Discovering how to detect grammar errors in thesis with AI is essential for ensuring clarity and professionalism in academic writing. Leveraging advanced AI tools can significantly streamline the proofreading process, allowing students and researchers to identify and correct language issues efficiently. Understanding how to effectively integrate these technologies into your editing workflow can lead to more polished and credible theses.
This guide explores the capabilities of AI-based grammar detection, detailed techniques for seamless integration, and best practices for verifying and presenting errors. By combining intelligent tools with manual review, authors can enhance their thesis quality while maintaining an academic tone and consistency throughout their work.
Overview of AI Tools for Grammar Error Detection in Theses

Recent advancements in artificial intelligence have significantly transformed the landscape of academic proofreading, particularly in the realm of thesis writing. AI-based tools now offer sophisticated functionalities that assist students and researchers in identifying and correcting grammatical errors with enhanced efficiency and accuracy. These tools leverage natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning algorithms to analyze complex sentence structures, detect inconsistencies, and suggest appropriate corrections, making the proofreading process more streamlined and reliable.
Employing AI-driven grammar checkers in thesis preparation offers numerous benefits. They help reduce human error, ensure consistency in language usage, and save valuable time during the editing phase. Moreover, AI tools can operate continuously, providing instant feedback that enhances the overall quality of academic writing. However, despite their impressive capabilities, these systems are not infallible and come with certain limitations.
Recognizing these limitations is crucial for users to avoid over-reliance and to ensure that the final thesis maintains high standards of clarity, coherence, and academic integrity.
Capabilities of AI-Based Language Tools
AI tools for grammar error detection are designed to perform a comprehensive analysis of text, identifying a wide range of issues such as syntax errors, punctuation mistakes, verb tense inconsistencies, subject-verb agreement problems, and improper use of articles. Advanced tools can also detect stylistic issues, repetitive phrasing, and contextual misuses that traditional spell checkers often overlook. Many AI systems incorporate machine learning models trained on extensive datasets of correct language usage, enabling them to adapt and improve over time.
Some prominent AI tools include Grammarly, Hemingway Editor, and Microsoft Editor, each offering features tailored to academic writing. For instance, Grammarly’s AI engine not only highlights grammatical errors but also provides explanations and suggestions to enhance clarity and tone. These tools often integrate seamlessly with word processors and online platforms, facilitating real-time editing and collaborative work, which is vital in thesis development.
Advantages of Using AI for Proofreading Academic Documents
Integrating AI-based proofreading tools into the thesis writing process offers several compelling advantages. Firstly, they enable quick initial scans of large documents, significantly reducing the time spent on manual proofreading. This efficiency allows students and researchers to focus more on content development rather than language correction. Additionally, AI tools provide consistent feedback, which helps maintain uniformity in language style throughout the document.
Furthermore, these tools often include contextual suggestions that improve sentence structure and coherence, thereby enhancing overall readability. The accessibility of AI proofreading systems also democratizes high-quality editing, making it feasible for users with varying levels of language proficiency to produce polished academic work. Moreover, AI tools can serve as educational resources, helping users learn from their mistakes and improve their language skills over time.
Limitations and Potential Pitfalls of AI Grammar Correction Systems
Despite their numerous benefits, AI grammar correction systems have inherent limitations that users should be aware of. One primary challenge is that these tools may struggle with the nuanced and complex nature of academic language, potentially missing contextual errors or misinterpreting intended meanings. For instance, AI may incorrectly flag specialized terminology or complex sentence structures common in thesis writing, leading to false positives or overlooked mistakes.
Another concern involves over-reliance on automation, which can diminish the user’s critical proofreading skills. Automated tools sometimes suggest changes that compromise the author’s voice or intended tone, especially in highly creative or technical sections. Additionally, AI systems are susceptible to biases present in their training data, which can result in inappropriate suggestions or errors. Therefore, while AI tools are invaluable assistants, they should complement, not replace, manual review by knowledgeable authors or professional editors to ensure the accuracy and integrity of the thesis content.
Techniques for Integrating AI to Detect Grammar Errors
Effectively incorporating AI-powered grammar checking tools into the thesis review process enhances accuracy and efficiency. This involves systematic procedures for uploading documents, customizing settings for optimal results, and establishing a workflow that maximizes the capabilities of these advanced platforms. Understanding these techniques ensures that researchers and students can leverage AI tools seamlessly and produce polished, error-free academic work.
Implementing AI for grammar correction requires a structured approach that begins with preparing the document for upload, followed by configuring the AI platform’s settings to suit the specific linguistic nuances of academic writing. A strategic workflow from initial scan to final review helps ensure comprehensive error detection and correction, reducing manual effort and the potential for overlooked mistakes.
Step-by-step Procedures for Uploading a Thesis Document into AI Grammar Checking Platforms
Ensuring a smooth upload process is fundamental for effective AI-based grammar checking. The following steps Artikel a typical procedure across various platforms:
- Access the selected AI grammar checking platform, such as Grammarly, ProWritingAid, or Ginger, through their website or desktop application.
- Log into your account or create a new account if you are a first-time user.
- Navigate to the document upload section, often labeled as “New Document,” “Upload,” or “Import.”
- Click the upload button and select the thesis file from your local storage. Most platforms support common formats like DOCX, PDF, or TXT.
- Allow the platform to process the document, which may involve parsing the text and preparing it for analysis.
- Once uploaded, ensure the entire document is visible and correctly formatted within the platform’s interface to facilitate comprehensive checking.
Some platforms also offer drag-and-drop functionality, simplifying the upload process further. It is essential to verify that the uploaded document retains its formatting to prevent misinterpretation by the AI system.
Customizing AI Settings to Enhance Detection Accuracy
Tailoring AI settings according to the specific requirements of academic writing can significantly improve error detection accuracy. These customizations may include:
- Language and Style Preferences: Select academic or formal language settings to align with thesis writing standards.
- Grammar and Style Rules: Enable or disable specific rules, such as comma placement, subject-verb agreement, or passive voice detection, based on the focus areas of your review.
- Vocabulary and Clarity Checks: Activate suggestions for precise terminology and sentence clarity, crucial in academic contexts.
- Exclusion Zones: Define sections like references, bibliography, or footnotes that should be excluded from error checks to avoid false positives.
- Sensitivity Levels: Adjust the strictness of error detection, balancing between over-flagging and missing errors.
Customizing AI settings to match the specific context of thesis writing ensures that the tools provide relevant, high-precision feedback, streamlining the revision process.
Comparison Table of Popular AI Tools for Grammar Error Detection
This table provides an overview of notable AI grammar checking platforms, highlighting their key features, user-friendliness, and compatibility to aid in selecting the most suitable tool for thesis proofreading.
| Tool | Features | Ease of Use | Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grammarly | Real-time grammar, punctuation, style suggestions; plagiarism detection; tone adjustment | Highly intuitive interface; browser extensions; desktop app | Windows, macOS, Chrome, MS Word, Google Docs |
| ProWritingAid | In-depth style analysis; contextual thesaurus; detailed reports | Moderate; integrates with MS Word, Google Docs, Scrivener | Windows, macOS, Chrome, MS Word, Google Docs |
| Ginger | Grammar and sentence rephrasing; translation; personal trainer feature | User-friendly; browser extension; desktop app | Windows, macOS, Chrome, MS Word, Safari |
| WhiteSmoke | Grammar, style, and translation; template-based editing | Simple; suitable for beginners | Windows, macOS, web-based |
Choosing the right tool depends on the specific needs of the thesis writer, including the level of detail required, ease of integration with writing platforms, and budget considerations.
Organizing the Workflow of AI-based Proofreading from Initial Scan to Final Review
A systematic workflow ensures thorough proofreading and maximizes the benefits of AI tools:
- Preparation: Format the thesis document according to the platform’s supported formats and remove any non-essential content such as comments or annotations.
- Initial Upload and Basic Scan: Upload the document into the AI platform and run an initial scan to identify basic grammatical errors and style issues.
- Customization of Settings: Adjust the platform’s settings for language, style, and specificity to tailor the error detection process to academic standards.
- Detailed Review and Corrections: Review the AI suggestions carefully, accepting relevant corrections and dismissing false positives. Pay special attention to complex sentences and technical terminology.
- Re-Scanning and Refinement: Conduct subsequent scans after making corrections to catch any remaining issues and ensure consistency throughout the document.
- Final Manual Review: Complement AI checking with manual proofreading to catch nuanced errors or contextual issues that AI may overlook.
Adopting a structured workflow from initial upload to final review ensures a comprehensive proofreading process, balancing AI efficiency with human oversight for optimal thesis quality.
Methods for Analyzing AI-Detected Grammar Errors
Effective analysis of AI-detected grammar errors is crucial for ensuring the accuracy and quality of thesis editing. While AI tools provide valuable suggestions, human oversight remains essential to verify correctness and contextual appropriateness. This process involves systematically reviewing AI outputs, verifying flagged errors, and employing best practices to maintain high editing standards. By following structured procedures, researchers and editors can confidently refine their theses, minimizing overlooked mistakes and false positives.
Systematic review of AI suggestions enhances the reliability of grammar correction processes. It involves carefully examining each flagged error, understanding the AI’s reasoning, and determining whether the correction aligns with proper grammatical rules. This approach helps in identifying false positives—instances where AI incorrectly flags correct sentences—and prevents unnecessary edits that could compromise the thesis’s clarity. Establishing a consistent methodology for error validation ensures thoroughness and maintains the integrity of the writing process.
Review Procedures for AI Suggestions
Implementing a structured review process involves multiple steps to evaluate AI-flagged errors effectively:
- Begin by reading each sentence with flagged errors in context, considering the overall coherence and style of the paragraph.
- Compare AI suggestions with established grammatical rules, consulting trusted grammar references when necessary.
- Assess whether the suggested correction preserves the original meaning and maintains academic tone.
- Identify false positives by verifying if the AI’s flagging is contextually appropriate, especially in cases involving technical terminology or complex sentence structures.
- Keep a record of errors confirmed for correction and instances where AI suggestions are rejected, to refine future review processes.
Best Practices for Verifying AI-Flagged Errors
To avoid false positives and ensure only genuine errors are corrected, adherence to best practices is recommended:
- Cross-reference AI flagged errors with authoritative grammar and style guides, such as the Chicago Manual of Style or the APA Publication Manual.
- Consult domain-specific language standards, particularly when technical terms or jargon are involved, to prevent incorrect corrections.
- Engage in peer review or seek feedback from colleagues to validate ambiguous errors flagged by AI.
- Utilize contextual clues within the thesis to determine if the AI’s correction aligns with intended meaning, especially in complex or nuanced sentences.
- Maintain an error log to track common false positives and adjust review strategies accordingly.
Manual Review Checklist for Post-AI Error Analysis
Employing a comprehensive manual review checklist ensures a meticulous editing process after AI detection. The checklist serves as a practical guide to confirm that all errors are appropriately addressed and no important corrections are overlooked:
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Context Verification | Assess whether the flagged error is relevant within the sentence’s context and maintains the overall coherence. |
| Rule Confirmation | Verify that the suggested correction aligns with standard grammatical rules and style guidelines. |
| Meaning Preservation | Ensure that the correction does not alter the intended meaning of the sentence or paragraph. |
| Technical Accuracy | Check for technical correctness, especially with domain-specific terminology and complex sentence structures. |
| False Positive Identification | Mark errors as false positives if the AI suggestion is unnecessary or incorrect, to avoid unwarranted changes. |
| Final Read-through | Conduct a final comprehensive reading to confirm that all corrections enhance clarity and correctness. |
Common Grammar Errors Identified by AI and How to Address Them
AI tools frequently detect a variety of common grammar mistakes encountered in thesis writing. Recognizing these errors and understanding the appropriate corrections is vital for manual validation and editing.
- Subject-Verb Disagreement: AI may flag sentences where the subject and verb do not agree in number. For example, “The data shows” should be corrected to “The data show.” Address by confirming subject number and ensuring verb tense matches.
- Incorrect Use of Tenses: AI might highlight inconsistent tense usage. For instance, switching from past to present tense unnecessarily. Correct by maintaining a consistent tense throughout the section, aligned with academic conventions.
- Run-On Sentences: AI detects sentences that are too lengthy or improperly connected. Break the sentence into shorter, clearer statements or use appropriate conjunctions.
- Punctuation Errors: Misplaced commas or missing periods are common. Review punctuation to enhance readability and adhere to style guides.
- Misplaced Modifiers: AI may flag sentences where descriptive phrases are ambiguously placed, leading to confusion. Reposition modifiers for clarity.
Addressing these errors involves applying grammatical rules precisely, ensuring consistency, and maintaining the formal tone required in academic writing. For example, when correcting a subject-verb disagreement, identify the core subject and match the verb accordingly, e.g., “The results indicate” instead of “The results indicates.” Regularly reviewing AI suggestions with these principles ensures a high-quality, error-free thesis.
Best Practices for Using AI to Improve Thesis Language Quality

Integrating AI tools into the thesis editing process offers a valuable opportunity to enhance language quality, accuracy, and consistency. However, to maximize their benefits, it is essential to adopt strategic approaches that harmonize automated suggestions with manual editing efforts. Employing best practices ensures that AI complements the scholar’s expertise, maintains the integrity of academic tone, and results in a polished, coherent document ready for submission.Effective use of AI in thesis proofreading requires a structured workflow that balances technological assistance with human judgment.
This involves establishing clear editing stages, where AI-generated recommendations are first reviewed, validated, or revised by the researcher or editor. Combining automated suggestions with manual editing allows for nuanced decisions, especially in complex sentences, specialized terminology, or context-dependent language. Moreover, maintaining an academic tone while correcting errors necessitates careful consideration of word choice, formality, and stylistic consistency, avoiding overly casual or ambiguous language introduced by automated corrections.
Consistency in terminology and stylistic conventions throughout the thesis is fundamental to academic professionalism. AI tools can assist in identifying inconsistent usage of key terms, abbreviations, and stylistic preferences, but human oversight remains crucial to ensure that the overall voice and tone align with disciplinary standards and personal authorial intent. By implementing these best practices, writers can leverage AI as a powerful adjunct to traditional editing, culminating in a thesis that is both linguistically precise and academically compelling.
Strategies for Integrating AI Proofreading into the Editing Workflow
Integrating AI into the thesis editing process requires a systematic approach to ensure seamless collaboration between automated tools and manual review. Initially, it is advisable to run the entire document through AI proofreading software early in the revision process. This provides a broad overview of potential errors, including grammatical inconsistencies, punctuation issues, and stylistic deviations. Subsequently, the researcher should focus on reviewing AI suggestions critically, accepting those that align with the intended meaning and rejecting or modifying those that may introduce inaccuracies or unnatural phrasing.To optimize efficiency, create a structured workflow with designated stages: initial AI scan, manual review of AI suggestions, second-pass editing for contextual coherence, and final proofreading.
This approach ensures that AI serves as an aid rather than a primary editor, promoting accuracy without sacrificing scholarly voice. Establishing clear guidelines for AI use—such as prioritizing corrections for basic grammar and punctuation, while handling stylistic nuances manually—helps maintain control over the editing process.Documenting the AI-assisted editing process by keeping track of changes and decisions enhances transparency and provides a record for future reference.
This practice not only improves the quality of the current thesis but also informs the development of personal editing standards that effectively incorporate AI tools over time.
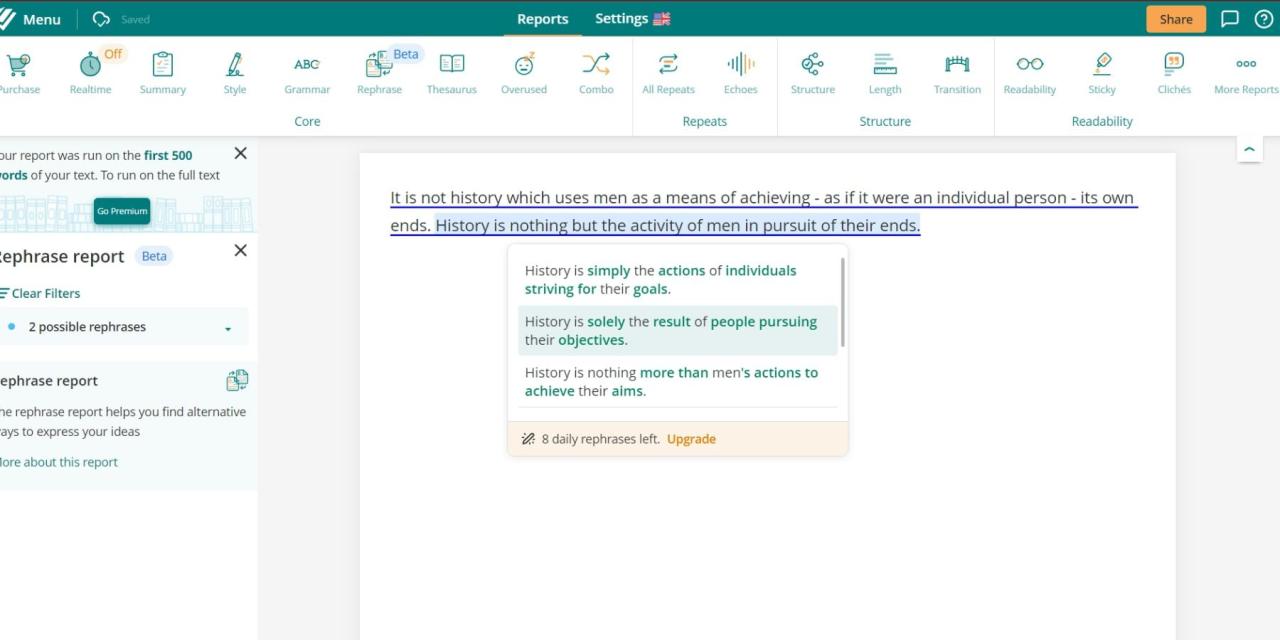
Methods for Combining AI Suggestions with Manual Editing for Optimal Results
Maximizing the benefits of AI-assisted proofreading involves carefully integrating machine suggestions with human judgment. A productive method is to first accept all AI recommendations related to straightforward grammatical errors and punctuation issues. These are typically clear-cut corrections that do not require deep contextual understanding. Following this, manually review sentences flagged by AI for more complex issues, such as ambiguous phrasing, inadequate transitions, or stylistic inconsistencies, paying close attention to the thesis’s academic tone.One effective approach is to use AI as a preliminary filter, then apply critical thinking to refine and adapt suggestions.
This can include paraphrasing AI-recommended changes to better suit the specific disciplinary context or adjusting terminology to match established conventions. In addition, it is beneficial to read sentences aloud or have a peer review the edits to ensure natural flow and clarity, especially in sections with dense technical content.Employing a side-by-side comparison of original and AI-edited versions helps identify areas where human judgment is necessary.
This dual review process ensures that corrections enhance clarity, precision, and formality, resulting in a polished document that accurately reflects the researcher’s voice and academic standards.
Approaches to Maintaining Academic Tone While Correcting Errors
Maintaining an appropriate academic tone during the correction process is vital for ensuring the thesis’s professionalism and credibility. When applying AI suggestions, it is important to evaluate each correction within the context of the discipline’s stylistic norms and the author’s intended voice. AI tools may sometimes recommend changes that, while grammatically correct, alter the formality or nuance of the original content.One effective approach is to establish clear stylistic guidelines prior to editing, such as preferred vocabulary, sentence complexity, and tone.
During correction, use these standards to assess whether AI suggestions align with academic conventions. For instance, replacing informal phrases with more formal equivalents or adjusting sentence structures to enhance clarity can help preserve a scholarly tone.Additionally, it is advisable to perform a final pass focused solely on tone and style after the initial grammatical corrections. This review should involve reading the thesis aloud or engaging a peer or supervisor to ensure that the language remains consistent, authoritative, and academically appropriate throughout.
Utilizing style guides pertinent to the discipline can also serve as valuable references for maintaining the desired tone.
Methods for Ensuring Consistency in Terminology and Style Throughout the Thesis
Consistency in terminology, abbreviations, and stylistic choices is essential for a coherent and professional thesis. AI tools can assist in identifying inconsistent usage of key terms or formatting styles, but human oversight remains indispensable for final validation. Implementing systematic methods enhances uniformity and reduces ambiguity.One effective method is to develop a style sheet or terminology database at the outset of the project, outlining preferred terminology, abbreviations, citation styles, and formatting rules.
This resource acts as a reference for both manual editing and AI tool customization, enabling more accurate identification and correction of inconsistencies.During editing, utilize AI features such as consistency checkers or custom dictionaries to flag deviations from the established style. Regularly review sections where terminology or style varies significantly, and standardize these terms according to the style guide. It is also beneficial to perform comprehensive cross-referencing of key terms across chapters or sections to ensure uniformity.Finally, maintain a detailed revision log that records major stylistic decisions and corrections.
This practice not only promotes consistency but also facilitates communication with advisors or peer reviewers, ensuring the thesis adheres to disciplinary norms and personal quality standards.
Enhancing AI Detection with Supplementary Editing Tools
Integrating AI-powered grammar checkers into the thesis review process significantly enhances the accuracy and quality of language correction. However, combining these tools with additional editing resources can further refine the drafting process, ensuring comprehensive language excellence. Supplementary editing tools such as plagiarism detectors and style analyzers serve to complement AI grammar checkers, creating a multi-layered approach to thesis editing that addresses not only grammatical issues but also originality and writing style consistency.
This integrated approach allows researchers and students to develop a more polished, credible, and well-structured thesis. By leveraging multiple tools within a cohesive workflow, users can identify nuanced language issues, enhance academic integrity, and adhere to disciplinary stylistic conventions more effectively. The following sections detail procedures for exporting AI-checked drafts, compare multi-functional AI tools, and Artikel methods for compiling comprehensive review reports.
Combining AI Grammar Checkers with Plagiarism Detectors and Style Analyzers
Effective thesis editing benefits from the synergy of AI grammar checkers with plagiarism detection and style analysis tools. These integrations enable a holistic review process that ensures linguistic precision, originality, and stylistic coherence. Combining these tools can be achieved through common workflows or integrated platforms that support multiple functionalities.
- Parallel Use: Run drafts through AI grammar checkers such as Grammarly or LanguageTool to correct grammatical errors, then analyze the same text with plagiarism detection tools like Turnitin or Urkund to verify originality. Subsequently, style analyzers such as Writefull or PerfectIt can assess consistency with disciplinary or journal standards.
- Integrated Platforms: Utilize proofreading platforms that support multiple functions within a single interface. For example, some advanced academic editing software integrates grammar checking, style analysis, and plagiarism detection, streamlining the review process.
- Workflow Automation: Automate the process by exporting the AI-checked draft into other tools via compatible file formats like Word (.docx) or PDF. This ensures seamless transitioning between different software, preserving formatting and annotations.
Procedures for Exporting AI-Checked Drafts into Other Editing Software
Efficiently transferring AI-reviewed documents into various editing platforms enables comprehensive revision and formatting. The process involves standardized exporting and importing methods that maintain the integrity of corrections and annotations.
- Finalize the AI-checked Draft: Review and accept all suggested corrections within the AI tool to ensure the draft is polished before export.
- Export to Compatible Formats: Save or export the document in formats such as .docx, .rtf, or .pdf, depending on the requirements of the target editing software. Microsoft Word remains the most versatile format for further editing.
- Import into Editing Software: Open the exported file in tools like MS Word, Google Docs, or Scrivener. Ensure that formatting, comments, and tracked changes are preserved during import.
- Utilize Additional Features: Apply style templates, citations, and referencing features available within the software to further enhance the thesis structure.
Comparative Overview of AI Tools Supporting Multiple Editing Functions
Several AI tools are designed to provide integrated editing functionalities, combining grammar checking, plagiarism detection, and style analysis. Evaluating these tools helps select the most suitable platform for thesis editing workflows.
| Tool Name | Supported Functions | User Interface | Key Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grammarly | Grammar, style, tone, plagiarism (premium) | Web, desktop app, browser extension | Comprehensive language feedback, real-time suggestions | Subscription-based for full features |
| ProWritingAid | Grammar, style, readability, plagiarism (via integrations) | Web, desktop, integrations with MS Word & Google Docs | In-depth reports, customizable style guides | Steeper learning curve |
| Turnitin | Primarily plagiarism detection; integrates with style checkers | Web-based platform | Robust originality verification, institutional integration | Limited grammar and style feedback |
| LanguageTool | Grammar, style, plagiarism (via extensions) | Web, browser extension, desktop | Open-source, multilingual support | Less comprehensive than premium tools |
Compiling a Comprehensive Review Report Using Multiple Tools
Creating a detailed review report involves synthesizing feedback from various editing platforms, providing a clear picture of the thesis’s language quality and integrity. An organized workflow ensures all issues are systematically identified and addressed.
- Aggregate Feedback: Collect comments, suggestions, and flagged issues from each tool. Use exported reports or integrated summaries where available.
- Categorize Errors and Recommendations: Group issues into categories such as grammatical errors, stylistic inconsistencies, originality concerns, and formatting issues. This facilitates targeted revisions.
- Prioritize Revisions: Address critical issues first, such as plagiarism or major grammatical errors, followed by stylistic and formatting improvements.
- Create a Summary Document: Compile an overview that details the identified issues, suggested corrections, and actions taken. Include references to specific tool feedback for transparency.
- Implement Revisions and Final Checks: Apply the necessary corrections within the draft, then rerun through selected tools to verify that all issues have been adequately addressed.
By integrating multiple AI-driven and supplementary editing tools into a cohesive workflow, thesis authors can significantly enhance the language quality, originality, and stylistic coherence of their work, resulting in a professional and academically rigorous document.
Epilogue
In conclusion, utilizing AI to detect grammar errors in thesis writing offers a powerful means to improve language accuracy and overall quality. When effectively combined with manual editing strategies and supplementary tools, AI can become an invaluable partner in the academic editing process. Embracing these technologies ensures your thesis stands out with precision, clarity, and professionalism.