Discover how to automate knowledge management using AI and transform organizational information processes. Leveraging advanced technologies such as machine learning and natural language processing, organizations can streamline data collection, classification, and retrieval to boost productivity and decision-making. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of implementing AI-driven solutions to create smarter, more responsive knowledge systems.
Overview of Automating Knowledge Management with AI
In an increasingly data-driven world, organizations seek innovative methods to streamline the handling and dissemination of knowledge. Automating knowledge management using artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a pivotal approach to enhance organizational efficiency, accuracy, and responsiveness. This overview explores the fundamental principles of knowledge management and the transformative role AI plays in automating these processes.
AI-powered solutions facilitate rapid information retrieval, intelligent categorization, and dynamic content updating, thereby reducing manual effort and minimizing errors. As organizations adopt AI-driven systems, understanding the core benefits and contrasting traditional methodologies with modern, automated approaches becomes essential for strategic decision-making and operational excellence.
Core Principles of Knowledge Management and AI Enhancement
Knowledge management (KM) is centered around capturing, organizing, sharing, and utilizing knowledge within an organization to support decision-making and foster innovation. The primary principles include creating a culture of knowledge sharing, ensuring data quality, and implementing effective information systems. Integrating AI enhances these principles by automating routine tasks, offering predictive insights, and enabling intelligent content management.
AI technologies such as natural language processing (NLP), machine learning, and data analytics empower KM systems to automatically classify documents, extract relevant information, and personalize knowledge delivery. This automation not only accelerates access to critical information but also improves accuracy by reducing human error and bias.
Benefits of Integrating AI into Knowledge Management Systems
Organizations that embed AI into their knowledge management infrastructure experience a multitude of advantages that drive operational efficiency and strategic agility. Key benefits include:
- Enhanced Efficiency: Automating data entry, classification, and retrieval processes significantly reduces time and resource expenditure.
- Improved Accuracy and Consistency: AI algorithms minimize human error, ensuring that information remains reliable and up-to-date.
- Personalized Knowledge Access: AI-driven systems analyze user behavior and preferences to deliver tailored content, boosting user engagement and productivity.
- Scalability: As organizational data grows exponentially, AI systems can effortlessly scale to accommodate increasing volumes without compromising performance.
- Real-time Insights: Predictive analytics and data visualization tools enable organizations to respond swiftly to emerging trends and challenges.
Furthermore, AI facilitates proactive knowledge management by identifying gaps and suggesting relevant content or expertise, fostering a culture of continuous learning.
Comparison of Traditional and AI-Driven Knowledge Management Approaches
Traditional knowledge management relies heavily on manual processes, human intervention, and static repositories. This approach often faces challenges such as slow information retrieval, inconsistent data quality, and limited scalability. Conversely, AI-driven KM systems leverage advanced algorithms to automate and optimize the entire knowledge lifecycle.
| Aspect | Traditional Knowledge Management | AI-Enhanced Knowledge Management |
|---|---|---|
| Data Handling | Manual data entry, classification, and updating | Automated data processing, classification, and real-time updating |
| Speed of Access | Slower retrieval due to manual searching and categorization | Instantaneous, intelligent search and retrieval using NLP and AI algorithms |
| Accuracy and Consistency | Dependent on human input, prone to errors and inconsistencies | High accuracy through automated validation and learning from data patterns |
| Scalability | Limited scalability, requiring additional human resources | High scalability with minimal additional effort |
| Adaptability | Rigid, requiring manual updates for new content or formats | Adaptive, capable of learning and evolving with new data and user behaviors |
“AI-driven knowledge management systems transform static repositories into dynamic, intelligent platforms capable of proactive and personalized information delivery, thereby revolutionizing organizational workflows.”
Key Technologies Enabling AI-Powered Knowledge Management
Advancements in artificial intelligence have transformed traditional knowledge management systems into dynamic, automated platforms. Central to this evolution are technologies such as machine learning, natural language processing, and data mining, which collectively enable organizations to efficiently capture, organize, and utilize their knowledge assets. Understanding these core technologies is essential for deploying effective AI-driven solutions that enhance decision-making, foster collaboration, and accelerate innovation.
These technologies work synergistically to automate the extraction, classification, and retrieval of information from vast and diverse data sources. They facilitate intelligent search capabilities, personalized knowledge delivery, and the continuous updating of repositories with minimal human intervention. By leveraging these tools, organizations can ensure their knowledge bases are more accurate, accessible, and aligned with evolving business needs.
Machine Learning in Knowledge Automation
Machine learning (ML) involves algorithms that improve automatically through experience, enabling systems to recognize patterns and make predictions or decisions based on data. In knowledge management, ML is instrumental in categorizing content, tagging documents, and identifying relevant information across repositories. For example, supervised learning models can classify incoming documents into predefined categories, such as technical support or HR policies, streamlining retrieval processes.
Unsupervised learning techniques, such as clustering, help uncover hidden relationships among data points, revealing insights that may not be immediately apparent. Reinforcement learning can optimize workflows by adapting to user feedback, thereby enhancing the relevance of recommendations and search results.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) for Knowledge Extraction
Natural language processing (NLP) enables machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language. This technology is vital in transforming unstructured textual data—such as emails, reports, and chat transcripts—into structured, searchable knowledge. NLP techniques like entity recognition, sentiment analysis, and summarization facilitate the automatic extraction of key information and contextual insights. For example, AI-powered chatbots utilize NLP to interpret user queries and provide accurate, contextually relevant responses.
Additionally, NLP-driven semantic search enhances the ability of knowledge bases to retrieve information based on meaning rather than exact matches, significantly improving user experience and efficiency.
Data Mining Techniques for Knowledge Discovery
Data mining involves analyzing large datasets to identify patterns, correlations, and trends that can inform strategic decisions. In knowledge management, data mining techniques help uncover valuable insights from diverse data sources, including structured databases and unstructured documents. Techniques such as association rule learning, anomaly detection, and classification are employed to predict future behaviors, detect inconsistencies, and categorize information. For example, organizations can analyze support ticket data to identify common issues and proactively develop solutions.
Implementing data mining within knowledge repositories ensures continuous learning and evolution of the knowledge base, aligning it more closely with organizational objectives.
Implementing AI Tools within Existing Knowledge Repositories
Integration of AI technologies into existing knowledge systems requires a strategic approach that ensures seamless operation and maximum benefit. The following table Artikels key features of AI tools, their benefits, and representative platforms that facilitate this integration:
| Features | Benefits | Tools/Platforms |
|---|---|---|
| Automated Content Tagging and Classification | Enhances searchability and organization of knowledge assets, reduces manual effort | IBM Watson Knowledge Studio, Google Cloud Natural Language API |
| Semantic Search and Query Understanding | Improves accuracy of search results by understanding intent and context | Microsoft Azure Cognitive Search, Elasticsearch with NLP plugins |
| Knowledge Extraction and Summarization | Enables quick comprehension of large documents, supports decision-making | Amazon Comprehend, SAS Text Analytics |
| Chatbots and Virtual Assistants | Provides immediate support and information retrieval, increases user engagement | Dialogflow, IBM Watson Assistant, Microsoft Bot Framework |
Examples of AI Platforms and Software Facilitating Knowledge Automation
Numerous AI platforms and software solutions are available to assist organizations in automating knowledge management processes. Notable examples include:
- IBM Watson Discovery: Utilizes NLP and ML to analyze large datasets, extract relevant insights, and support decision-making processes.
- Microsoft Azure Cognitive Services: Offers a suite of APIs for language understanding, speech recognition, and image analysis, which can be integrated into knowledge systems.
- Google Cloud AI Platform: Provides tools for building, deploying, and managing machine learning models that can automate content classification, extraction, and summarization tasks.
- Elasticsearch with Machine Learning: An open-source search engine with advanced analytics capabilities that enable semantic search and anomaly detection within knowledge repositories.
These platforms facilitate the development of tailored AI solutions, allowing organizations to modernize their knowledge management infrastructure effectively. They support seamless integration with existing systems, scalability, and continuous learning, thereby ensuring that knowledge assets remain current, accurate, and easily accessible.
Designing an AI-Driven Knowledge Management Workflow
Creating an effective AI-driven knowledge management workflow requires a structured approach that ensures accurate data handling, efficient classification, and swift retrieval. This process integrates advanced AI technologies to streamline organizational knowledge, reduce redundancy, and enhance decision-making capabilities. Designing such workflows involves multiple interconnected stages that facilitate continuous learning and adaptation, ensuring the organization’s knowledge base remains relevant and comprehensive.
Implementing a well-designed workflow begins with clearly defining data collection methods, followed by sophisticated classification and retrieval mechanisms. Equally important is training AI models on organizational data to boost their accuracy and relevance over time. The following Artikeld steps provide a systematic approach to developing and maintaining a dynamic, AI-powered knowledge management system.
Structuring Knowledge Collection, Classification, and Retrieval with AI
Establishing a seamless process for capturing, organizing, and accessing knowledge is vital for maximizing AI efficiency. The workflow typically follows these stages:
- Knowledge Collection: Gather data from diverse sources such as documents, emails, databases, and social media. Use AI-powered data extraction tools to automate the ingestion process, ensuring comprehensive and up-to-date information.
- Data Cleansing: Remove redundancies, correct inaccuracies, and standardize formats to enhance data quality. Techniques include duplicate detection, normalization, and validation against organizational standards.
- Data Tagging and Annotation: Apply semantic labels, s, and tags to facilitate precise classification. AI models learn to recognize contextual relationships during this stage, improving future retrieval accuracy.
- Indexing: Organize data within searchable structures such as vectors, taxonomies, or ontologies. Indexing enables rapid retrieval through algorithms optimized for large datasets.
- Knowledge Classification: Utilize machine learning models like classifiers or clustering algorithms to categorize knowledge into relevant topics, departments, or expertise areas.
- Knowledge Retrieval: Deploy natural language processing (NLP) techniques to interpret user queries and fetch relevant information swiftly, utilizing the organized knowledge base.
Procedures for Training AI Models on Organizational Data
Training AI models effectively on organizational data enhances their ability to interpret, classify, and retrieve knowledge accurately. The process involves several key procedures:
- Data Preparation: Aggregate historical data, documents, and interaction logs, ensuring that the dataset encompasses diverse organizational knowledge. Conduct data cleansing to eliminate noise and inconsistencies before training.
- Feature Engineering: Extract meaningful features from raw data, such as s, sentiment scores, or contextual embeddings. These features enable models to understand the nuances of organizational language and concepts.
- Model Selection and Training: Choose appropriate AI algorithms—such as supervised classifiers, unsupervised clustering, or deep learning models—and train them iteratively on labeled datasets. For example, training a classifier to categorize internal reports into predefined topics enhances automated tagging accuracy.
- Model Validation and Testing: Evaluate model performance using metrics like precision, recall, and F1-score on validation datasets. Adjust parameters to optimize accuracy and avoid overfitting.
- Deployment and Feedback Loop: Integrate models into the knowledge management system. Continuously monitor performance and gather user feedback to identify areas for improvement.
- Continuous Learning: Regularly update models with new organizational data, retraining as necessary to adapt to evolving knowledge and terminologies. This ensures sustained relevance and accuracy in knowledge classification and retrieval.
Effective AI training hinges on high-quality data, iterative validation, and ongoing refinement, enabling the system to adapt to organizational changes and expand its knowledge base.
Data Preparation and Integration Strategies
Efficient data preparation and seamless integration are fundamental to the success of AI-driven knowledge management systems. This process involves aggregating data from various sources, ensuring its quality and consistency, and establishing reliable data flow channels. Proper strategies enable organizations to leverage diverse data assets effectively, thereby enhancing the accuracy and relevance of AI insights within their knowledge ecosystems.Effective data preparation sets the foundation for reliable AI processing by transforming raw data into structured, clean, and accessible formats.
Integration strategies ensure that data from disparate sources—such as documents, emails, and databases—flows smoothly into the system, enabling comprehensive analysis and knowledge retrieval. Employing robust methods for data collection, cleaning, and integration significantly boosts the overall efficiency and scalability of knowledge management solutions powered by AI.
Gathering Diverse Data Sources
Organizations utilize multiple channels to collect a broad spectrum of data that enriches their knowledge repositories. These sources include structured and unstructured data repositories, requiring tailored approaches for each.
- Documents and Files: Collect enterprise documents, reports, manuals, and presentations stored in file systems, content management systems, or cloud storage platforms.
- Emails: Extract relevant information from email servers or platforms like Outlook and Gmail, focusing on metadata, attachments, and content relevant to organizational knowledge.
- Databases and Data Warehouses: Integrate structured data stored in relational databases (e.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL) and cloud-based data warehouses such as Amazon Redshift or Google BigQuery for analytical purposes.
- APIs and External Data Feeds: Connect with third-party APIs to access external data sources like social media feeds, news outlets, or industry-specific data providers.
| Data Source | Characteristics | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Documents & Files | Unstructured, diverse formats | Metadata extraction, format standardization |
| Emails | Semi-structured, rich in context | Filtering relevant content, attachment handling |
| Databases | Structured, relational data | Schema understanding, query optimization |
| APIs & External Feeds | Dynamic, real-time data | Authentication, rate limits, data consistency |
Data Cleaning, Normalization, and Formatting
Ensuring data quality is pivotal for AI systems to generate accurate insights. This involves systematic procedures to remove inconsistencies, standardize formats, and prepare data for processing.
Data cleaning encompasses identifying and rectifying errors, removing duplicates, and handling missing values. For instance, inconsistent date formats or misspelled s in text data can lead to inaccurate analysis if not addressed. Normalization involves transforming data into a standardized format, such as converting all text to lowercase, unifying date formats, or harmonizing categorical variables across datasets. Formatting ensures that data structures align with AI model requirements, facilitating efficient processing.
“High-quality, well-structured data reduces processing errors and enhances model accuracy, ultimately improving knowledge retrieval and decision-making outcomes.”
Automation tools play a significant role in these procedures, utilizing scripts and workflows to systematically clean and normalize data at scale. For example, natural language processing (NLP) techniques can be employed to correct spelling errors and standardize terminology within textual data. Similarly, data normalization scripts can convert date and currency formats across multiple datasets, ensuring consistency before integration.
Integrating External APIs and Cloud Services
Achieving seamless data flow often relies on integrating external APIs and cloud platforms, enabling real-time data access and scalable storage solutions.
APIs serve as bridges between internal systems and external data providers, allowing automated data extraction, updates, and synchronization. Proper API integration requires handling authentication protocols, managing rate limits, and designing robust error handling mechanisms to prevent data loss or inconsistency. For instance, integrating with social media APIs can supply real-time insights into trending topics relevant to the organization’s domain.
Cloud services facilitate centralized storage, processing power, and additional functionalities like machine learning model deployment. Leveraging cloud platform APIs—such as AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions, or Azure Data Factory—enables dynamic data pipelines that automatically ingest, process, and update knowledge bases. This approach ensures that the knowledge management system remains current, scalable, and resilient against data volume fluctuations.
| Integration Strategy | Advantages | Implementation Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| External API Integration | Real-time data access, expanded data sources | Authentication, API rate limits, data security |
| Cloud Service Integration | Scalability, reliable storage, processing capabilities | Cost management, data privacy, service compatibility |
Automating Knowledge Curation and Updating

Efficient management of organizational knowledge requires not only initial collection but ongoing curation and updates to ensure information remains accurate, relevant, and valuable. Leveraging AI techniques enables organizations to automate these processes, reducing manual effort and minimizing errors. This approach ensures that knowledge bases evolve dynamically, reflecting the latest insights, data, and business developments.
Automating knowledge curation involves employing AI to categorize, tag, and enrich assets systematically. Continuous updating and validation are achieved through feedback loops that incorporate new data and user interactions. Incorporating version control and audit trails further strengthens the integrity, transparency, and compliance of knowledge repositories, facilitating trust and accountability within the organization.
Techniques for Automatic Categorization, Tagging, and Enrichment of Knowledge Assets
Effective knowledge curation relies on AI-driven methods to organize and enhance knowledge assets. These techniques ensure that information is appropriately classified, easily retrievable, and enriched with relevant metadata, leading to better searchability and usability.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP algorithms analyze the textual content of documents to identify key themes, concepts, and entities. This enables automatic classification and tagging based on semantic understanding. For example, AI can distinguish between financial reports and HR policies in a document repository.
- Machine Learning Classification Models: Supervised learning models trained on labeled datasets can categorize new knowledge assets into predefined categories with high accuracy. For instance, classifying customer feedback into sentiment-based categories or product issues.
- Metadata Enrichment: AI algorithms automatically generate descriptive metadata, such as s, summaries, and tags, which improve searchability. This process often involves extracting entities like dates, locations, or product names from unstructured data.
- Semantic Tagging: Using semantic analysis, AI assigns contextually relevant tags that capture the nuanced meaning of content, facilitating more sophisticated search and retrieval operations.
Procedures for Continuous Updating and Validation of Knowledge Bases with AI Feedback Loops
Maintaining an accurate and current knowledge base necessitates ongoing validation and updates. Implementing AI feedback loops allows systems to learn from new data, user interactions, and validation results, fostering continuous improvement.
- Data Ingestion and Monitoring: Regularly feed new data sources and monitor existing content for relevance and accuracy. AI models evaluate incoming data to determine if updates are needed.
- Automated Validation: AI systems cross-reference new information against existing data, flagging discrepancies or outdated entries for review. For example, AI can detect when a policy has been superseded by newer regulations.
- User Feedback Integration: Collect feedback from users on the usefulness and accuracy of assets. AI models analyze this feedback to identify assets requiring updates or reclassification.
- Scheduled Retraining and Refinement: Periodically retrain classification algorithms and enrichment models with updated datasets and validation outcomes, ensuring continuous improvement in accuracy.
Version Control and Audit Trails within Knowledge Repositories
Implementing robust version control and audit trails is essential for tracking changes, ensuring transparency, and complying with regulatory requirements. AI-enhanced version management enables organizations to maintain integrity and facilitate rollback if necessary.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Version History Tracking | AI systems automatically record each modification, including details of the changes made, by whom, and when. This creates a comprehensive history that supports accountability and traceability. |
| Automated Change Detection | AI algorithms monitor content repositories for alterations, highlighting significant updates and generating reports for review. This process ensures that stakeholders are aware of modifications over time. |
| Audit Trail Generation | Every action performed on knowledge assets, such as edits, deletions, or reclassifications, is logged with contextual information. AI tools facilitate the aggregation and analysis of these logs for compliance audits and troubleshooting. |
| Rollback and Version Comparison | AI-enabled tools allow users to compare different versions of a document or asset visually and revert to previous versions if necessary, maintaining the integrity of the knowledge base. |
By integrating these techniques for curation, updating, and version control, organizations can create resilient, up-to-date knowledge management systems that adapt to changing information landscapes, support decision-making, and uphold compliance standards.
Enhancing Search and Retrieval with AI

Efficient search and retrieval mechanisms are vital components of any knowledge management system. Leveraging artificial intelligence transforms traditional search capabilities, enabling systems to deliver more accurate, relevant, and personalized results. This section explores the strategic design of AI-powered search algorithms, methods for implementing semantic search, autocomplete features, and personalized recommendations, as well as practical steps to develop intuitive search interfaces that harness AI’s full potential.Artificial intelligence enhances search functionalities by understanding the context and semantics behind user queries, thereby moving beyond simple matching.
This leads to improved relevance in search results, faster retrieval times, and a more engaging user experience. Organizations that implement advanced AI-driven search features can significantly increase productivity and knowledge sharing efficiency across teams and departments.
Design Strategies for AI-Powered Search Algorithms
Creating effective search algorithms involves integrating machine learning models that analyze user queries, document content, and user interaction patterns to deliver highly pertinent results. Key strategies include:
- Contextual Understanding: Use natural language processing (NLP) models to interpret the intent and context of user queries, reducing ambiguity and enhancing accuracy.
- Relevance Ranking: Implement learning-to-rank algorithms that adapt based on user feedback and interaction data, ensuring the most useful results appear first.
- Feature Integration: Incorporate metadata, tags, and user behavior data into search models to refine relevance scoring and improve search precision.
- Continuous Optimization: Regularly analyze search logs and user feedback to adjust algorithms, ensuring they evolve with changing information needs and language trends.
Implementing Semantic Search, Autocomplete, and Personalized Recommendations
Semantic technologies allow search systems to grasp the meaning behind queries and documents, significantly improving search quality. Autocomplete and personalized recommendations further enhance user engagement by making search more intuitive and tailored.
Semantic search techniques analyze the relationships between words and concepts, enabling the system to understand synonyms, related terms, and context, thus returning more relevant results even when exact s are absent.
Autocomplete features leverage predictive algorithms to suggest complete queries based on partial inputs, significantly reducing user effort and errors. These suggestions can be enhanced with AI to consider user history and common search patterns for more accurate predictions.
Personalized recommendations utilize user profiles, interaction histories, and content preferences to suggest relevant documents, articles, or knowledge assets. Machine learning models analyze aggregated user data to identify patterns and deliver tailored content, fostering a more engaging and efficient knowledge retrieval experience.
Steps to Develop Intuitive Search Interfaces Leveraging AI Capabilities
Designing user-friendly, AI-enhanced search interfaces involves several critical steps:
- Define User Needs and Contexts: Gather insights into typical search scenarios, user behaviors, and specific organizational knowledge requirements to tailor the interface accordingly.
- Integrate Advanced Search Technologies: Implement NLP-based semantic search, autocomplete, and filtering options directly into the interface, ensuring they work seamlessly with underlying algorithms.
- Design for Clarity and Simplicity: Use clean layouts, clear labels, and minimal input fields to reduce friction. Visual cues such as icons and highlighting improve discoverability of features.
- Incorporate Personalization Features: Enable user profiles and history tracking within the interface to facilitate personalized recommendations and search histories.
- Implement Feedback Mechanisms: Provide easy ways for users to give feedback on search results, which can be used to further train and refine AI models.
- Test and Iterate: Conduct usability testing with diverse user groups, analyze interaction patterns, and continuously refine the search interface based on real-world feedback and performance metrics.
Security, Privacy, and Ethical Considerations
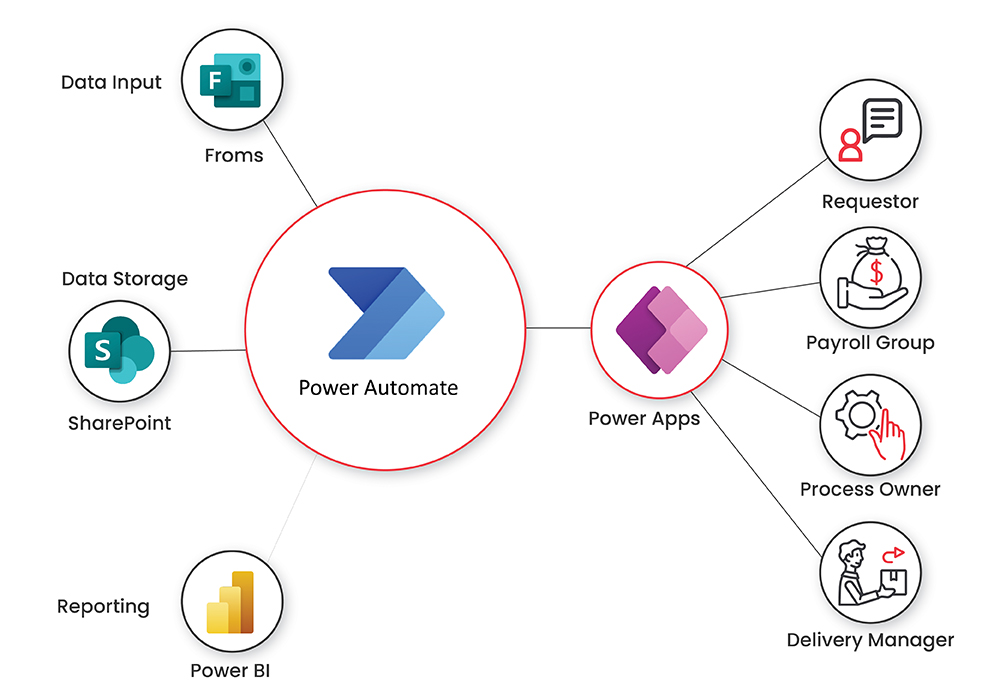
Implementing AI-driven automation in knowledge management necessitates a comprehensive approach to safeguarding sensitive information, ensuring compliance with data regulations, and upholding ethical standards. As organizations increasingly rely on AI systems to handle vast amounts of knowledge, it becomes imperative to address potential risks associated with data security, privacy breaches, and ethical misuse. This section explores best practices and strategies to navigate these critical aspects effectively, fostering trust and integrity in automated knowledge workflows.Ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive knowledge is fundamental to maintaining organizational trust and compliance.
AI systems, by their nature, often require access to large datasets, which may include proprietary information, personal data, or confidential client details. Without proper safeguards, these could be vulnerable to unauthorized access, breaches, or misuse. Moreover, the ethical implications of automating knowledge processes extend beyond mere data protection, encompassing issues such as bias, transparency, and accountability. Organizations must therefore implement robust frameworks that balance technological capabilities with responsibility and ethical standards.
Safeguarding Sensitive Knowledge During AI Automation
Effective protection of sensitive knowledge involves a combination of technical, procedural, and organizational measures. The following best practices help ensure data security throughout the AI automation lifecycle:
- Encryption: Employ strong encryption protocols for data at rest and in transit, preventing unauthorized interception or access.
- Data anonymization: Apply anonymization or pseudonymization techniques to eliminate personally identifiable information (PII) from datasets used in AI models, reducing privacy risks.
- Secure data storage: Use secure, access-controlled environments for storing sensitive knowledge, including cloud-based services with compliance certifications like ISO 27001 or SOC 2.
- Regular security audits: Conduct periodic audits and vulnerability assessments to identify and mitigate potential security gaps in knowledge management systems.
- Role-based access controls (RBAC): Limit data access based on user roles, ensuring only authorized personnel can view or modify sensitive information.
- Audit trails: Maintain comprehensive logs of data access and modifications, enabling traceability and accountability in case of security incidents.
Managing Access Controls and Ensuring Compliance
Proper management of access controls is critical in maintaining data privacy and ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements. Organizations should adopt structured procedures and policies to manage access effectively:
Access control strategies should be aligned with organizational roles, responsibilities, and data sensitivity levels. Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA), periodic review of user privileges, and automated alerts for suspicious activities are key components of a robust access management framework.
Compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, or HIPAA involves regular assessment of data handling practices, user consent management, and establishing data retention policies. Maintaining documentation of data processing activities and demonstrating compliance through audits help organizations avoid penalties and reputational damage.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) | Assigns permissions based on user roles, limiting access to necessary data |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Requires multiple verification factors for user authentication |
| Data Encryption | Secures data during storage and transmission |
| Audit and Monitoring | Tracks access and modifications to ensure transparency and detect anomalies |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adheres to regional and industry-specific data protection laws |
Ethical Implications and Risk Mitigation in AI-Driven Knowledge Management
Automation of knowledge processes with AI raises significant ethical considerations that organizations must proactively address. These include issues related to bias, transparency, accountability, and the potential for misuse of information. Failing to manage these concerns can undermine trust, lead to legal repercussions, and impair organizational reputation.To mitigate these risks, organizations should establish clear ethical guidelines for AI deployment, emphasizing fairness, transparency, and responsibility.
Techniques such as bias detection and correction, explainable AI (XAI), and regular ethical audits help ensure AI systems produce equitable and understandable outcomes. Transparency with stakeholders about how AI models operate and how decisions are made fosters trust and accountability.Furthermore, organizations must be vigilant about preventing unintended consequences, such as reinforcing existing prejudices or enabling malicious activities. Implementing human-in-the-loop processes allows for oversight and intervention, especially in critical decision-making scenarios.
Building a culture of ethical awareness and continuous education among staff is essential for aligning AI practices with organizational values and societal expectations.
Measuring Success and Continuous Improvement
Implementing AI-driven knowledge management systems marks a significant advancement in organizational efficiency and information accessibility. However, to ensure these systems deliver on their expected benefits, organizations must establish robust mechanisms for measuring success and fostering ongoing improvements. This process involves identifying relevant metrics, collecting insightful data, and creating a culture of iterative refinement to adapt to evolving needs and technologies.
Effective evaluation and continuous enhancement are vital for maximizing the return on investment in AI-powered knowledge management, ensuring the system remains aligned with organizational goals, and maintaining high user satisfaction. Regular assessment not only highlights areas for improvement but also enables organizations to scale their solutions effectively, fostering innovation and sustained operational excellence.
Developing Metrics to Assess System Effectiveness
Organizations need to define clear, measurable indicators that reflect the performance and impact of their AI-based knowledge management systems. These metrics should encompass quantitative data, qualitative insights, and strategic alignment to holistically evaluate success.
- User Engagement Metrics: Tracking login frequency, session duration, and content interaction rates helps gauge how actively users utilize the system. Increased engagement typically indicates relevance and ease of use.
- Search Accuracy and Relevance: Measuring the precision of search results, including click-through rates and user satisfaction ratings, ensures the AI effectively retrieves pertinent information.
- Knowledge Base Completeness: Monitoring the percentage of relevant topics covered, gaps identified, and the rate of content updates offers insights into the system’s comprehensiveness.
- Response Time and System Availability: Evaluating how quickly the system delivers answers and its uptime stability contributes to user experience assessment.
- Impact on Productivity and Decision-Making: Quantifying improvements in task efficiency or decision quality resulting from knowledge access provides strategic value metrics.
Collecting User Feedback and Performance Data
Gathering qualitative and quantitative data from system users and performance analytics is crucial for understanding system effectiveness and identifying improvement opportunities. Multiple channels and methods should be employed for comprehensive data collection.
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Regularly distributing structured feedback forms helps capture user satisfaction, challenges faced, and suggestions for enhancements.
- Usage Analytics: Leveraging system logs, clickstream analysis, and AI performance dashboards provides real-time insights into how the system is being used, common search queries, and content engagement patterns.
- User Interviews and Focus Groups: Conducting direct conversations allows deeper understanding of user experiences, frustrations, and aspirations.
- Automated Feedback Collection: Embedding feedback prompts within the system, such as rating search results or content relevance, facilitates continuous input without disrupting workflows.
Combining these approaches ensures a balanced view of system performance, blending quantitative metrics with qualitative insights for nuanced assessments.
Procedures for Iterative Refinement and Scaling
Establishing structured procedures for ongoing system enhancement is essential to maintain relevance and effectiveness as organizational needs evolve. These procedures should promote a culture of continuous improvement through regular review cycles and scalable practices.
- Regular Performance Reviews: Schedule periodic evaluations of metrics and feedback data to identify trends, successes, and areas needing attention. These reviews should involve cross-disciplinary teams to gain diverse perspectives.
- Agile Development and Deployment: Adopt agile methodologies allowing incremental updates, testing, and deployment of improvements based on real-world feedback.
- Knowledge Base Expansion and Updating: Prioritize content curation and automation to continuously enrich the knowledge repository, ensuring it adapts to changing organizational contexts and external environments.
- Scaling Strategies: As confidence in the system grows, expand its scope by incorporating additional data sources, integrating with other enterprise systems, and deploying AI models across new use cases.
- Training and Change Management: Facilitate user training sessions and communicate updates effectively to foster adoption and optimize the benefits of AI-driven knowledge management solutions.
Effective measurement and continuous improvement rely on a data-driven approach, where insights from performance metrics and user feedback inform strategic decisions and foster innovation.
Wrap-Up

In conclusion, automating knowledge management with AI offers substantial benefits in efficiency, accuracy, and scalability. By integrating cutting-edge technologies and following structured workflows, organizations can ensure their knowledge bases remain current and accessible. Embracing these innovations paves the way for smarter, more agile information management systems that support ongoing growth and success.