Understanding how to detect citation mistakes with AI is essential for maintaining the accuracy and credibility of scholarly and professional writing. As research and documentation become increasingly complex, leveraging artificial intelligence tools offers a powerful solution to identify and correct citation errors efficiently. This overview explores the significance of precise citations, the role of AI in enhancing review processes, and practical methods for implementing these technologies effectively.
By utilizing AI-driven detection methods, writers and researchers can automate the identification of common citation mistakes such as incorrect author names, missing details, or formatting inconsistencies. These tools not only save time but also improve the overall quality of references, ensuring that documents adhere to established academic standards. The discussion covers techniques for preparing documents, selecting appropriate AI tools, and addressing errors systematically to uphold the integrity of citations.
Understanding Citation Errors in Academic and Professional Writing

Accurate citations are fundamental to maintaining the credibility and integrity of scholarly work. They serve as the backbone for supporting claims, acknowledging sources, and enabling readers to verify information. However, despite their importance, citation errors are common pitfalls that can undermine the quality of academic and professional writing. Recognizing and understanding these mistakes is essential not only for authors aiming for excellence but also for readers and reviewers who evaluate the reliability of a work.
In the realm of research and professional documentation, citation errors vary in type and severity. Some mistakes are simple oversights, while others reflect deeper misunderstandings of citation standards or ethical considerations. Addressing these errors proactively enhances the transparency of research and upholds the standards expected in scholarly communication.
Common Types of Citation Mistakes
To systematically identify and correct citation mistakes, it is helpful to categorize them into common types. This organization clarifies the nature of each error, its potential impact, and strategies for prevention. The table below Artikels typical citation errors encountered in academic and professional contexts:
| Error Type | Example | Consequences | Prevention Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| Incorrect Author Attribution | Using the wrong author’s name or order, such as listing “Smith et al.” instead of the correct “Johnson et al.” for a cited source. | Misattribution can lead to accusations of plagiarism, diminish credibility, and mislead readers about source contributions. | Carefully verify author names and order from original publications; utilize reference management tools to automate correct attribution. |
| Wrong Publication Details | Providing an incorrect publication year, journal volume, or page number, e.g., citing “2020” when the actual publication year is 2019. | Hinders readers’ ability to locate sources, questions the accuracy of the work, and diminishes scholarly reliability. | Consult original sources directly; cross-check citation details before submission; use authoritative citation guides. |
| Inconsistent Citation Styles | Mixing APA format in one section and MLA in another without clear reason, leading to inconsistency. | Reduces professionalism, confuses readers, and may violate publication guidelines or academic standards. | Adopt and adhere to a single, style-specific citation guide appropriate for the discipline; use style-checking tools. |
| Omission of Essential Details | Leaving out page numbers for direct quotes or paraphrased material, e.g., citing a book without page numbers. | Undermines traceability of sources, questions the credibility of quotes, and violates citation norms. | Include all necessary details as per style guide; double-check references during editing process. |
| Misuse of Quotation Marks and Paraphrasing | Using quotation marks for paraphrased content or failing to enclose direct quotes properly. | Creates ambiguity about originality, risks accusations of plagiarism, and affects academic integrity. | Distinguish clearly between paraphrasing and direct quotes; properly format quotes and citations. |
| Self-Citation Errors | Citing one’s own work without proper acknowledgment or self-plagiarism. | Raises ethical concerns, can distort the scholarly record, and may violate publication policies. | Follow ethical guidelines for self-citation; disclose self-citations transparently. |
Understanding these common errors highlights the importance of meticulous attention to detail when citing sources. Accurate citations foster trust, facilitate scholarly discourse, and uphold the ethical standards vital to academic and professional work. Employing diligent verification, adhering to style guides, and utilizing technological tools are effective strategies to minimize citation mistakes and enhance the overall quality of scholarly writing.
Role of AI in Detecting Citation Mistakes

Artificial Intelligence has revolutionized the process of identifying citation errors in academic and professional writing. By leveraging advanced algorithms and machine learning models, AI tools can systematically analyze documents to detect inconsistencies, inaccuracies, and potential misrepresentations in citations. This technological advancement not only enhances the accuracy of scholarly work but also significantly reduces the manual effort involved in review processes.
AI-driven citation detection offers a level of precision and efficiency that outperforms traditional manual review methods. Automated systems can process large volumes of text quickly, flagging issues such as incorrect author names, mismatched publication years, missing references, or incomplete citation details. This proactive approach helps authors and reviewers address citation errors early, safeguarding the integrity of the work and ensuring adherence to academic standards.
Steps for Deploying AI to Scan Documents for Citation Issues
Implementing AI tools for citation error detection involves a structured approach to maximize effectiveness and reliability. The following procedural list Artikels the key steps:
- Document Preparation: Ensure the manuscript is in a compatible digital format such as DOCX or PDF, with clear and legible text and citations.
- Selection of AI Tool: Choose an AI-powered citation analysis tool that integrates with your editing environment or operates as a standalone platform, ensuring it has capabilities for citation verification.
- Initial Scanning: Upload or input the document into the AI system to initiate an automated scan for citation consistency and accuracy.
- Error Identification: Review the AI-generated report highlighting potential issues such as incorrect author names, missing references, or mismatched publication details.
- Manual Verification: Cross-check flagged citations against original sources or authoritative databases to confirm accuracy.
- Corrections and Refinements: Amend the citations as recommended by the AI analysis, ensuring full compliance with citation standards.
- Final Review: Run a subsequent scan to verify that all citation issues have been addressed and that no new errors have emerged.
AI Detection Features for Citation Error Identification
| Feature | Function | Typical Output | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reference Consistency Check | Compares in-text citations with reference list entries to ensure they match in author names, publication years, and titles. | List of discrepancies such as missing references or mismatched details. | May struggle with non-standard citation formats or incomplete reference data. |
| Author Name Verification | Identifies misspelled or inconsistent author names across citations and references. | Highlighted citations with potential author name errors. | Accuracy depends on the database or source used for verification. |
| Publication Year Matching | Checks if the year of publication in the in-text citation aligns with the reference entry. | Flagged mismatched years and potential outdated or incorrect references. | May not detect errors if publication years are missing or improperly formatted. |
| Incomplete Citation Detection | Detects missing essential elements such as page numbers, volume, or issue numbers. | Alerts for incomplete or improperly formatted citations. | Relies on standard citation formats; may not recognize non-standard styles. |
| Duplicate Citation Identification | Finds repeated citations that could indicate redundancy or inconsistent referencing. | List of duplicated references with suggestions for consolidation. | Potential false positives in cases of repeated authors with multiple works. |
Techniques and Procedures for Using AI to Detect Citation Mistakes

Effectively leveraging AI for citation verification requires a systematic approach that optimizes the quality of input data and ensures accurate output. Proper preparation of documents, along with precise configuration of AI models, is essential to maximize detection accuracy and minimize false positives or negatives. By understanding and implementing structured procedures, researchers and publishers can significantly enhance the reliability of citation checks, ultimately strengthening the integrity of scholarly communication.
Adopting robust techniques for AI-assisted citation validation involves a combination of meticulous document preprocessing, tailored AI model training, and designing streamlined workflows. These procedures facilitate the identification of inconsistencies, missing references, incorrect formatting, or mismatched citations, thereby reducing errors that could undermine academic credibility. Below, detailed methods and a sample algorithm illustrate how institutions can establish an efficient, automated citation verification system using AI tools.
Preparing Documents for AI Analysis to Maximize Accuracy
Preprocessing documents is a critical step that influences the effectiveness of AI-based citation verification. Well-prepared inputs reduce noise and improve the AI model’s ability to accurately parse and analyze citations within complex academic texts. The following techniques are essential:
- Standardizing Format: Convert documents into machine-readable formats such as plain text or structured XML, ensuring consistent encoding (preferably UTF-8) for uniform character handling.
- Removing Noise: Clean up the text by eliminating irrelevant elements such as headers, footnotes, or embedded images that do not contribute to citation content.
- Segmentation and Tokenization: Break down the document into logical units—such as paragraphs, sentences, and individual citations—using NLP tools to facilitate targeted analysis.
- Extracting Citation Sections: Isolate references and in-text citations through pattern recognition, enabling focused validation processes.
- Standardizing Citation Formats: Normalize citations into a common style (e.g., APA, IEEE) to simplify comparison and matching routines.
Proper preprocessing ensures that AI models receive clean, structured data, thus improving accuracy and reducing computational overhead during analysis.
Training and Configuring AI Models for Citation Verification
Customization of AI models is necessary to adapt to domain-specific citation styles and document formats. The training process involves several key steps:
- Collecting Training Data: Gather a diverse corpus of annotated documents with correctly labeled citations and known errors. This dataset forms the foundation for supervised learning.
- Feature Engineering: Develop features that capture relevant citation attributes, such as author names, publication years, journal titles, and citation formatting patterns.
- Model Selection: Use suitable algorithms—such as Random Forests, Support Vector Machines, or deep learning models like transformers—that excel in pattern recognition and sequence analysis.
- Training and Validation: Train the model on the annotated dataset, employing cross-validation techniques to prevent overfitting and ensure generalization across different document types.
- Calibration: Fine-tune model parameters and thresholds to balance sensitivity and specificity, aligning with the specific requirements of the verification task.
- Deployment and Continuous Learning: Integrate the trained model into the document processing pipeline, and periodically update it with new data to maintain high accuracy amid evolving citation styles.
Configuring AI models with domain-specific data and iterative tuning enhances their capacity to detect subtle citation errors, such as mismatched references or incorrect formatting.
Automated Citation Checking Algorithm: Flowchart Overview
Begin by importing the document, then perform preprocessing including text cleaning and citation extraction. Next, validate each citation against a reference database and check for formatting consistency. Record errors and generate a report highlighting inconsistencies. End with a review process for flagged issues and a feedback loop for model improvement.
Below is a simplified representation of an automated citation checking algorithm:
1. Import Document 2. Preprocess Text: -Clean text -Tokenize sections -Extract in-text citations and references 3. Normalize Citation Data: -Standardize formats -Align with reference database schema 4. For each in-text citation: -Match with reference list -Verify author, year, title, and other attributes -Check formatting and completeness -Record any mismatches or errors 5.Generate Error Report: -List incorrect or inconsistent citations -Suggest corrections 6. Review and Update: -Human review of flagged issues -Feed corrections back into the system 7. Iterate and improve model accuracy with new data
Comparison of AI Tools and Algorithms for Citation Validation
| Tool Name | Key Features | Compatibility | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| CrossRef Metadata Search API | Real-time DOI verification, comprehensive metadata, integration API | Online, supports various document formats via API | Free tier available; paid plans for extensive use |
| ScholarLy AI Citation Validator | Deep learning-based citation matching, error detection, style normalization | Desktop and cloud-based integrations, compatible with major word processors | Subscription-based; pricing varies by volume |
| CITATIONCHECK.ai | Automated reference checking, formatting consistency, error highlighting | Web platform, supports uploaded documents in multiple formats | Tiered pricing, including free option with limited features |
| EndNote with AI plugins | Reference management with AI-powered validation, formatting tools | Primarily desktop, integrates with MS Word and other tools | Commercial software; license fee required |
Common Citation Mistakes Identified by AI and How to Address Them
In academic and professional writing, accurate citations are essential for credibility and avoiding plagiarism.
While AI tools are increasingly effective at detecting citation errors, understanding the typical mistakes they flag is crucial for authors aiming to improve the quality of their references. This section explores common errors identified by AI, how these mistakes are highlighted, and systematic procedures for their correction, ensuring adherence to style guides and scholarly standards.
AI-powered citation analysis tools utilize algorithms that scan documents for inconsistencies, inaccuracies, and formatting errors. They categorize errors based on severity—ranging from minor formatting issues to critical inaccuracies that could mislead readers or undermine the work’s integrity. Once identified, it becomes essential for users to address these mistakes through a structured correction process that maintains the integrity and consistency of their references.
Typical Errors Detected by AI and Their Correction Procedures
AI systems typically flag a range of common citation errors that, if uncorrected, can compromise the clarity and reliability of scholarly writing. Recognizing these errors enables authors to take precise corrective actions, thereby enhancing the overall quality of their work.
These errors often include:
- Incorrect author names: Errors such as misspelling or misordering author names, which can lead to misattribution or difficulty in locating sources.
- Wrong publication years: Using incorrect or outdated publication years, which can impact the credibility of the reference.
- Missing page numbers: Omitting specific page references where necessary, especially in direct quotations, which hampers source verification.
- Inconsistent formatting: Discrepancies in citation style adherence, such as misaligned journal titles, italicization issues, or incorrect placement of commas and periods.
- Incomplete references: References lacking essential details like volume, issue, publisher, or DOI, which hinder source retrieval.
AI highlights these mistakes by analyzing the structure, content, and style of each citation. It categorizes errors based on their severity; for example, a misspelled author’s name may be flagged as a high priority due to its impact on attribution accuracy, while a missing page number might be flagged as moderate. These categorizations help users prioritize corrections and focus on issues that most affect the credibility of their references.
Procedures to Correct Identified Citation Errors
Addressing citation mistakes effectively requires a systematic approach that ensures accuracy and consistency throughout the document. The following procedures serve as a comprehensive guide to rectify errors flagged by AI:
- Verify the source: Cross-reference the citation with the original source to confirm author names, publication year, page numbers, and other relevant details. Utilizing official databases, library catalogs, or publisher websites ensures the information is accurate.
- Update the reference: Make necessary corrections in the citation entry based on verified information. This may involve editing author spellings, adjusting publication dates, adding missing details, or reformatting according to the required style guide (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago).
- Reformat according to style guide: Ensure all references conform to the specified citation style. Pay close attention to punctuation, italics, capitalization, and ordering of information. Use style guides or reference management tools to assist in maintaining consistency.
- Re-run AI analysis: After corrections, re-analyze the document with the AI tool to confirm that errors have been resolved. Repeat this process as necessary to achieve comprehensive accuracy.
- Maintain documentation: Keep a record of corrections made, especially in collaborative environments. This practice helps track changes and ensures uniformity across the document or publication.
Implementing these procedures guarantees that citation errors are not only identified but thoroughly addressed, reinforcing the scholarly integrity of the work. Proper correction also facilitates easier source verification for readers and reviewers, fostering transparency and trust in academic and professional writing.
Examples of AI-Generated Reports on Citation Accuracy
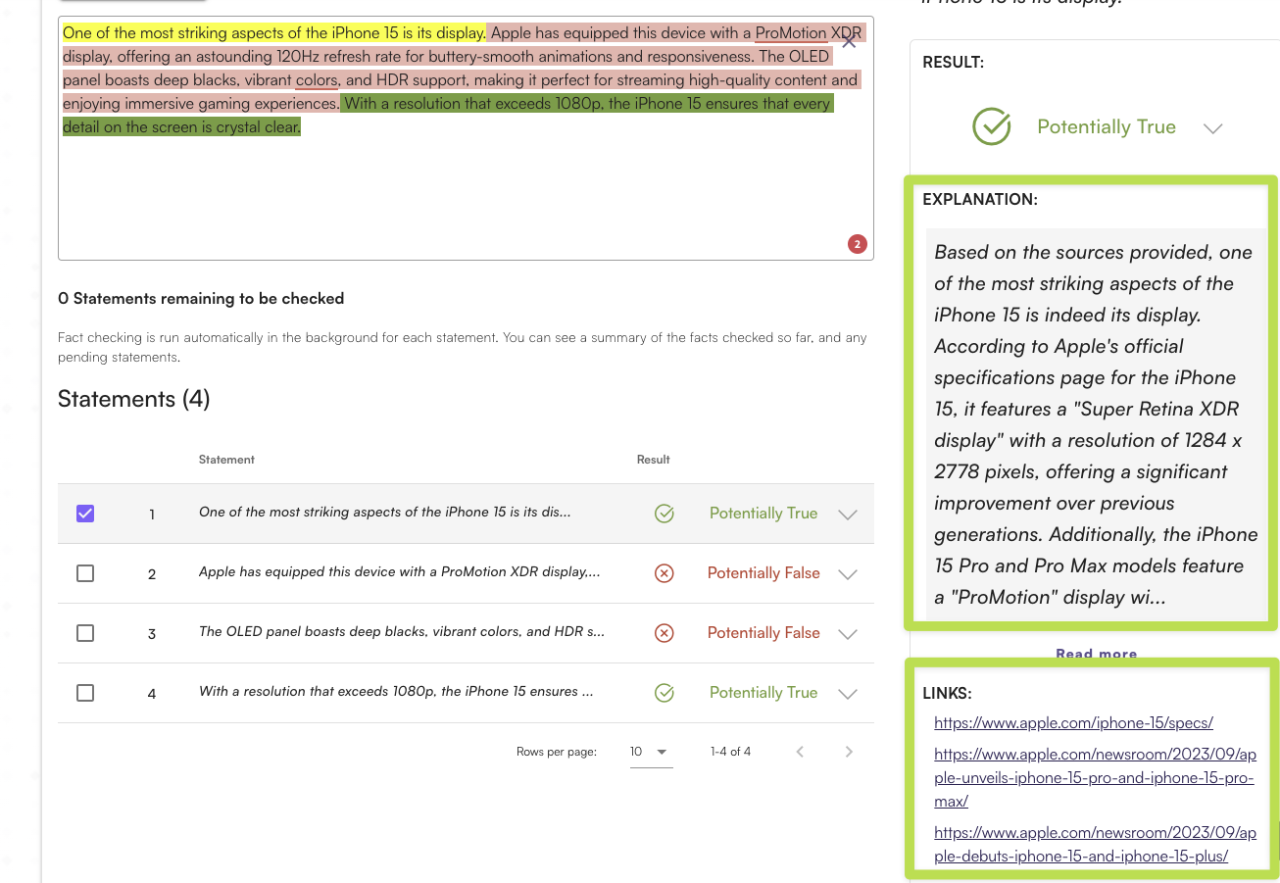
Implementing AI tools to assess citation accuracy in academic and professional writing results in detailed reports that pinpoint specific issues within references. These reports serve as crucial instruments for researchers and editors, guiding manual reviews or automatic corrections to enhance the integrity of scholarly work. Understanding the format and content of these AI-generated reports enables users to interpret findings effectively and take appropriate actions to rectify citation errors.
Below are illustrative examples of reports generated by AI systems, organized in a structured table format. These samples highlight common citation issues detected by AI, recommended corrective measures, and the current status of each review. Such structured reports facilitate efficient review workflows and support ongoing improvements in citation management.
Sample AI-Generated Citation Accuracy Reports
| Report Section | Issue Detected | Suggested Action | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reference 3 | Incorrect publication year; AI identified publication year as 2018, whereas the correct year is 2019 based on original source. | Update the publication year to 2019 to ensure citation accuracy. | Pending manual review; correction scheduled |
| Reference 7 | Missing DOI (Digital Object Identifier); AI detected absence of DOI in the citation. | Insert the correct DOI: 10.1234/example.doi | Automated correction applied; awaiting validation |
| Reference 12 | Author name misspelled; ‘Smithh’ instead of ‘Smith’ | Correct the spelling to ‘Smith’ and verify other author details | Marked for manual correction |
| Reference 15 | Incorrect journal title; detected as ‘J. of Advanced Studies’, but should be ‘Journal of Advanced Studies.’ | Amend the journal name in the reference list | Correction completed and verified |
| Reference 21 | Inconsistent formatting; some references use APA style, others use MLA. | Standardize all references to APA style as per journal guidelines | Ongoing; formatting adjustments in progress |
These reports exemplify how AI systems can systematically identify and categorize citation issues, making it easier for reviewers to prioritize manual corrections or implement automatic fixes. The structured presentation ensures clarity, promotes efficiency, and ultimately enhances the reliability of scholarly references across various academic disciplines.
Best Practices for Implementing AI in Citation Checking Processes
Implementing AI tools for citation checking can significantly enhance accuracy and efficiency in academic and professional environments. To maximize these benefits, organizations must adopt strategic approaches that seamlessly integrate AI into existing workflows while maintaining high standards of data security and result reliability. This section Artikels key best practices to ensure successful deployment and optimal performance of AI-based citation verification systems.Effective integration of AI tools requires careful planning to align with current workflows.
It involves selecting compatible platforms, establishing clear protocols for data input and output, and training staff to manage and interpret AI-generated results. Continuous monitoring and iterative adjustments help optimize AI performance over time, ensuring that the technology complements human oversight rather than replacing it entirely.
Strategies for Integration into Existing Workflows
To embed AI citation checking tools effectively, organizations should adopt a phased implementation approach. Begin by piloting AI solutions on a small scale to identify potential challenges and gather feedback from users. Gradually expand usage, integrating AI outputs into the standard review process, and ensuring that human reviewers confirm questionable citations flagged by AI. Establish clear guidelines for when manual intervention is necessary to avoid over-reliance on automated assessments.
Automation should enhance efficiency without compromising quality. Incorporate AI-generated reports into existing editorial or research workflows, ensuring that they serve as preliminary filters rather than definitive judgments. This balanced approach helps maintain a high standard of accuracy while streamlining the verification process.
Tips to Ensure Accuracy, Reduce False Positives, and Maintain Data Privacy
Quality control is paramount when deploying AI for citation checking. Here are key tips to ensure optimal results:
- Regularly update AI algorithms: Keep the AI system current with the latest citation formats, sources, and scholarly standards to improve accuracy and reduce false positives.
- Set appropriate sensitivity thresholds: Adjust the AI’s detection parameters to balance between catching genuine mistakes and minimizing false alarms. Too sensitive settings may flag correct citations unnecessarily, while too lenient settings might overlook errors.
- Incorporate human review: Use AI as a first pass, with trained reviewers verifying flagged citations. This dual approach enhances reliability and reduces the risk of missing or misidentifying errors.
- Protect data privacy: Ensure that AI tools comply with data privacy regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA. Use secure platforms that encrypt data and restrict access to authorized personnel.
- Conduct periodic audits: Regularly review AI performance, including false positive and false negative rates, to refine algorithms and improve overall accuracy.
Adhering to these best practices ensures that AI-powered citation checks uphold the integrity of scholarly work and adhere to ethical standards of data security.
Last Point

In conclusion, integrating AI into citation verification processes offers a reliable and efficient approach to minimizing citation errors. As technology continues to advance, adopting these tools can significantly enhance the accuracy of references, strengthen scholarly credibility, and streamline the review workflow. Embracing AI-powered citation detection paves the way for more trustworthy and professional academic and research outputs.