data collection strategies, and even drafting initial reports or publications.
Overall, the integration of AI into research workflows offers a compelling advantage in handling large-scale data, reducing human bias, and accelerating the pace of discovery. While manual research remains valuable for nuanced interpretation and critical thinking, AI-driven automation provides a powerful complementary tool that enhances overall efficiency and accuracy in the research process.
Key Components and Technologies in AI-Driven Research Automation
In the realm of automating research workflows, several core AI components and technological advancements serve as the backbone for enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and scalability. Understanding these elements is essential for designing effective AI-powered research systems that can handle vast data volumes, extract meaningful insights, and facilitate decision-making processes with minimal human intervention.
Each technology integrates into research workflows by automating specific tasks—from literature review and data analysis to hypothesis generation and reporting—thereby transforming traditional research paradigms into dynamic, intelligent processes. The synergy among these components ensures a seamless flow of information and supports continuous learning and adaptation within research environments.
Essential AI Technologies in Research Automation
| Features | Applications | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Language Processing (NLP) AI technique enabling machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language with high accuracy. |
Automates literature reviews, extracts key information from research papers, summarizes findings, and facilitates question-answering systems. | Enhances speed and scale of reviewing vast scientific literature, improves accuracy of information extraction, and supports multilingual research. | Potential misunderstandings of context or sarcasm, requires high-quality training data, and may struggle with highly specialized terminology. |
| Machine Learning (ML) Algorithms that improve automatically through experience, enabling predictive analytics, classification, and pattern recognition. |
Predicts research trends, classifies research data, identifies novel patterns, and optimizes experimental designs. | Enables adaptive systems that refine results over time, uncovers hidden insights, and supports personalized research recommendations. | Dependent on quality and quantity of training data, risk of overfitting, and sometimes limited interpretability. |
| Data Mining Process of discovering implicit, valid, and useful patterns from large datasets through computational techniques. |
Automates the extraction of valuable insights from extensive datasets, including bibliometric data, experimental results, and clinical records. | Facilitates uncovering relationships and trends that might be missed by manual analysis, supports decision-making with evidence-based insights. | Computationally intensive, sensitive to noisy or incomplete data, and requires domain expertise to interpret findings accurately. |
Integration of these components into research workflows typically involves sequential or parallel processes where NLP filters and summarizes vast literature, ML models analyze experimental data to generate hypotheses or predictions, and data mining techniques identify overlooked correlations. When combined effectively, these technologies significantly accelerate discovery cycles and improve research quality.
Designing an Automated Research Workflow
Creating an effective automated research workflow requires careful planning to align research objectives with appropriate AI tools and processes. This involves systematically mapping out tasks that can be optimized through automation, ensuring efficiency, consistency, and accuracy throughout the research lifecycle. A well-designed workflow not only accelerates data collection and analysis but also allows researchers to focus on high-level interpretation and strategic decision-making.
In designing such workflows, it is vital to identify repeatable, data-intensive, and rule-based tasks suitable for automation. Structuring these tasks into a coherent process involves defining stages, selecting appropriate AI technologies, and establishing clear procedures to facilitate smooth transitions between steps. Visualizing this process through flowcharts helps clarify the sequence of activities and ensures that each component integrates seamlessly into the overall research strategy.
Procedures to Map Out Research Tasks Suitable for Automation
Effective mapping begins with a comprehensive assessment of the research process to pinpoint tasks that are repetitive, time-consuming, or data-driven. This process typically involves:
- Breaking down the research workflow into discrete activities, such as literature review, data collection, data cleaning, statistical analysis, and report generation.
- Evaluating each activity for potential automation based on complexity, standardization, and availability of AI tools.
- Prioritizing tasks that offer the greatest efficiency gains or significant error reduction when automated.
- Consulting with domain experts to ensure that automation does not compromise research integrity or quality.
Documenting these tasks with detailed descriptions, inputs, outputs, and dependencies creates a clear map that guides subsequent workflow design. This mapping serves as a foundation for selecting suitable AI tools and defining procedural steps.
Step-by-Step Process for Building a Research Automation Workflow
Constructing a workflow that effectively incorporates AI tools involves a systematic, stepwise approach. The key stages include:
- Define Research Objectives: Clarify the goals and scope of the research to determine which tasks are eligible for automation.
- Identify Automatable Tasks: Use the task mapping to select activities suitable for AI integration, such as literature screening or data extraction.
- Select Appropriate AI Technologies: Choose tools like natural language processing (NLP) for text analysis, machine learning algorithms for predictive modeling, or automation platforms for data handling.
- Design Workflow Architecture: Artikel the sequence of tasks, decision points, and data flows, ensuring logical progression and minimal manual intervention.
- Develop and Integrate Components: Build or customize AI modules and integrate them into existing research platforms or pipelines.
- Test and Validate: Run pilot tests to verify accuracy, efficiency, and robustness, making adjustments as necessary.
- Document and Automate Execution: Establish documented procedures and leverage automation scheduling tools to streamline ongoing research activities.
This structured approach promotes clarity, reproducibility, and scalability of research workflows, enabling researchers to systematically incorporate AI-driven automation into their routines.
Flowchart Structure for Research Automation Process
Visualizing the stages of an automated research workflow through a flowchart enhances understanding of process flow and interdependencies. Here is a structured representation using HTML table tags:
| Stage | Description | Decision Point | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Research Planning | Define objectives, scope, and research questions. | – | Clear research framework established. |
| 2. Task Identification | Break down research activities to identify automatable tasks. | Are tasks repetitive or data-heavy? | If yes, proceed to selection; if no, manual processing continues. |
| 3. Tool Selection | Choose suitable AI tools for each task (e.g., NLP for text mining). | – | Tools integrated into workflow. |
| 4. Workflow Design | Map tasks sequentially, define data flow, and automation points. | Are dependencies well-defined? | If yes, proceed; if no, revisit design. |
| 5. Implementation | Develop and deploy AI modules within the research environment. | – | Workflow components operational. |
| 6. Testing & Validation | Run pilot tests to ensure accuracy and efficiency. | Are results satisfactory? | If yes, move to full deployment; if no, refine models. |
| 7. Automation & Monitoring | Automate routine tasks and monitor performance. | – | Ongoing, reliable research automation process. |
This flowchart provides clarity on each stage, decision points, and outcomes, facilitating a structured approach to designing comprehensive automated research workflows.
Implementing AI Tools for Literature Review and Data Collection
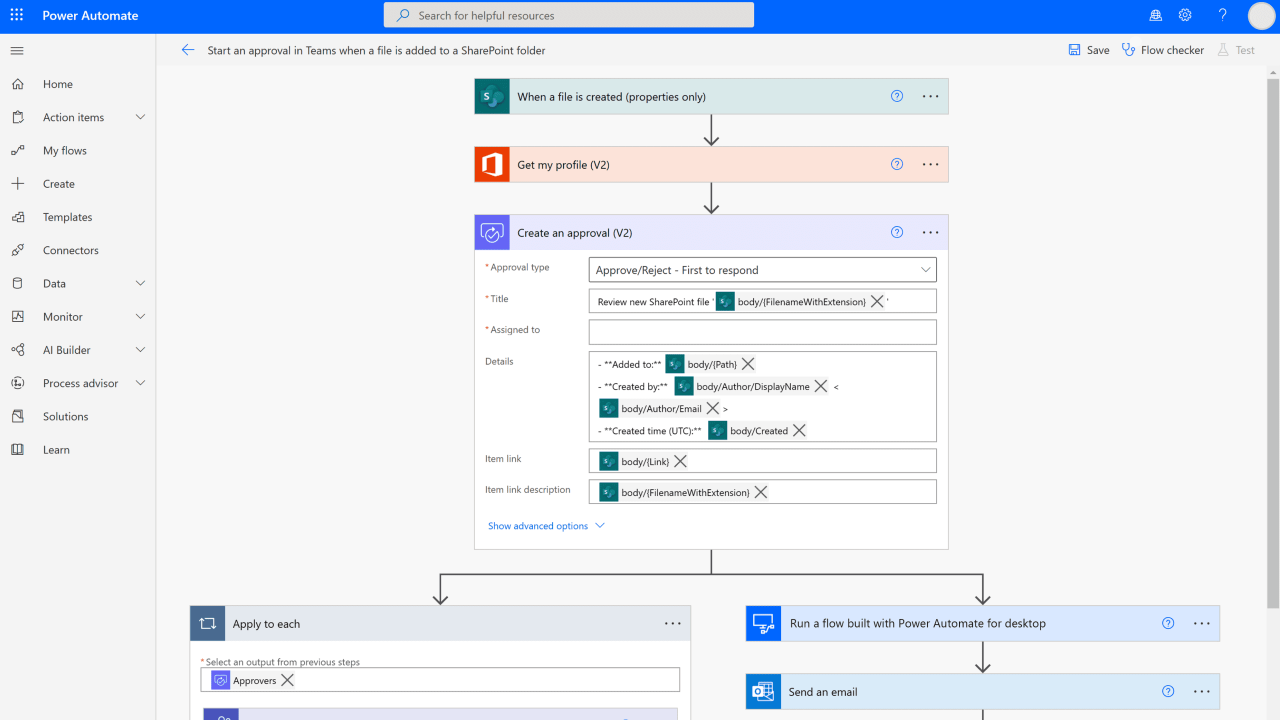
Efficient literature review and data collection are foundational to successful research workflows. Leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) tools can significantly streamline these processes by automating the search, screening, and extraction of relevant information across multiple data sources. This not only accelerates the research cycle but also enhances the comprehensiveness and accuracy of the collected data.
By integrating AI-driven solutions, researchers can automate repetitive tasks, reduce human error, and focus more on analysis and interpretation. The following sections detail effective methods for utilizing AI in literature gathering and screening, along with practical templates and key features to consider when selecting suitable AI tools for data collection.
Methods to Leverage AI for Literature Gathering and Screening
Applying AI in literature review involves combining natural language processing (NLP), machine learning algorithms, and automation scripts to identify, retrieve, and filter relevant academic articles, reports, or data sources. The core approach consists of setting up automated search queries, employing AI models to evaluate relevance, and continuously updating datasets as new publications emerge.
Key methods include:
- Automated and Topic-Based Searches: Using AI to craft complex search queries that encompass synonyms, related terms, and evolving terminology to capture the breadth of literature in a given field.
- Semantic Search Capabilities: Employing NLP models that understand the context and meaning behind search terms, allowing for more nuanced retrieval beyond simple matching.
- Intelligent Screening and Relevance Filtering: Applying machine learning classifiers trained on manually labeled datasets to automatically exclude irrelevant articles or data points, thus narrowing down the most pertinent sources.
- Continuous Data Monitoring: Setting up AI tools to track new publications or data sources in real-time, ensuring the latest information is incorporated into the review process.
Sample Templates and Scripts for Automating Literature Searches
Automation scripts serve as the backbone for executing routine data gathering tasks across multiple databases. Below is a simplified example of a Python-based template using popular libraries such as requests for web interaction and BeautifulSoup for parsing HTML content. This script can be adapted for specific databases with APIs or web scraping mechanisms.
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# Define search parameters
search_terms = ["machine learning", "neural networks", "deep learning"]
base_url = "https://example-database.org/search"
# Loop over search terms
for term in search_terms:
params = 'query': term, 'limit': 50
response = requests.get(base_url, params=params)
if response.status_code == 200:
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'html.parser')
# Extract article titles and links
articles = soup.find_all('div', class_='article-entry')
for article in articles:
title = article.find('h2').text
link = article.find('a')['href']
print(f"Title: title\nLink: link\n")
else:
print(f"Failed to retrieve data for term")
Researchers can adapt this script to multiple databases such as PubMed, IEEE Xplore, or Scopus by utilizing their respective APIs and adjusting parsing logic accordingly. Automation tools like Python scripts, R packages, or specialized platforms such as Zapier or Integromat can facilitate large-scale, repeated searches with minimal manual intervention.
Key Features to Look for in AI Tools for Data Collection
Selecting the right AI tools for literature review and data collection involves assessing specific features that align with research needs. The following features are critical for ensuring comprehensive, effective, and user-friendly data gathering:
- Multi-Database Integration: Ability to connect with various academic databases, repositories, and data sources through APIs or web scraping.
- Semantic Search and NLP Capabilities: Understanding context and meaning to improve relevance of retrieved articles, especially when dealing with complex or ambiguous terminology.
- Automation and Scheduling: Support for scheduled searches, periodic updates, and batch processing to keep datasets current without manual prompts.
- Relevance Filtering and Classification: Built-in machine learning models to automatically rank, filter, or classify results based on predefined criteria.
- User-Friendly Interface and Customization: Easy setup with options to customize search parameters, relevance thresholds, and output formats.
- Data Export and Integration: Compatibility with data analysis tools, export options in formats like CSV, JSON, or RIS, and integration with reference management software.
- Tracking and Version Control: Features to manage updates, track changes, and maintain version histories of collected datasets.
Customization and Optimization of Research Automation Systems

Tailoring AI-driven research workflows to specific goals and disciplines enhances their effectiveness and relevance. Customization involves adapting tools and processes to align with the unique needs, methodologies, and datasets pertinent to particular fields of study. Optimization ensures these systems operate at peak performance, delivering accurate, reliable, and efficient results through continuous refinement.
Achieving a well-calibrated research automation system requires a strategic approach that considers both the specific research objectives and the evolving nature of data and techniques. This process involves selecting suitable AI models, configuring parameters, and establishing feedback mechanisms that foster ongoing improvements. Proper customization and optimization can significantly accelerate research timelines while maintaining high standards of quality and validity.
Aligning AI Workflows with Specific Research Goals and Disciplines
To effectively tailor AI workflows, it is essential to thoroughly understand the unique requirements of the research project and discipline. This involves identifying key research questions, desired outcomes, and the types of data most relevant for analysis. Different disciplines, such as biomedical research, social sciences, or engineering, have distinct data sources, terminologies, and validation standards, necessitating customized AI models and workflows.
Strategies for alignment include:
- Utilizing domain-specific language models or training existing models on discipline-specific datasets to improve contextual understanding.
- Configuring data preprocessing steps to handle unique data formats or noise characteristics inherent to the research field.
- Defining custom metrics for evaluating AI performance based on discipline-specific benchmarks, ensuring relevance and accuracy.
Testing and Refining Automation Processes for Accuracy and Reliability
Consistent testing and refinement are vital to ensure the robustness of AI-driven research workflows. This process involves implementing validation protocols and iterative cycles of evaluation, adjustment, and re-evaluation. Through systematic testing, researchers can identify weaknesses, biases, or inaccuracies within the automation system, allowing targeted improvements.
Key methods include:
- Using annotated datasets to benchmark AI outputs against human expert assessments, quantifying accuracy and precision.
- Applying cross-validation techniques to prevent overfitting and ensure generalizability across different data samples.
- Monitoring system performance over time, analyzing discrepancies, and conducting error analysis to pinpoint sources of inaccuracies.
Regular validation and iterative refinement are indispensable for maintaining high standards of reliability in AI-driven research workflows.
Organizing Best Practices for Continuous Improvement Using Feedback Loops
Embedding feedback loops within research workflows fosters ongoing enhancement of AI systems. This approach involves collecting input from researchers, automated performance metrics, and real-world results to inform subsequent adjustments. Continuous improvement practices help adapt the automation system to evolving research needs, data changes, and technological advancements.
Best practices include:
- Establishing routine review cycles where AI outputs are evaluated qualitatively and quantitatively, ensuring alignment with research goals.
- Implementing user feedback mechanisms that allow researchers to flag inaccuracies or suggest improvements, directly influencing system tuning.
- Utilizing automated performance dashboards that track key metrics such as precision, recall, and processing time, guiding iterative modifications.
- Employing adaptive learning techniques where AI models update themselves based on new data and feedback, maintaining optimal performance over time.
Ethical Considerations and Challenges in AI-Powered Research

As the integration of artificial intelligence into research workflows advances, addressing the ethical implications becomes paramount to ensure responsible innovation. Researchers and organizations must navigate complex issues surrounding data privacy, bias, and transparency to maintain integrity and public trust in AI-driven methodologies. Implementing robust protocols and ethical standards is essential for sustainable and fair research practices.
AI-powered research offers remarkable efficiencies and insights but also introduces potential risks that can compromise ethical standards. These challenges necessitate careful management, continuous oversight, and proactive governance to align technological capabilities with societal values and legal requirements. Fostering an environment of transparency and accountability helps mitigate ethical concerns and promotes responsible AI deployment in research settings.
Managing Data Privacy, Bias, and Transparency in Automated Workflows
In automated research workflows, safeguarding data privacy involves implementing strict data access controls, anonymization techniques, and compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA. As AI systems often process sensitive information, establishing clear data governance policies ensures that personal and proprietary data are handled ethically and securely.
Bias mitigation is critical to prevent skewed or unfair research outcomes. AI models trained on biased datasets can perpetuate stereotypes or lead to inaccurate conclusions. Strategies include using diverse, representative datasets, conducting bias audits, and applying fairness-aware machine learning techniques to enhance model neutrality.
Transparency in AI processes underpins trust and accountability. Documenting algorithm development, data sources, and decision-making criteria allows stakeholders to understand how conclusions are derived. Techniques such as explainable AI (XAI) facilitate interpretability, enabling researchers to identify potential biases or errors and justify automated decisions effectively.
Procedures for Auditing AI Processes to Ensure Ethical Compliance
Establishing systematic auditing procedures is vital for verifying that AI systems adhere to ethical standards throughout their lifecycle. Audits should be conducted regularly and encompass various aspects such as data integrity, model fairness, and decision explainability.
Key steps in AI auditing include:
- Documentation Review: Ensuring comprehensive records of data sources, model training processes, and decision logs are maintained.
- Bias and Fairness Testing: Conducting statistical analyses to detect bias in outputs and assessing fairness across different demographic groups.
- Explainability Assessment: Verifying that AI systems provide clear, understandable rationales for their decisions to facilitate stakeholder review.
- Compliance Verification: Cross-checking AI operations against relevant legal and ethical guidelines, including data privacy laws and institutional policies.
Automated auditing tools and third-party evaluations can supplement internal reviews, providing unbiased insights and ensuring continuous compliance.
Key Challenges and Solutions in Implementing AI for Research Purposes
Implementing AI within research contexts presents several challenges that require targeted solutions to optimize outcomes while maintaining ethical standards.
Challenges include:
- Data Quality and Accessibility: Obtaining comprehensive, high-quality datasets can be difficult due to privacy restrictions or proprietary limitations. Solutions involve developing data-sharing agreements, leveraging synthetic data, and applying data augmentation techniques.
- Algorithmic Bias: Biases in training data can lead to unfair or invalid results. Addressing this requires rigorous bias detection, balanced datasets, and fairness-aware algorithms.
- Interpretability and Explainability: Complex models like deep neural networks often act as “black boxes,” making it hard to interpret decisions. Employing explainable AI methods and simplifying models where possible improve transparency.
- Ethical and Regulatory Compliance: Navigating evolving legal frameworks can be intricate. Establishing multidisciplinary oversight committees and staying informed about regulatory updates help ensure adherence.
By proactively confronting these challenges with innovative solutions, research institutions can harness AI’s potential while safeguarding ethical principles, thereby fostering trust and integrity in scientific advancement.
Final Review

In conclusion, mastering how to automate research workflows with AI offers a transformative advantage in the landscape of research and data analysis. Embracing these technologies paves the way for innovative discoveries and provides a competitive edge in various disciplines. Continuous optimization and adherence to ethical standards will ensure these systems remain effective and trustworthy in the long term.