Understanding how to detect plagiarism with AI is essential in maintaining integrity across educational and professional environments. As content creation evolves, traditional manual methods have given way to advanced artificial intelligence solutions that offer faster and more precise detection capabilities. Leveraging AI not only enhances the efficiency of identifying copied or similar content but also introduces sophisticated features such as semantic analysis and pattern recognition that outshine conventional techniques.
This overview explores the mechanisms, tools, procedures, and ethical considerations involved in deploying AI for plagiarism detection, providing valuable insights for effective implementation.
Introduction to Detecting Plagiarism with AI
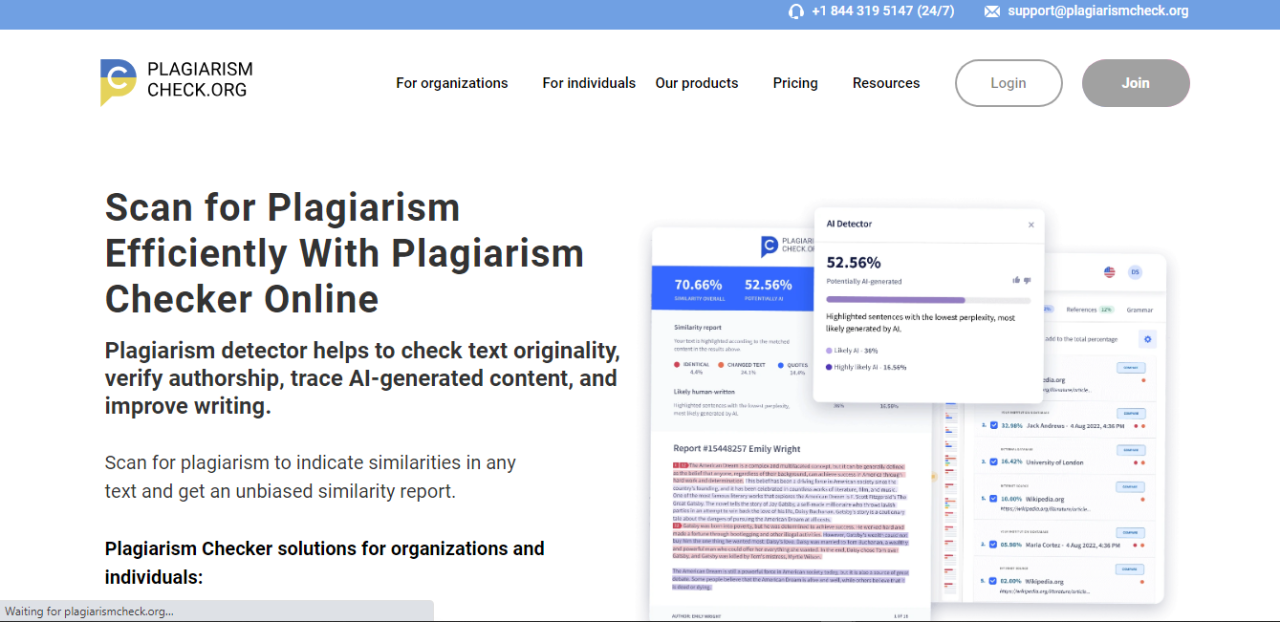
In both educational and professional environments, maintaining originality and academic integrity is paramount. The advent of artificial intelligence (AI) has revolutionized the way plagiarism is identified, offering more efficient and accurate solutions compared to traditional manual methods. AI-based plagiarism detection tools utilize advanced algorithms to scan, analyze, and compare vast amounts of textual data swiftly, ensuring the originality of content with a high degree of precision.
The significance of AI in plagiarism detection stems from its ability to handle large datasets, recognize paraphrased content, and adapt to evolving writing patterns. As academic institutions and corporations increasingly rely on digital content, traditional methods such as manual review or simple searches have proved insufficient. AI-powered solutions address these limitations by providing automated, scalable, and intelligent analysis, making the process more reliable and less time-consuming.
Distinguishing Features of AI-Based Plagiarism Detection Tools
AI detection tools stand out from conventional methods through several key features that enhance their effectiveness and usability. Understanding these features helps in appreciating their role in safeguarding originality:
- Advanced Pattern Recognition: AI algorithms can identify subtle similarities, paraphrased content, and disguised plagiarism that basic searches might overlook.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Leveraging NLP allows AI systems to understand context, semantics, and syntactic structures, enabling them to detect nuanced instances of copied material.
- Scalability and Speed: Unlike manual checks that are time-consuming, AI tools can analyze thousands of documents or large datasets within seconds, providing quick results for educators and professionals.
- Continuous Learning and Adaptation: Machine learning capabilities enable AI systems to improve over time, adapting to new writing styles and emerging forms of plagiarism, thus maintaining high accuracy levels.
- Comprehensive Reporting: AI tools typically generate detailed reports highlighting similarities, sources, and the degree of overlap, facilitating informed decisions and transparent assessments.
These distinguishing features not only improve detection rates but also streamline the entire process, making AI an indispensable asset in upholding integrity across various sectors.
How AI Detects Plagiarism
Artificial Intelligence has revolutionized the way plagiarism is identified by enabling more sophisticated, accurate, and efficient detection methods. Unlike traditional techniques that rely heavily on manual or -based comparisons, AI employs advanced algorithms and machine learning models to analyze content at deeper levels. This technological evolution allows for the detection of subtle similarities, paraphrased content, and even intentionally disguised copying, making plagiarism detection more reliable and comprehensive in various academic and professional settings.
AI-based plagiarism detection integrates multiple techniques that work together to analyze textual data, assess contextual similarities, and provide reliable results. These methods leverage pattern recognition, semantic understanding, and stylistic analysis to identify potential instances of copied or paraphrased content. As a result, organizations and educators can ensure the integrity of work with a higher degree of confidence, maintaining fairness and academic honesty across diverse fields.
Algorithms and Machine Learning Models Used to Identify Similar or Copied Content
Detecting plagiarism with AI involves deploying a range of algorithms and machine learning models designed to analyze textual data from different perspectives. These models learn from vast datasets of legitimate and plagiarized content, enabling them to recognize complex patterns and anomalies indicative of copying. The primary algorithms and models include:
- Pattern Recognition Algorithms: These algorithms analyze text for repetitive patterns, sequences, and structures that are characteristic of copied content. They compare document fragments against large databases to find exact or near-exact matches.
- Semantic Analysis Models: Utilizing Natural Language Processing (NLP), these models assess the meaning behind words and phrases, enabling the detection of paraphrased or synonymously altered content. Techniques like word embeddings (e.g., Word2Vec, GloVe) help measure semantic similarity beyond surface-level matching.
- Stylometry and Authorship Attribution: These models analyze writing style features such as vocabulary usage, sentence structure, punctuation, and syntax. Significant deviations from an author’s typical style can indicate potential plagiarism, especially in cases of disguised copying.
- Deep Learning Approaches: Advanced neural networks, like Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), are trained to recognize nuanced textual similarities that traditional algorithms might miss. These models improve detection accuracy, especially for paraphrased content.
Comparison of AI Detection Techniques
Different AI detection techniques are employed based on their strengths and specific application contexts. Understanding these methods helps in selecting the most suitable approach for a given scenario.
| Technique | Core Functionality | Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pattern Recognition | Identifies exact and near-exact textual matches through sequence comparison | High precision for direct copies; fast processing | Less effective against paraphrased or modified content |
| Semantic Analysis | Assesses the meaning and context of text to detect paraphrasing | Detects disguised copying; understands contextual similarity | Requires significant computational resources; may produce false positives |
| Stylometry | Analyzes writing style features to attribute or detect anomalies | Effective against disguised copying in authored documents | Dependent on consistent writing style; less effective with collaborative work |
| Deep Learning | Uses neural networks to learn complex textual patterns | Highly adaptable; improves over time with more data | Computationally intensive; requires large datasets for training |
Combining these techniques often yields the most accurate results, leveraging the strengths of each to compensate for their individual limitations. For example, pattern recognition quickly identifies obvious matches, while semantic analysis and deep learning models uncover more subtle instances of plagiarism, such as paraphrasing or stylistic alterations.
AI-Based Plagiarism Detection Flowchart
The process of identifying plagiarism through AI can be visualized in a flowchart that Artikels each step from data input to the final result. This process ensures transparency and helps in understanding how various algorithms interact to produce a conclusive report.
Step 1: Data Input – The document under review is uploaded or submitted for analysis.
Step 2: Preprocessing – The text is cleaned and segmented into manageable units such as sentences or paragraphs.
Step 3: Pattern Recognition – The system compares segments against a vast database to find direct matches or similarities.
Step 4: Semantic Analysis – Natural Language Processing techniques evaluate the meaning behind the content to identify paraphrased or semantically similar text.
Step 5: Stylometric Analysis – The writing style of the document is analyzed for inconsistencies or deviations from known authorship patterns.
Step 6: Integration & Scoring – Results from all analyses are aggregated, and a similarity score is generated based on predefined thresholds.
Step 7: Report Generation – A detailed report highlights the detected similarities, potential issues, and confidence levels.
Step 8: Final Decision – The system provides a conclusion on whether the document is likely plagiarized, assisting human review as needed.
Common AI Tools and Software for Plagiarism Detection
As the use of artificial intelligence becomes increasingly integrated into academic and professional environments, a variety of AI-driven tools have emerged to streamline the process of plagiarism detection. These software solutions leverage advanced algorithms to analyze large volumes of text swiftly and accurately, helping educators, publishers, and organizations uphold integrity and originality in their content.
The efficacy of these tools depends on their ability to identify similarities, paraphrasing, and potential sources of copied material, often across multiple languages and formats. While each tool employs unique techniques and features, their common goal remains consistent: to ensure content authenticity and prevent intellectual theft effectively.
Overview of Popular AI-Driven Plagiarism Detection Programs
Below is a table summarizing some of the most widely used AI-powered plagiarism detection software, highlighting their main features and estimated accuracy levels based on user reviews and independent evaluations.
| Tool Name | Features | Accuracy Level |
|---|---|---|
| Turnitin |
|
High (approx. 95%) |
| Grammarly Premium |
|
Moderate to High (approx. 90%) |
| Copyscape |
|
High (approx. 92%) |
| Quetext |
|
Moderate to High (approx. 88%) |
| SmallSEOTools Plagiarism Checker |
|
Moderate (approx. 80%) |
Analysis Methods Employed by AI Tools for Originality Detection
AI-based plagiarism detection tools utilize sophisticated analysis techniques to ensure thorough evaluation of content originality. These methods include pattern recognition, semantic analysis, and source comparison, which collectively enable the tools to identify both direct copying and more subtle forms of paraphrasing or text modification.
For example, the process often begins with tokenization, where the text is broken into smaller units such as words or phrases. The AI then compares these units against extensive databases, including online sources, academic repositories, and previously submitted documents. Machine learning algorithms further enhance this process by recognizing contextual similarities that might not be apparent through simple string matching.
Criteria Used to Flag Potential Plagiarism
AI tools employ specific criteria to determine whether content may be plagiarized. These criteria are based on multiple factors, ensuring comprehensive evaluation and reducing false positives.
- Textual Similarity: The degree of match between the submitted text and existing sources, often expressed as a percentage. Higher similarity percentages typically indicate potential plagiarism.
- Paraphrasing Detection: The ability to recognize reworded content that retains the original meaning but has altered phrasing or sentence structure.
- Source Credibility: The origin of matched content, with higher concern assigned to sources like academic journals or proprietary publications.
- Citation and Reference Analysis: Evaluation of whether proper citations are provided, and detection of missing or incorrect referencing that may suggest uncredited copying.
- Semantic and Contextual Analysis: Advanced AI algorithms assess the overall context to identify paraphrased or summarized content that may evade simple string matching.
By combining these criteria, AI tools provide a nuanced and reliable assessment of content originality, assisting users in maintaining high standards of integrity in their work.
Procedures for Using AI to Detect Plagiarism
Implementing AI tools for plagiarism detection involves a systematic approach to ensure accuracy and reliability. Properly submitting content, understanding the interpretation of results, and adhering to best practices are essential steps for effective detection. This process not only enhances the integrity of academic and professional work but also streamlines the verification process, saving time and resources.
Follow these structured procedures to maximize the benefits of AI-powered plagiarism detection platforms, ensuring that your evaluations are thorough, precise, and defensible in academic or professional settings.
Submitting Content to AI Detection Platforms
Submitting content correctly is foundational for accurate results. The process generally involves uploading or pasting the document into the platform and configuring relevant settings. Ensuring the content is in the accepted format and free from technical issues helps avoid false positives or missed matches.
- Access the chosen AI plagiarism detection platform, such as Turnitin, Grammarly, or Copyscape.
- Register or log into your account, ensuring you have the necessary permissions or subscriptions.
- Select the option to submit a new document, often labeled as “Upload,” “New Submission,” or similar.
- Upload the document file in supported formats (e.g., .docx, .pdf, .txt). Alternatively, copy and paste the content directly into the platform’s text box if such an option exists.
- Configure detection settings, such as selecting the scope (internet, academic databases, or proprietary repositories), and choosing sensitivity levels if available.
- Initiate the scan by clicking the “Check” or “Start” button. The platform will process the content against its database.
For large documents or batch submissions, consider dividing content into smaller sections to manage processing time and review results more efficiently.
Interpreting Results: Confidence Scores and Matched Sections
Results from AI plagiarism detection platforms typically include a similarity report highlighting potential matches. Understanding the components of this report is critical for accurate interpretation and subsequent action.
- Similarity Percentage: Indicates the proportion of the submitted content that matches other sources. A higher percentage suggests greater similarity, but it does not necessarily imply plagiarism—context matters.
- Matched Sections Highlighting: The report visually emphasizes areas of concern by highlighting text segments that resemble sources in the database. These highlights help reviewers quickly identify problematic content.
- Source Links and Citations: Each highlighted segment usually links to or cites the original source, aiding in verifying whether proper attribution exists.
- Confidence Scores: Many platforms assign a confidence score reflecting the likelihood that a match is actual plagiarism. Scores close to 100% denote strong matches, while lower scores suggest possible false positives or common phrases.
Effective interpretation involves reviewing highlighted sections in detail, considering the context, and verifying sources before making determinations about plagiarism.
Best Practices Checklist for Accurate Detection
Adhering to established best practices enhances the reliability of AI-based plagiarism checks. These guidelines support consistent and fair evaluation processes across different cases.
- Ensure the submitted content is complete, clear, and free of formatting issues that could interfere with analysis.
- Use the most recent version of the AI detection platform to benefit from updated databases and algorithms.
- Calibrate detection sensitivity settings based on the nature of the content; for example, academic papers may require stricter settings than casual writing.
- Review the similarity report thoroughly, focusing on matched sections’ context and source credibility rather than relying solely on the similarity percentage.
- Cross-verify highlighted sources and matched texts with original sources to assess whether proper citation or paraphrasing has been employed.
- Document findings with screenshots or exported reports for record-keeping, especially in formal evaluations or academic submissions.
- In case of ambiguous results, consider manual review or supplementary detection tools to confirm the findings.
- Maintain awareness of platform limitations, such as the inability to detect content in images or non-digital sources, and supplement with human judgment when necessary.
Limitations and Challenges of AI Detection Methods
%20(21).png)
While AI-based tools have significantly improved the efficiency and accuracy of plagiarism detection, they are not without their limitations. Recognizing these challenges is essential for users to interpret results correctly and to understand the potential pitfalls of relying solely on automated systems. AI detection methods, although sophisticated, can sometimes produce false positives or negatives, especially in complex textual scenarios. Additionally, issues such as accurately identifying paraphrased or translated content and mitigating algorithmic biases are ongoing concerns that require careful attention and continual refinement.
Understanding the inherent limitations of AI in plagiarism detection enables educators, researchers, and institutions to implement more balanced approaches, combining technological tools with human judgment. This approach ensures improved reliability and fairness in assessing originality, while also fostering awareness of the contexts in which AI might struggle or mislead.
False Positives and False Negatives in AI Detection
The effectiveness of AI detection tools depends largely on their algorithms and training datasets. However, these systems can sometimes generate false positives—incorrectly flagging original work as plagiarized—or false negatives—failing to identify actual instances of plagiarism. Such inaccuracies can arise due to various factors:
- Similar Writing Styles: AI might falsely identify common phrases or stylistic patterns as plagiarism, especially in specialized fields where terminology and phrasing are consistent across multiple texts.
- Limited Training Data: When AI models are trained on insufficient or non-representative datasets, they may lack the nuance needed to distinguish between legitimate similarity and illicit copying.
- Context Ambiguity: AI tools may misinterpret content that is common knowledge, quotes, or properly cited material, leading to false accusations.
Furthermore, false negatives are particularly problematic as they can allow plagiarized content to go undetected, undermining the integrity of the evaluation process. To mitigate these issues, it is recommended to interpret AI results alongside human review, especially in borderline cases.
Challenges in Detecting Paraphrased and Translated Content
One of the most significant hurdles for AI-based plagiarism detection is accurately identifying paraphrased or translated material. These forms of content modification are designed to obscure direct copying, making detection more complex:
- Paraphrasing: Skilled writers can rephrase sentences while retaining the original meaning, which can evade -based algorithms. Advanced AI models struggle to detect nuanced paraphrasing, particularly when it involves sophisticated language use or domain-specific terminology.
- Translation: Content translated from one language to another often loses some lexical similarity, complicating detection efforts. AI tools trained primarily on monolingual datasets may fail to recognize translated text as plagiarism, especially if the translation is natural and contextually accurate.
- Semantic Equivalence: Detecting paraphrased or translated content requires understanding semantic equivalence beyond superficial matching. This demands more advanced natural language understanding capabilities, which are still evolving.
To address these challenges, integrating semantic analysis and cross-lingual detection techniques can improve accuracy. Nonetheless, human expertise remains vital for confirming suspected cases of paraphrasing or translation-based plagiarism.
Biases in AI Algorithms and Mitigation Strategies
AI detection systems are trained on datasets that may contain inherent biases, which can influence their outputs. These biases might lead to unfair treatment of certain groups or types of content, affecting the validity of the detection process:
- Dataset Bias: If the training data over-represents specific writing styles, topics, or languages, the AI may be more effective in some contexts than others, potentially leading to disparities in detection performance.
- Cultural and Linguistic Biases: AI models may struggle with content written in less-represented languages or dialects, increasing the risk of false negatives in these cases.
- Confirmation Bias: Overreliance on AI outputs without human oversight may reinforce existing biases, resulting in unfair accusations or overlooked instances of plagiarism.
Mitigating these biases involves diverse and representative training datasets, continual model evaluation and updating, and incorporating human review into the detection process. Transparency about the limitations and decision criteria of AI systems also plays a critical role in fostering fairness and trust.
Enhancing Detection Accuracy with AI
![10 Best AI Plagiarism Checker - Side-By-Side Comparison [2024] 10 Best AI Plagiarism Checker - Side-By-Side Comparison [2024]](https://teknobits.web.id/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/9ceecbc5822bda5.jpg)
As the use of AI in plagiarism detection continues to evolve, the focus shifts toward improving the precision and reliability of these tools. Combining AI technology with manual review processes, refining models through targeted training, and updating algorithms to recognize emerging forms of content manipulation are essential strategies to bolster detection accuracy. These approaches ensure that institutions and individuals can effectively identify sophisticated instances of plagiarism while minimizing false positives.
Implementing a multifaceted approach that leverages the strengths of AI alongside human expertise enhances the overall effectiveness of plagiarism detection systems. Continuous refinement of AI models and adaptive techniques are vital to staying ahead of increasingly complex content alteration methods employed by plagiarists.
Combining AI Tools with Manual Review Processes
To maximize detection accuracy, integrating AI-driven tools with manual review processes creates a robust verification system. While AI can efficiently scan large volumes of text and flag potential matches, human reviewers bring critical judgment and contextual understanding that AI may lack. This symbiotic relationship reduces errors, confirms genuine cases, and minimizes false positives.
Strategies for effective integration include establishing clear protocols where AI findings are first reviewed by trained professionals who assess the context and validity of flagged content. Regular training for reviewers on the latest AI outputs and potential manipulation techniques ensures consistency and improves decision-making accuracy. Employing collaborative platforms where reviewers can annotate and comment on AI-detected anomalies further enhances the review process.
Organizing Strategies for Training AI Models
Improving the capacity of AI models to detect sophisticated forms of plagiarism requires well-structured training methodologies. Incorporating diverse datasets that include various writing styles, subject areas, and known instances of content manipulation helps the model learn to recognize subtle similarities and paraphrasing tactics.
Key strategies include:
- Curating extensive, high-quality datasets containing both genuine content and known plagiarized examples, including paraphrased or translated texts.
- Employing supervised learning techniques where human experts label training data, guiding the AI to identify nuanced patterns of plagiarism.
- Utilizing transfer learning to adapt models trained on general language understanding to specific domains, such as academic writing or creative content.
“A well-trained AI model adapts to the evolving landscape of content manipulation, maintaining high detection rates even against sophisticated plagiarism techniques.”
Updating AI Algorithms to Recognize New Content Manipulation Forms
Content manipulation techniques are constantly advancing, necessitating regular updates to AI algorithms. This proactive process involves monitoring emerging trends, such as paraphrasing, synonym substitution, and automated content generation, which plagiarists employ to evade detection.
Effective techniques include:
- Implementing continuous learning frameworks where models are periodically retrained with fresh data reflecting new manipulation tactics.
- Leveraging feedback loops from manual reviews to identify false negatives, enabling the AI to learn from its mistakes.
- Incorporating natural language processing advancements, such as semantic analysis and deep contextual understanding, to better grasp the meaning behind manipulated content.
For example, AI systems that analyze semantic similarity rather than surface-level wording are more effective in detecting paraphrased content. Staying ahead in this domain involves a dynamic process of algorithm refinement, data updating, and embracing cutting-edge NLP techniques to ensure detection systems remain robust and accurate over time.
Ethical and Legal Considerations
Implementing AI-based plagiarism detection systems requires careful attention to ethical standards and legal frameworks to ensure responsible use within academic and professional environments. While these tools offer powerful capabilities to uphold integrity, their deployment must respect individual rights, confidentiality, and fairness.
Addressing ethical and legal dimensions involves understanding the responsibilities of institutions and users in safeguarding privacy, maintaining transparency, and avoiding misuse of data. This section discusses the critical considerations that organizations must observe to utilize AI effectively and ethically in detecting plagiarism.
Privacy and Data Security
AI-driven plagiarism detection often involves analyzing extensive amounts of sensitive or proprietary content, such as student submissions, research data, or corporate documents. Ensuring the privacy of individuals and protecting proprietary information is paramount to prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, or misuse.
Institutions should establish protocols for data handling that include encryption, restricted access, and secure storage solutions. It is essential to collect only the necessary data for detection purposes and to anonymize content when possible to reduce privacy risks. Transparency regarding data collection and processing practices fosters trust among users and aligns with privacy laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA).
Fair Use and Transparency
When deploying AI tools, organizations must develop clear guidelines that delineate fair use boundaries and ensure transparency in their operation. This involves informing users about how their content is being analyzed, the criteria used for plagiarism detection, and the potential consequences of flagged content.
Providing detailed reports that specify the nature of similarities and the sources involved helps maintain fairness and trust. Furthermore, organizations should offer avenues for individuals to contest or review detection outcomes, fostering a culture of accountability and ethical responsibility.
“Transparency and fairness are fundamental to maintaining integrity when utilizing AI for plagiarism detection, ensuring that all stakeholders understand and trust the process.”
Adherence to legal standards also involves respecting intellectual property rights and avoiding false accusations that could harm reputations. Ethical deployment of AI detection tools ensures that the technology supports integrity without infringing on individual rights or fostering biases.
Case Studies and Practical Applications
Real-world instances where AI-driven plagiarism detection has been successfully implemented highlight the technology’s profound impact across various sectors. These case studies offer valuable insights into effective methodologies, demonstrate the tangible benefits of AI in maintaining academic integrity, and provide lessons that can inform future best practices. Exploring these practical applications underscores not only the effectiveness of AI tools but also their evolving role in safeguarding originality in a digital age.
By analyzing these high-profile cases, educators, publishers, and organizations can better understand the real-world capabilities and limitations of AI-based plagiarism detection. The lessons learned from successful implementations serve as benchmarks for developing more robust, accurate, and ethical detection systems. Below are detailed descriptions of notable examples illustrating AI’s crucial role in uncovering instances of plagiarism, along with procedural insights and best practices derived from these experiences.
Case Study: Academic Institution Detects Sophisticated Plagiarism Using AI
An elite university employed advanced AI algorithms integrated with natural language processing (NLP) to analyze student submissions across multiple disciplines. The AI system was designed to detect paraphrased content and cross-reference vast databases of scholarly articles, internet sources, and previous submissions. This case exemplifies AI’s capability to identify complex forms of plagiarism that traditional methods might overlook.
Results revealed several instances where students had paraphrased sources extensively, making manual detection difficult. The AI identified patterns of text similarity, stylistic inconsistencies, and unoriginal content, prompting further investigation by academic integrity officers. The outcome reinforced the importance of using AI as a complementary tool to human judgment, effectively deterring potential violations and upholding academic standards.
Case Study: Publishing House Catches Plagiarism in a High-Profile Book
A leading publishing company integrated AI-powered plagiarism detection software into its editorial workflow to ensure the originality of manuscripts before publication. By deploying machine learning models trained on extensive datasets, the software could compare new submissions against millions of existing texts, including online articles, academic papers, and previous publications.
In one instance, the AI flagged significant sections of a manuscript that bore striking similarities to an earlier work by a different author. The system highlighted specific overlapping phrases, structural similarities, and thematic parallels. This early detection prevented the publication of plagiarized content, saving the publisher from potential legal and reputational damages. The case exemplifies AI’s role in quality control and intellectual property protection within the publishing industry.
Lessons Learned and Best Practices from Practical Applications
Examination of these real-world cases reveals several key lessons and best practices for effectively leveraging AI in plagiarism detection:
- Combine AI tools with human expertise for comprehensive analysis, especially in nuanced or complex cases.
- Regularly update AI databases and algorithms to keep pace with emerging forms of text manipulation and new sources.
- Use AI to identify potential issues, then conduct detailed manual reviews to confirm instances of plagiarism.
- Train staff and users on interpreting AI-generated reports accurately to avoid false positives and negatives.
- Maintain transparency with users regarding how AI detection systems operate and their limitations, fostering trust and ethical use.
“AI detection systems should be viewed as intelligent adjuncts, not infallible arbiters, in the ongoing effort to preserve originality and integrity.”
Overall, these case studies demonstrate that when integrated thoughtfully into workflows, AI-powered plagiarism detection can significantly enhance accuracy, efficiency, and integrity in various professional settings. Balancing technological capabilities with human oversight and continuous improvement remains essential for optimal outcomes.
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, mastering how to detect plagiarism with AI is crucial for upholding originality and trustworthiness in various content domains. By combining cutting-edge AI algorithms with manual review processes and staying aware of current limitations, organizations can significantly improve detection accuracy. Embracing these intelligent tools and adhering to ethical practices ensures a reliable, transparent approach to content verification that adapts to the evolving landscape of content manipulation.