Understanding how to analyze qualitative research with AI opens new horizons for researchers seeking more efficient and insightful data interpretation. Integrating artificial intelligence with traditional qualitative methods offers a powerful approach to uncovering patterns, themes, and deeper meanings within complex data sets. This fusion not only accelerates the analysis process but also enhances accuracy, enabling researchers to derive richer insights and make informed decisions with greater confidence.
This approach involves preparing diverse data formats, applying advanced AI algorithms for thematic detection, leveraging specialized tools and platforms, and interpreting AI-generated results through iterative human review. Addressing ethical considerations and biases remains crucial to maintaining research integrity. Real-world case studies further illuminate how AI can transform qualitative research, paving the way for future innovations that combine human expertise with machine learning capabilities.
Overview of Qualitative Research and AI Integration
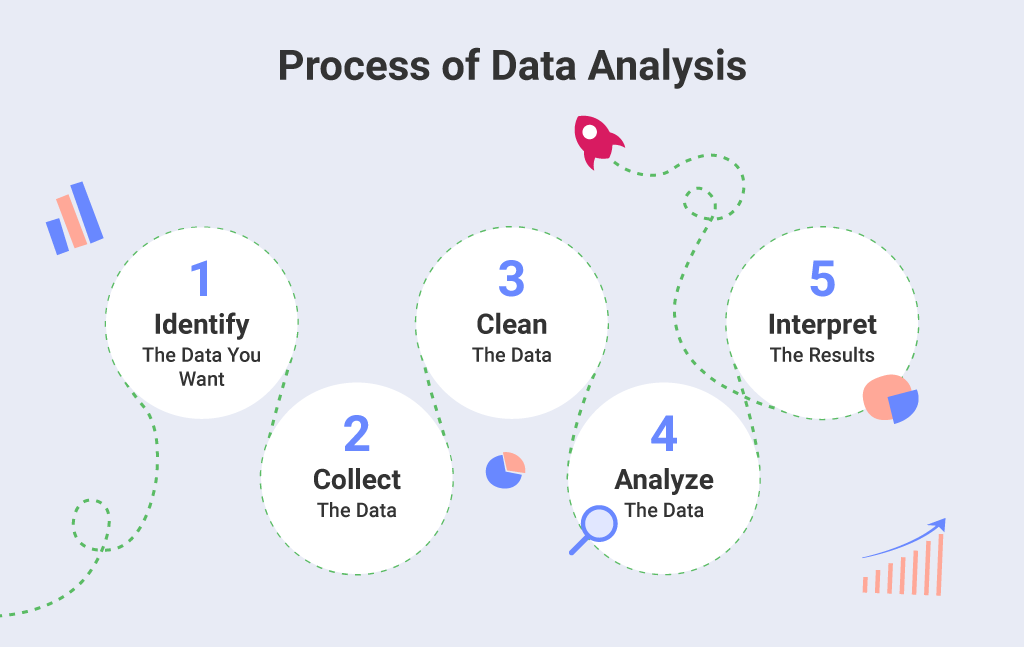
Qualitative research is a fundamental approach in social sciences, emphasizing an in-depth understanding of human behaviors, experiences, and social phenomena. Traditionally, this method involves collecting rich, descriptive data through interviews, focus groups, observations, and textual analysis. In recent years, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) has opened new avenues for enhancing qualitative research, allowing researchers to analyze large volumes of unstructured data more efficiently and accurately.
Combining AI tools with traditional methods can lead to more nuanced insights, improved consistency, and the capability to handle complex datasets that would otherwise be time-consuming or impractical to analyze manually.
By leveraging AI, researchers can automate aspects of data coding, identify patterns and themes with greater precision, and perform sentiment analysis or semantic interpretation at scale. This synergy between human interpretation and machine-driven analysis offers a powerful means to deepen understanding while maintaining the richness characteristic of qualitative inquiry. The integration of AI into qualitative research not only accelerates the analytical process but also enhances its depth, reliability, and scope, making it invaluable in fields such as healthcare, social policy, education, and market research.
Fundamental Principles of Qualitative Research Methods
Qualitative research is grounded in principles that prioritize context, depth, and subjective understanding over numerical measurement. It seeks to explore how individuals interpret their experiences and the meanings they assign to social phenomena. Central to this approach is the use of flexible, iterative data collection methods, such as interviews, ethnographies, and content analysis, which allow researchers to adapt their inquiries based on emerging insights.
Emphasizing a holistic perspective, qualitative research aims to uncover underlying motivations, social interactions, and cultural norms that shape human behavior.
Another core principle involves maintaining rigor through transparency, reflexivity, and systematic documentation. Researchers meticulously record their processes, ensuring reproducibility and credibility of findings. Qualitative studies often employ techniques like thematic analysis, narrative analysis, or discourse analysis, which require interpretative skills and a nuanced understanding of context. These methods prioritize depth over breadth, providing rich, detailed narratives that capture the complexity of social realities.
Enhancement of Qualitative Data Interpretation through AI
Artificial intelligence dramatically expands the capacity of qualitative researchers to interpret complex and voluminous datasets. Machine learning algorithms, natural language processing (NLP), and pattern recognition technologies can automate the coding of textual data, identify recurring themes, and extract meaningful insights that might be overlooked in manual analysis. For example, sentiment analysis can reveal emotional tones within interview transcripts, while topic modeling can uncover hidden themes across numerous documents.
These AI-driven techniques improve the consistency of coding, reduce human bias, and allow for the analysis of data at a scale that was previously unattainable.
AI tools also facilitate the identification of subtle patterns and relationships within data, such as social network interactions or evolving discourse over time. They enable researchers to perform cross-comparative analyses across large datasets, providing a broader contextual understanding. By integrating AI with qualitative approaches, researchers can generate hypotheses, streamline data processing, and focus more on interpretive synthesis, ultimately enriching the depth and breadth of qualitative insights.
Benefits of Combining AI Tools with Traditional Qualitative Analysis Techniques
The fusion of AI technology with traditional qualitative methods offers numerous advantages that enhance research outcomes. These benefits include increased efficiency, allowing researchers to process extensive datasets rapidly, thus saving time and resources. AI-driven analysis provides consistency in coding and theme identification, minimizing human bias and ensuring replicability of results. Additionally, the ability of AI to handle unstructured data—such as video transcripts, social media comments, and open-ended survey responses—broadens the scope of qualitative inquiry.
Furthermore, this integration supports more comprehensive analyses by enabling multi-layered insights. For instance, AI can perform initial thematic coding, which researchers can then interpret within contextual frameworks, ensuring depth while maintaining analytical rigor. The combination also fosters a more collaborative approach, where human expertise guides AI outputs, and AI amplifies human interpretative capabilities. As a result, qualitative research becomes more robust, scalable, and capable of addressing complex social questions with a richer and more nuanced understanding.
Preparing Data for AI-Driven Qualitative Analysis

Effective preparation of qualitative data is a crucial step in ensuring accurate and meaningful analysis using AI tools. This process involves organizing, cleaning, and anonymizing diverse data formats such as textual and multimedia content, to optimize AI model performance and uphold data privacy standards. Properly prepared data enhances the reliability of insights derived from AI-driven qualitative research, enabling researchers to uncover nuanced patterns and themes more efficiently.
Successfully preparing data entails a systematic approach that includes identifying suitable data formats, standardizing content, removing sensitive information, and ensuring data quality. These steps are essential not only for facilitating seamless AI processing but also for complying with ethical research practices. The following procedures Artikel how to organize and clean qualitative data effectively before deploying AI analysis tools.
Organizing and Processing Data for AI Analysis
To enable AI systems to interpret qualitative data accurately, researchers must follow a structured process to organize both textual and multimedia content. This involves categorizing data sources, converting multimedia files into analyzable formats, and establishing a consistent data structure. Implementing these steps ensures that AI algorithms can efficiently process and analyze large volumes of diverse data types, leading to comprehensive insights.
- Data Collection and Cataloging: Gather all relevant qualitative data, including interview transcripts, open-ended survey responses, audio recordings, videos, and images. Create an inventory that includes metadata such as source, date, participant identifiers, and content type to facilitate easy retrieval and categorization.
- Standardization of Data Formats: Convert all data into compatible formats suitable for AI tools. For example, textual data should be saved in UTF-8 encoded plain text or CSV files, while multimedia content may require transcription or extraction of key features. Maintaining uniform formats simplifies subsequent processing stages.
- Transcription of Multimedia Content: Audio and video recordings should be transcribed using reliable speech-to-text tools, ensuring accuracy and retaining contextual nuances. This step transforms multimedia files into textual data that AI algorithms can analyze effectively.
- Structuring Data: Organize data into coherent structures, such as databases or JSON files, that clearly label each data point, its source, and associated metadata. Consistency in structure enhances the efficiency of AI analysis workflows.
Data Format Compatibility for AI Analysis
Understanding which data formats are suitable for AI-driven qualitative analysis is vital. Different AI tools have specific requirements, and selecting appropriate formats ensures compatibility and optimal performance. The following table provides an overview of common data formats used in qualitative research processing for AI applications.
| Data Format | Description | Suitable AI Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Plain Text (.txt) | Simple ASCII or UTF-8 encoded text files containing transcribed interview data, open-ended survey responses, or notes. | Text mining, sentiment analysis, extraction, thematic modeling. |
| Comma-Separated Values (.csv) | Tabular data format ideal for organizing multiple data points, including metadata, codes, and annotations. | Quantitative coding, thematic clustering, data visualization. |
| JavaScript Object Notation (.json) | Hierarchical data structure that enables nested data storage, suitable for complex datasets with multiple attributes. | Integrating multimedia annotations, multi-dimensional analysis, machine learning models. |
| Audio Files (.wav, .mp3) | Raw speech recordings requiring transcription for text-based analysis or direct audio feature extraction. | Speech recognition, acoustic pattern analysis, speaker identification. |
| Video Files (.mp4, .avi) | Multimedia content that can be transcribed or analyzed for visual patterns, gestures, and contextual cues. | Visual content analysis, facial recognition, event detection. |
| Images (.jpg, .png) | Visual data suitable for image recognition, object detection, or visual content coding. | Visual qualitative analysis, thematic coding of imagery. |
Cleaning and Anonymizing Qualitative Data
Prior to AI analysis, qualitative data must be meticulously cleaned and anonymized to ensure data quality and protect participant privacy. This process involves multiple techniques aimed at removing errors, inconsistencies, and personally identifiable information. Effective cleaning enhances the accuracy of AI insights, while anonymization maintains ethical standards and complies with data protection regulations.
- Data Validation and Error Correction: Review textual transcripts and multimedia transcriptions for accuracy, correcting typos, misinterpretations, and formatting inconsistencies. Use spell-check and grammar tools to improve text clarity and coherence.
- Removing Irrelevant Content: Filter out extraneous data or noise, such as background conversations or unrelated annotations, which may skew analysis results.
- Identifying and Masking Sensitive Information: Detect personally identifiable information (PII) such as names, addresses, phone numbers, or sensitive demographic details. Use automated tools or manual review to replace these with generic placeholders or pseudonyms, ensuring data remains meaningful without compromising privacy.
- Standardizing Language and Coding: Normalize terminology, correct inconsistent spelling, and apply uniform coding schemes to facilitate comparative analysis. This step ensures that AI models interpret data consistently across different sources.
“Anonymization is a fundamental step to uphold ethical standards in qualitative research, especially when leveraging AI tools that require large datasets.”
Techniques for Applying AI in Qualitative Data Analysis
Integrating artificial intelligence into qualitative research offers powerful avenues for identifying themes, patterns, and insights within complex datasets. Employing appropriate AI techniques enhances the efficiency, consistency, and depth of qualitative analyses, enabling researchers to derive more nuanced understandings from textual and multimedia data sources. This section explores various AI algorithms suitable for thematic and pattern detection, illustrating how these tools can be systematically incorporated into qualitative workflows.
Effective application of AI in qualitative analysis involves selecting algorithms tailored to the specific nature of the data and research objectives. The following discussion highlights prominent AI models, visual workflow approaches, and validation strategies that ensure the reliability and validity of AI-derived insights.
AI Algorithms and Models for Thematic and Pattern Detection
Numerous AI algorithms are applicable to qualitative data analysis, each offering unique strengths in uncovering themes, sentiments, and underlying patterns. The choice of algorithm depends on the research questions, data formats, and desired outputs.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP models facilitate understanding and extracting meaningful information from textual data, such as interview transcripts or open-ended survey responses. Techniques like tokenization, part-of-speech tagging, and named entity recognition are foundational for subsequent analysis.
- Topic Modeling: Algorithms such as Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) help identify latent topics within large text corpora. These models can reveal prominent themes and how they interrelate across different data segments.
- Clustering Algorithms: Methods like K-means and hierarchical clustering categorize data points based on feature similarities, enabling the identification of natural groupings or patterns within qualitative datasets.
- Deep Learning Models: Neural networks, including transformers like BERT, excel at capturing contextual nuances and complex semantic relationships, greatly enhancing thematic detection in unstructured data.
Workflow Diagram for AI-Assisted Coding and Categorization
Designing an effective workflow diagram ensures clarity in how AI integrates into the qualitative analysis process. The workflow typically involves sequential stages where AI algorithms assist or automate specific tasks, from initial data processing to final categorization.
- Data Preparation: Raw textual or multimedia data undergo cleaning, normalization, and annotation to facilitate AI processing.
- Feature Extraction: Employ NLP techniques to convert unstructured data into numerical representations, such as embeddings or term frequency-inverse document frequency (TF-IDF) vectors.
- Pattern Detection and Topic Modeling: Apply algorithms like LDA or clustering methods to identify themes, concepts, or groupings within the data.
- Automated Coding and Categorization: Use classification models or rule-based systems to assign codes or categories based on detected patterns.
- Human Validation: Researchers review AI-generated codes to ensure accuracy and contextual relevance, making adjustments as necessary.
Envision the workflow as an iterative cycle where AI outputs inform manual review, and insights from human validation refine subsequent AI processing, fostering a dynamic and robust analysis process.
Procedures for Validating AI-Generated Insights
Ensuring the credibility of AI-driven analysis requires systematic validation procedures that compare automated outputs against manual coding and expert judgment. These procedures bolster confidence in the insights derived from AI models and prevent potential biases or inaccuracies from influencing research conclusions.
- Inter-Coder Reliability Comparison: Compare AI-generated codes with those assigned by human coders to assess consistency. High agreement indicates reliable AI performance.
- Manual Review and Adjustment: Researchers should review a sample of AI-coded data to verify thematic relevance and contextual accuracy, making adjustments when discrepancies occur.
- Cross-Validation Techniques: Divide data into training and testing subsets to evaluate the performance of AI models, especially in classification tasks, ensuring generalizability across different data segments.
- Use of Validation Metrics: Employ metrics such as precision, recall, F1-score, and Cohen’s kappa to quantify the accuracy and reliability of AI outputs relative to manual coding standards.
- Iterative Refinement: Continuously improve AI models by incorporating feedback from manual reviews, updating algorithms, and retraining models on revised datasets.
Through these validation procedures, researchers can confidently integrate AI insights into qualitative research, ensuring that technological efficiencies do not compromise analytical rigor and interpretive depth.
Tools and Platforms for AI-Assisted Qualitative Research
Integrating AI into qualitative research requires selecting the right tools and platforms that facilitate efficient data analysis, coding, and interpretation. The landscape of AI-assisted qualitative research tools has expanded significantly, offering researchers a diverse array of options tailored to various analytical needs. Understanding the features, usability, and integration capabilities of these tools is essential for optimizing research workflows and deriving meaningful insights from complex datasets.
Choosing appropriate AI platforms involves evaluating factors such as ease of use, compatibility with existing software, customization options, and support for collaborative research. Many tools also offer automation of tasks like text coding, theme detection, sentiment analysis, and visualization, which help streamline qualitative analysis and enhance accuracy. Setting up these tools within research environments requires consideration of technical infrastructure, data security, and user training to ensure seamless adoption and effective utilization.
Comparison of Popular AI Software Tools and Platforms for Qualitative Data
Below is a comparative overview of some widely used AI platforms tailored for qualitative research. The table highlights key features, user-friendliness, and integration options to assist researchers in making informed decisions based on their specific project requirements.
| Tool/Platform | Key Features | Usability | Integration Options |
|---|---|---|---|
| NVivo with AI Extensions | Text coding automation, sentiment analysis, visualization, integration with cloud services | User-friendly interface suitable for beginners and advanced users | Supports integration with R, Python, and cloud platforms like Azure and AWS |
| ATLAS.ti with AI Capabilities | Machine learning-assisted coding, semantic analysis, collaborative features | Intuitive for qualitative researchers with moderate technical background | API access for integrating with external tools and data sources |
| QDA Miner with Text Analytics | Automated coding, content analysis, sentiment scoring, thematic mapping | Accessible interface designed for social scientists | Supports import/export with MAXQDA, R, and Python |
| Leximancer | Automated concept mapping, theme detection, relationship analysis | DRiven by visual outputs; minimal technical setup required | Provides API integrations and export options for reports |
| MonkeyLearn | Customizable text classifiers, sentiment analysis, extraction | Web-based platform with straightforward setup and use | Integrates easily with data pipelines via API; compatible with Excel, Zapier, and more |
Guidelines for Setting Up AI Tools in Research Environments
Implementing AI tools in qualitative research environments necessitates a structured approach to ensure operational efficiency and data security. Initial steps include assessing technical infrastructure, such as computing resources and network capabilities, to support the chosen platform. Data management protocols should be established to maintain confidentiality and compliance with ethical standards.
Installation and configuration involve selecting appropriate software versions, setting up user accounts, and integrating with existing data repositories or analysis workflows. Training researchers and supporting staff on tool functionalities and best practices enhances adoption and maximizes analytical capabilities. Regular updates, backups, and performance monitoring are vital to sustain long-term usability and to adapt to evolving research needs.
Interpreting AI-Generated Results
Understanding and analyzing the outputs produced by AI in qualitative research is a pivotal step toward deriving meaningful insights. While AI can identify patterns, themes, and relationships within large datasets efficiently, it is essential for researchers to interpret these results within the broader contextual framework of their study. This process involves a careful examination of AI outputs to ensure accuracy, relevance, and depth in understanding human experiences and perspectives.
Effective interpretation of AI-suggested themes requires a systematic approach to contextualize patterns, validate findings, and refine insights through human judgment. Combining AI’s computational power with the researcher’s contextual knowledge enhances the overall robustness and credibility of qualitative analysis, making it possible to uncover nuanced understandings that might be overlooked by automated methods alone.
Steps to Analyze and Contextualize AI-Suggested Themes or Patterns
To thoroughly analyze AI-generated results, researchers should follow a structured process that involves validation, exploration, and integration of insights. These steps help ensure that AI findings are meaningful, accurate, and aligned with the research objectives.
- Review AI Outputs with a Critical Lens: Begin by examining the patterns or themes identified by AI. Assess whether these are consistent with known literature, theoretical frameworks, or preliminary insights. Look out for any anomalies or unexpected results that warrant further investigation.
- Validate Themes Through Human Judgment: Engage in a detailed review of sample data segments that the AI has grouped under specific themes. Cross-reference these with original qualitative data such as interview transcripts or open-ended survey responses to determine if the AI’s categorization accurately reflects the underlying narratives.
- Refine and Contextualize Findings: Incorporate contextual knowledge and domain expertise to interpret patterns. Consider cultural, social, or situational factors that AI may not fully capture. Adjust or re-label themes as necessary to better reflect the nuances of the data.
- Assess Relevance and Significance: Determine the importance of each pattern or theme in relation to the research questions. Prioritize insights that offer substantial contributions to understanding the studied phenomenon.
- Iterative Review and Feedback Loop: Repeat the review process, incorporating feedback from multiple researchers or stakeholders. Use this iterative approach to enhance the validity of interpretations and achieve consensus on the meaning of AI patterns.
- Document Interpretations and Rationale: Record the reasoning behind accepting or modifying AI-suggested themes. This documentation supports transparency and reproducibility in qualitative research.
Sample AI Outputs and Interpretative Notes
| AI Output | Interpretative Notes |
|---|---|
| Theme: “Lack of Trust in Technology” | Indicates a prevalent concern among participants regarding privacy and security. Needs to be contextualized within recent data breaches or societal debates on digital privacy. Validate by reviewing specific responses that mention mistrust and relate them to demographic or experiential factors. |
| Pattern: “Positive Sentiment in Customer Feedback” | Suggests overall satisfaction but may mask underlying issues. Cross-check with the original feedback for specific complaints or suggestions that the AI might have overlooked. Consider if sentiment analysis aligns with thematic coding for more detailed insights. |
| Emerging Topic: “Desire for Personalization” | Reflects an expressed need for tailored experiences. Contextualize within current market trends and technological capabilities. Review sample data to ensure the AI’s identification captures diverse perspectives across different user groups. |
Refining AI insights through iterative human review involves repeatedly analyzing the outputs, comparing them with raw data, and adjusting themes or patterns based on contextual understanding. This process enhances the accuracy and depth of qualitative interpretation, ensuring that AI-assisted analysis remains grounded in the real-world meanings within the dataset. Incorporating human judgment at each step enables researchers to balance computational efficiency with nuanced understanding, leading to more comprehensive and credible findings in qualitative research.
Ethical Considerations and Bias in AI-Enhanced Qualitative Research
Integrating artificial intelligence into qualitative research introduces significant ethical considerations that researchers must address diligently. While AI offers powerful tools for analyzing complex data, it also raises concerns about potential biases, transparency, and accountability. Ensuring ethical integrity in AI-assisted qualitative studies is essential to maintain trustworthiness, respect participant rights, and uphold the standards of rigorous research practices.
This section explores the ethical issues that can arise from the use of AI in qualitative analysis, examines sources of bias, and offers practical guidelines and best practices to mitigate these challenges and promote transparent, responsible research.
Potential Ethical Issues and Biases Introduced by AI Analysis
AI systems, although designed to be objective, are inherently susceptible to biases originating from their development and deployment processes. These biases can inadvertently influence the interpretation of qualitative data, leading to skewed results and potentially unethical outcomes. Common ethical issues include:
- Data Privacy and Confidentiality: Ensuring participant data remains secure and anonymized when processed by AI tools is paramount. Unauthorized access or improper data handling can breach privacy rights.
- Algorithmic Bias: AI models trained on unrepresentative or biased datasets may reinforce stereotypes or marginalize certain groups, compromising fairness and equity in research findings.
- Transparency and Explainability: The complexity of AI algorithms can obscure how conclusions are derived, challenging researchers’ ability to explain findings comprehensively and ethically.
- Misinterpretation and Overreliance: Relying solely on AI outputs without human oversight may lead to misinterpretation of nuanced qualitative insights, risking misrepresentation of participants’ perspectives.
Guidelines to Mitigate Bias and Ensure Ethical Integrity
Implementing robust guidelines is essential to address the ethical challenges associated with AI in qualitative research. These guidelines help promote fairness, transparency, and accountability throughout the research process:
- Data Diversity and Representativeness: Ensure datasets used for training and analysis encompass diverse perspectives and are free from systemic biases. Regularly audit datasets for imbalance.
- Bias Detection and Correction: Utilize tools and techniques to identify biases in AI models. Implement adjustments or re-training with balanced data to mitigate unfair influences.
- Transparency and Documentation: Maintain detailed records of data sources, preprocessing steps, model configurations, and decision-making processes. Clearly document limitations and potential biases.
- Human Oversight and Critical Evaluation: Combine AI outputs with expert interpretation. Human researchers should validate findings, especially when dealing with sensitive or complex qualitative data.
- Participant Confidentiality: Apply strict data anonymization protocols and adhere to ethical standards for participant privacy, complying with relevant regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA.
Best Practices for Transparent Reporting of AI-Assisted Findings
Transparent reporting enhances credibility and allows for critical appraisal of AI-enhanced qualitative research. Adopting established best practices ensures that audiences understand the role and limitations of AI tools in the analysis:
- Explicitly Describe AI Methods: Clearly specify the AI techniques, algorithms, and parameters employed in the analysis. Include information about training data, model validation, and performance metrics.
- Disclose Bias Mitigation Measures: Report steps taken to detect, address, and minimize biases within AI models, including dataset adjustments or model refinements.
- Highlight Human Involvement: Emphasize the role of human judgment in interpreting AI outputs, ensuring transparency about the collaborative nature of analysis.
- Address Limitations and Uncertainties: Acknowledge potential biases, data limitations, and areas where AI results may be less reliable, fostering an honest representation of findings.
- Provide Access to Data and Code: When appropriate, share anonymized datasets, analysis code, and models to facilitate reproducibility and peer review.
Maintaining ethical standards in AI-enhanced qualitative research is essential for fostering trust, ensuring fairness, and advancing responsible scientific inquiry.
Case Studies and Practical Applications of AI in Qualitative Research

Integrating AI into qualitative research has demonstrated significant potential to enhance data analysis, uncover nuanced insights, and streamline workflows. Real-world case studies serve as valuable examples of how AI tools are effectively employed across various research contexts, illustrating the practical benefits and challenges encountered during implementation.
This section highlights diverse applications of AI in qualitative research by detailing specific case studies. These examples showcase the procedures followed, the innovative techniques applied, and the outcomes achieved, providing a comprehensive understanding of AI’s role in advancing qualitative methodologies.
Market Research in Consumer Behavior Analysis
This case study explores how AI-powered natural language processing (NLP) was employed to analyze open-ended survey responses from thousands of consumers. The goal was to identify overarching themes, sentiment trends, and emerging preferences related to a new product line.
- Procedure: Data collection involved aggregating thousands of textual responses from online surveys and social media comments.
- Preprocessing: Text data was cleaned and tokenized using AI-driven algorithms to ensure high-quality input for analysis.
- Analysis: Advanced sentiment analysis and topic modeling tools identified prevalent themes and emotional valence associated with product features.
- Outcomes: The insights informed targeted marketing strategies, with AI revealing subtle sentiment shifts and hidden customer preferences that manual coding might overlook.
Healthcare Qualitative Research on Patient Experiences
In healthcare settings, AI was utilized to analyze interview transcripts and patient feedback to improve service delivery and patient satisfaction. The case study underscores the importance of AI in processing large volumes of narrative data efficiently.
- Procedure: Transcripts of patient interviews and feedback forms were collected and digitized for analysis.
- Preprocessing: Natural language processing techniques filtered out irrelevant data and standardized terminologies across different sources.
- Analysis: Machine learning algorithms clustered similar patient experiences and highlighted common themes related to care delivery, communication, and emotional well-being.
- Outcomes: The healthcare providers gained granular insights into patient needs, leading to targeted improvements in communication protocols and patient-centered care models.
Academic Research in Social Sciences
Academic researchers employed AI to analyze extensive ethnographic and interview data in social science studies. AI facilitated the discovery of complex social patterns and cultural narratives that would be challenging to discern manually due to data volume and complexity.
- Procedure: Researchers digitized and compiled diverse qualitative data sources, including field notes, interview transcripts, and visual materials.
- Preprocessing: Text normalization and coding algorithms structured the data for computational analysis.
- Analysis: AI-driven thematic analysis and network analysis identified key social themes, power dynamics, and cultural symbols within the data.
- Outcomes: The findings provided nuanced insights into social interactions and cultural identities, demonstrating AI’s capacity to handle complex, multi-layered qualitative data.
Policy Research and Public Opinion Monitoring
This case study describes the application of AI to analyze vast datasets of public comments and policy documents to inform government decision-making. The approach enabled rapid synthesis of public opinions and policy impacts.
- Procedure: Large-scale data collection from online comment sections, forums, and official documents was undertaken.
- Preprocessing: Text data underwent cleaning, language detection, and segmentation for effective analysis.
- Analysis: Topic modeling and sentiment analysis algorithms mapped public concerns and policy support levels over time.
- Outcomes: Policymakers gained real-time insights into public sentiment shifts, allowing for more responsive and evidence-based policy development.
Key Takeaway: Successful AI integration in qualitative research relies on meticulous data preparation, appropriate algorithm selection, and contextual interpretation of results, ensuring the insights are both valid and applicable in real-world scenarios.
Future Trends in AI and Qualitative Methodologies
The integration of artificial intelligence into qualitative research is poised for significant evolution as emerging technologies continue to reshape analytical capabilities. These developments promise to enhance depth, efficiency, and accuracy in understanding complex social phenomena. As AI continues to advance, researchers will have access to increasingly sophisticated tools that foster deeper insights while also posing new challenges to traditional methodologies.
Future trends highlight a convergence of innovative AI technologies with human interpretative skills, fostering hybrid approaches that leverage machine learning’s computational strengths and human judgment’s contextual understanding. This synergy is expected to unlock new dimensions in qualitative analysis, transforming research paradigms and expanding the scope of inquiry. Nonetheless, these advancements require careful navigation of ethical considerations and potential biases, ensuring responsible and equitable implementation of AI-driven methods.
Emerging AI Technologies Influencing Qualitative Research
Several cutting-edge AI technologies are emerging as influential forces in qualitative research. Natural language processing (NLP) continues to evolve, enabling more nuanced sentiment analysis, thematic extraction, and narrative understanding from vast unstructured data sources such as interview transcripts, social media posts, and open-ended survey responses. Deep learning models, including transformers like GPT and BERT, facilitate context-aware language understanding, allowing researchers to identify subtle nuances and complex patterns within qualitative data.
Additionally, advancements in computer vision and multimodal AI open new avenues for analyzing visual and audio data, broadening the scope beyond text. For example, facial expression analysis and gesture recognition can enrich insights from video recordings of focus groups or interviews. Such technologies bolster the ability to capture non-verbal cues and emotional responses, offering a more comprehensive understanding of participant experiences.
Evolving Analytical Techniques Combining Human Insight with Machine Learning
The future of qualitative analysis lies in hybrid models that seamlessly integrate machine learning algorithms with human expertise. These techniques aim to automate routine coding and categorization tasks, freeing researchers to focus on interpretation and theory development. Machine learning can identify patterns and relationships in large datasets that would be impractical to detect manually, providing a preliminary analytical framework.
At the same time, human oversight remains crucial for contextual validation, ethical judgment, and interpretive depth. This collaboration enhances reliability and validity, ensuring AI tools augment rather than replace expert insight. Techniques such as active learning, where human feedback iteratively refines AI models, exemplify this symbiosis, leading to more accurate and meaningful analyses over time.
Opportunities and Challenges for Future Research Developments
Emerging AI technologies offer unparalleled opportunities to expand qualitative research’s reach and depth. They facilitate handling larger and more diverse datasets, enabling cross-cultural and longitudinal studies that provide richer insights into social phenomena. Enhanced automation reduces time and resource constraints, accelerating the research cycle and enabling real-time analysis, which is valuable in dynamic contexts like crisis response or public health surveillance.
However, these opportunities are accompanied by notable challenges. The complexity of AI models demands ongoing technical expertise and transparency to ensure interpretability. Ethical concerns regarding privacy, consent, and data security must be rigorously addressed, particularly as AI analysis often involves sensitive personal information. Additionally, biases embedded within training data can perpetuate stereotypes and distort findings, emphasizing the need for diligent bias mitigation strategies.
The future of AI and qualitative methodologies will likely be characterized by adaptive, transparent, and ethically grounded approaches that maximize benefits while minimizing risks. Collaborative efforts among technologists, social scientists, and ethicists will be essential to realize the full potential of these innovations in advancing understanding of human experiences.
Wrap-Up
In summary, mastering how to analyze qualitative research with AI empowers researchers to streamline their workflows, enhance accuracy, and uncover deeper insights. As technology continues to evolve, embracing these innovative methods promises to shape the future of qualitative research, opening new avenues for discovery and understanding. Staying informed about emerging AI tools and ethical practices will be essential to maximizing their potential while maintaining integrity in research endeavors.