Leveraging artificial intelligence to review research findings offers a transformative approach to evaluating data with efficiency and precision. As research datasets become increasingly complex, integrating AI tools provides valuable insights, enhances credibility checks, and streamlines the validation process. This guide explores how AI can be harnessed effectively to elevate research review practices, ensuring thorough and objective evaluations.
From preparing data for analysis to ethical considerations and collaborative review strategies, understanding the role of AI in research assessment equips professionals with the skills to interpret findings accurately. Embracing these techniques fosters a more rigorous and transparent review process, ultimately advancing the quality and reliability of research outcomes.
Understanding the Importance of Reviewing Research Findings with AI
In an era driven by rapid technological advancements, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into research review processes has become increasingly vital. Leveraging AI tools allows researchers and analysts to evaluate vast amounts of data swiftly and accurately, transforming traditional methods into more efficient and reliable workflows. This shift not only accelerates the pace of scholarly and practical discoveries but also enhances the overall quality and credibility of research outcomes.
Utilizing AI in reviewing research findings offers a strategic advantage by assisting users in verifying the credibility, relevance, and integrity of data. Through sophisticated algorithms and machine learning models, AI can identify inconsistencies, detect potential biases, and cross-reference findings against extensive databases of peer-reviewed literature. This capability ensures that research conclusions are grounded in validated and high-quality sources, thus reducing the risk of misinformation and improving decision-making processes in various fields.
Enhancement of Credibility and Relevance Verification
AI-driven tools enable a comprehensive assessment of research data, making it easier to filter out unreliable or outdated information. For instance, natural language processing (NLP) algorithms analyze the content of research papers to determine their relevance to specific topics. Additionally, AI can assess the citation patterns and publication sources to gauge the credibility of the findings, providing a layered approach to validation that manual reviews might not efficiently achieve.
Furthermore, AI systems can automatically flag discrepancies or inconsistencies in datasets, such as statistical anomalies or conflicting results across multiple studies. This capability allows researchers to focus on the most pertinent and validated findings, facilitating more accurate syntheses and interpretations. AI also supports the rapid updating of reviews by continuously scanning new publications and integrating emerging evidence into existing research evaluations.
Scenario Applications and Practical Benefits
In practical scenarios, AI facilitates large-scale literature reviews where manual methods would be prohibitively time-consuming. For example, in clinical research, AI tools can sift through thousands of studies on a particular drug’s efficacy, identifying the most relevant and high-quality evidence to inform policy decisions or treatment guidelines. Similarly, in environmental science, AI algorithms analyze data from multiple sources, such as satellite imagery and sensor reports, to validate climate change models and predictions.
Another notable application is in systematic reviews and meta-analyses, where AI streamlines the extraction of data points, reduces human error, and ensures consistency across datasets. This efficiency not only expedites the review process but also enhances the reproducibility and transparency of findings, fostering greater trust and acceptance within the scientific community.
Integrating AI into research review processes transforms how data credibility and relevance are assessed, leading to more accurate, efficient, and trustworthy outcomes.
Preparing Data and Research Materials for AI Review
Effective preparation of research data and materials is a vital step in harnessing AI tools for comprehensive and accurate analysis. Proper organization, cleaning, and annotation of research documents ensure that AI systems can interpret and process information efficiently, reducing errors and enhancing the quality of insights derived. This process not only streamlines the review workflow but also maximizes the potential of AI to identify relevant patterns, summarize findings, and support decision-making.
Implementing systematic procedures for data preparation ensures compatibility with various AI platforms, facilitates targeted review, and maintains the integrity of the research materials throughout the analysis process. Careful attention to data organization, formatting, and annotation is essential for achieving reliable and actionable outcomes from AI-powered research reviews.
Organizing Research Data for Optimal AI Analysis
Organizing research data involves structuring information in a manner that allows AI systems to quickly locate, interpret, and analyze pertinent details. This includes categorizing data based on research topics, methodologies, outcomes, and sources, which helps in creating a logical hierarchy that mirrors the research framework.
To optimize AI analysis, researchers should implement a consistent file-naming convention, utilize folder hierarchies that reflect research themes, and maintain metadata that describes the content and context of each document. Such organization enhances searchability and facilitates automated extraction of relevant segments during AI review sessions.
- Develop a standardized labeling system for digital files, incorporating elements such as author initials, publication year, and research focus.
- Group related documents into folders categorized by research phase or thematic area, such as data collection, analysis, and conclusions.
- Use metadata tags within documents or file properties to include s, abstract summaries, or key findings for quick filtering.
Cleaning and Formatting Research Documents for AI Compatibility
Preparing research documents for AI review requires cleaning and formatting to ensure compatibility and to facilitate accurate interpretation by AI algorithms. This process involves removing extraneous information, standardizing formats, and correcting inconsistencies that could hinder analysis.
Researchers should convert all documents into machine-readable formats such as plain text, PDF/A, or structured Word files. Removing irrelevant elements like watermarks, headers, footers, and annotations ensures that AI focuses solely on core content. Consistent use of headings, bullet points, and numbered lists enhances readability and segmentation for better AI comprehension.
Ensuring uniform formatting across research materials reduces processing errors and improves the efficiency of AI analysis.
Steps to clean and format research documents include:
- Convert all documents into a preferred, AI-compatible format that preserves text integrity.
- Remove non-essential elements such as images, watermarks, or comments unless they contain critical data.
- Standardize font styles, sizes, and heading hierarchies to create a uniform structure.
- Use clear section headings and subheadings to delineate different parts of the research, such as methodology, results, and discussion.
- Apply consistent citation styles and reference formatting to support accurate cross-referencing during analysis.
Annotating Key Sections for Targeted Review
Annotation involves marking specific sections of research documents to guide AI tools in focusing on critical information areas. Proper annotation enhances targeted review, enabling AI to prioritize essential data such as hypotheses, key findings, limitations, or conclusions.
Annotated research materials facilitate efficient extraction of relevant insights and support focused analysis, saving time and increasing accuracy. This process also aids in training AI models to recognize and interpret important research elements consistently across multiple documents.
Guidelines for effective annotation include:
- Highlighting or tagging key sections such as research questions, hypotheses, results, or limitations using standardized labels or color codes.
- Adding inline comments or metadata tags that specify the importance or context of certain passages.
- Using annotation tools compatible with AI review platforms to create structured annotations that AI can interpret programmatically.
- Ensuring consistency in annotation practices across all materials to enable reliable pattern recognition by AI systems.
For example, tagging the “Results” section with a specific label helps the AI focus on numerical data and statistical significance, while annotating limitations guides the AI in weighing the reliability of findings. This targeted approach streamlines the review process and enhances the depth and precision of AI-supported research analysis.
Techniques for Analyzing Research Findings Using AI

Analyzing research findings with AI involves leveraging advanced algorithms to uncover meaningful insights, patterns, and themes within complex datasets. These techniques enable researchers to process large volumes of data efficiently, ensuring a more thorough and objective interpretation of results. By applying these AI-driven methods, researchers can enhance the accuracy, consistency, and depth of their analyses, leading to more reliable conclusions and informed decision-making.
Adopting effective AI techniques for research analysis involves understanding various approaches that can identify key themes, assess data validity, and synthesize insights. These methods range from natural language processing (NLP) to machine learning models capable of classifying, clustering, or extracting relevant information. Implementing the right combination of techniques depends on the nature of the research data, the specific objectives, and the desired depth of analysis.
Identifying Key Themes and Patterns with AI Algorithms
Spotting recurring themes and patterns within research data is fundamental to extracting valuable insights. AI algorithms, particularly natural language processing (NLP) techniques, facilitate this process by systematically analyzing textual data, such as interview transcripts, survey responses, or literature reviews. Clustering algorithms and topic modeling are among the most effective tools for this purpose.
Clustering algorithms, such as K-means or hierarchical clustering, group similar data points together based on shared features, revealing underlying themes. Topic modeling methods like Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) automatically identify dominant topics within large text corpora, providing a high-level overview of key themes. These approaches help researchers quickly identify prevalent ideas, trends, and areas requiring further exploration.
Assessing the Validity of Research Findings with AI Approaches
Ensuring the credibility and accuracy of research findings is crucial. AI offers various approaches to evaluate the validity of data and conclusions. For instance, anomaly detection algorithms can identify inconsistencies or outliers that may indicate errors or biases in the dataset. Cross-validation techniques in machine learning models help verify the robustness and generalizability of results by testing models on different data subsets.
Furthermore, ensemble methods combine multiple AI models to improve assessment accuracy, reducing the likelihood of false positives or negatives. Comparing results obtained from different algorithms provides a comprehensive perspective on the reliability of findings. These AI-based validation techniques enhance confidence in the research outcomes and support evidence-based decision-making.
Designing Templates for Summarizing Research Insights Generated by AI
Effectively communicating AI-analyzed research insights requires well-structured templates that systematically organize findings. Templates should facilitate clarity, comparability, and ease of interpretation. A typical template may include sections for key themes, patterns identified, validation metrics, and actionable conclusions.
For example, an AI-generated research summary template could comprise:
- Research Objective: Brief description of the study’s purpose.
- Key Themes: List of major topics identified by AI algorithms, with brief descriptions.
- Patterns and Trends: Summary of recurring behaviors or associations detected in the data.
- Validation Metrics: Results from AI validation techniques, such as confidence scores or outlier detection outcomes.
- Conclusions and Recommendations: Data-driven insights and suggested next steps based on AI analysis.
Designing such templates ensures that research insights are presented consistently and comprehensively, enabling stakeholders to grasp complex findings efficiently and make informed decisions based on AI-supported analysis.
Validation and Cross-Verification of Research Results with AI
Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of research findings is a critical step in the research process, especially when leveraging AI for analysis. Cross-verification across multiple AI models enhances confidence in results by identifying consistencies and detecting discrepancies. This process not only strengthens the validity of conclusions but also reveals potential biases or anomalies that may require further investigation. Implementing systematic validation procedures enables researchers to establish robust evidence supporting their hypotheses and ensures that findings are reproducible and trustworthy.Effective validation involves utilizing diverse AI models that employ different algorithms, architectures, or training datasets to analyze the same research data.
This multi-model approach provides a comprehensive perspective, highlighting areas where models agree or diverge. When discrepancies arise, it becomes essential to scrutinize the underlying causes—be it model limitations, data quality issues, or interpretative differences. Paper-based or digital comparison tools, coupled with visualization techniques, aid in synthesizing these insights, making the validation process more transparent and manageable.
Procedures for Cross-Checking Research Conclusions through Multiple AI Models
Cross-checking research results with multiple AI models involves a structured approach to ensure thorough validation:
- Start by selecting diverse AI models that are appropriate for the research context, including different machine learning algorithms such as decision trees, neural networks, and support vector machines.
- Run the same dataset through each model independently, ensuring consistent preprocessing and parameter settings to maintain comparability.
- Collect the outputs, focusing on key metrics such as classification accuracy, confidence scores, or regression errors, depending on the research type.
- Analyze the results to identify areas of agreement, where models produce similar conclusions, and areas of divergence that warrant deeper examination.
- Document the validation outcomes meticulously, noting model-specific strengths and limitations for comprehensive reporting.
Best Practices for Highlighting Discrepancies and Inconsistencies
Discrepancies and inconsistencies in research findings can indicate critical insights or potential issues within the data or methodologies. To effectively manage these, adhere to the following best practices:
- Utilize visual comparison tools such as side-by-side charts, heatmaps, or difference plots to clearly illustrate where models disagree.
- Establish thresholds for acceptable variation, recognizing that some degree of divergence may be natural due to model differences.
- Investigate specific cases or data points where inconsistencies occur, checking for anomalies, outliers, or biases that may influence results.
- Engage in iterative refinement by adjusting model parameters, data preprocessing steps, or feature selection to resolve discrepancies.
- Document all identified inconsistencies, along with the interpretation and actions taken, to maintain transparency and reproducibility.
Generating Comparison Tables for AI Validation Outputs
Comparison tables provide a clear, organized view of how different AI models perform and align in their outputs. They facilitate quick identification of consensus and discrepancies:
| Research Metric | Model A Output | Model B Output | Model C Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 92% | 89% | 91% |
| Confidence Level | 0.85 | 0.78 | 0.83 |
| Key Discrepancies | Model A predicts positive outcome; others predict negative | Disagreement in classification of borderline cases | Minor variations in confidence scores |
This structured comparison enables researchers to delineate areas of agreement, pinpoint potential sources of errors, and make informed decisions about the reliability of findings. When discrepancies are significant, additional validation steps, such as manual review or alternative analytical methods, are recommended to ensure the robustness of conclusions derived with AI.
Ethical and Bias Considerations in AI-Assisted Review

Integrating AI into the research review process brings significant benefits, including increased efficiency and the ability to handle large datasets. However, it also introduces unique ethical challenges and potential biases that must be carefully managed. Recognizing and addressing these issues is essential to maintaining the integrity, objectivity, and credibility of research evaluations when utilizing AI tools.
Ensuring that AI-assisted reviews are conducted responsibly involves understanding the sources of bias, implementing guidelines for objective interpretation, and establishing transparency and reproducibility protocols. These measures help prevent skewed analyses and uphold ethical standards across research assessments.
Identifying Potential Biases Introduced by AI in Research Evaluation
The effectiveness of AI in research review depends on the quality and neutrality of the data it processes. Biases can inadvertently be embedded within AI algorithms through various pathways, including training data, algorithm design, and model assumptions. Recognizing these biases is pivotal in mitigating their influence on research outcomes.
Potential sources of bias include:
- Training Data Bias: AI models trained on datasets that lack diversity or contain historical biases may perpetuate or amplify these biases during analysis.
- Algorithmic Bias: Certain modeling choices or feature selections may favor specific outcomes or perspectives, skewing results.
- Confirmation Bias: AI might reinforce pre-existing assumptions if not properly calibrated, leading to selective interpretation of findings.
To identify such biases, evaluators should conduct comprehensive audits of training datasets, analyze model outputs for patterns indicative of bias, and compare AI-driven insights against human judgments or alternative methods. Regularly updating training data to reflect diverse and representative research can also reduce bias introduction.
Guidelines for Maintaining Objectivity When Interpreting AI-Driven Insights
While AI can uncover valuable insights, it is crucial to interpret these findings within a framework that preserves objectivity and scientific rigor. Clear guidelines help researchers and reviewers avoid over-reliance on automated outputs and ensure balanced evaluations.
Key principles include:
- Cross-Verification: Always corroborate AI recommendations with manual review and domain expertise to validate findings.
- Critical Assessment: Question the assumptions and potential biases inherent in AI outputs, considering alternative explanations.
- Contextual Understanding: Interpret AI findings in light of the broader research context, including existing literature and methodological limitations.
- Documentation: Record decision-making processes and rationale behind accepting or rejecting AI-driven insights to promote transparency.
Implementing these guidelines fosters a culture of critical thinking and reduces the risk of misinterpretation or undue influence from automated analyses.
Methods to Ensure Transparency and Reproducibility of AI-Assisted Reviews
Transparency and reproducibility are cornerstones of credible research review processes, especially when AI technologies are involved. These practices ensure that findings can be independently verified and that the review process remains accountable and ethically sound.
Effective methods include:
- Documenting Data Sources and Preprocessing: Clearly record datasets used, preprocessing steps, and any data augmentation techniques to allow others to replicate the review process.
- Sharing Model Architectures and Parameters: Provide detailed descriptions of AI models, including their configurations, training procedures, and hyperparameters.
- Utilizing Open-Source Tools and Frameworks: Employ transparent, community-supported AI platforms that facilitate auditing and validation by third parties.
- Implementing Version Control: Track changes in datasets, models, and scripts to ensure consistent and reproducible workflows.
- Publishing Audit Trails: Maintain comprehensive logs of all analysis steps, decision points, and rationale throughout the review process.
Adhering to these practices not only enhances the credibility of AI-assisted research evaluations but also aligns with broader open science principles, fostering trust and collaborative improvement within the research community.
Enhancing Collaborative Review Processes with AI
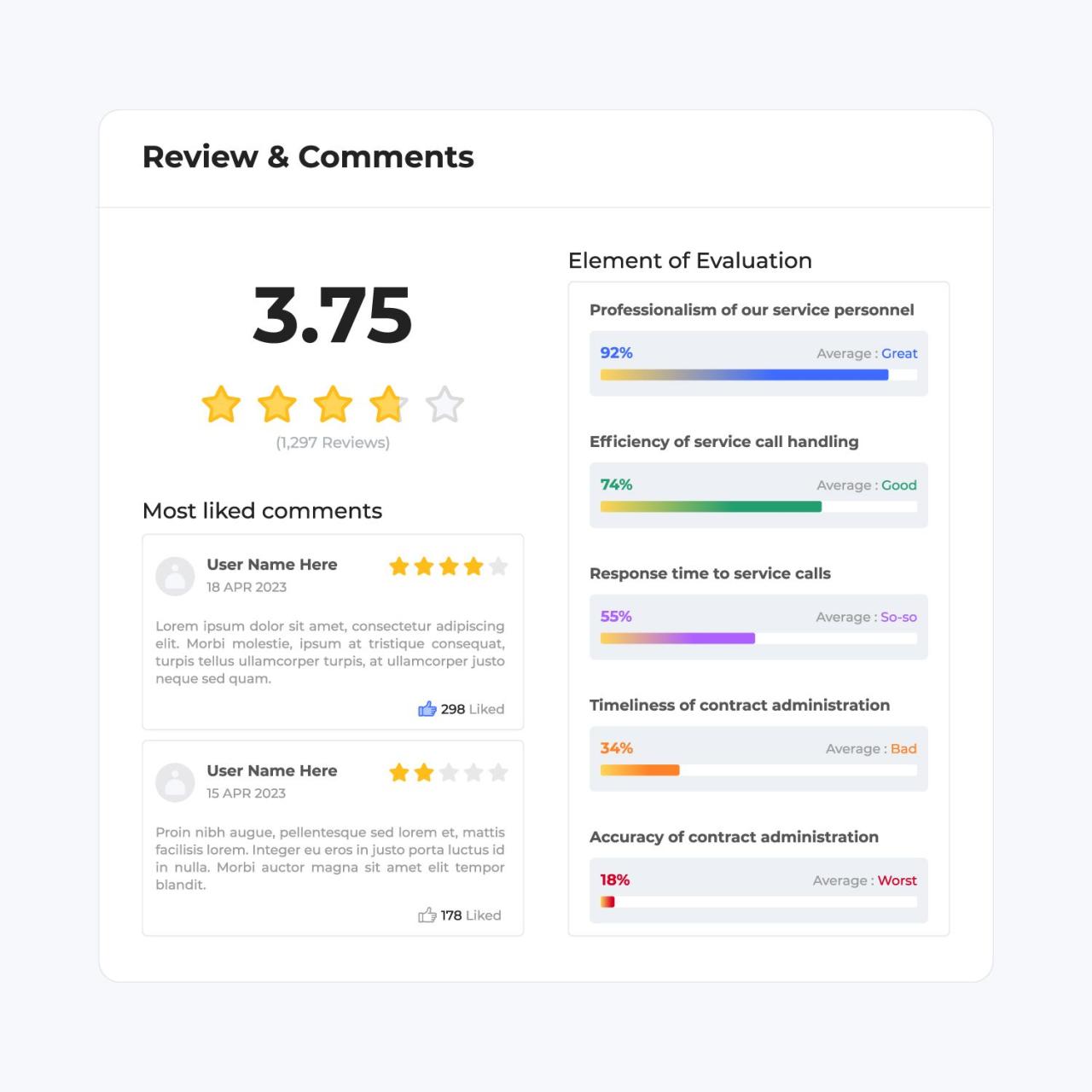
Effective collaboration in research review processes is fundamental to ensure comprehensive analysis and quality assurance. Integrating AI tools into collaborative review workflows offers new opportunities for teams to evaluate research findings more efficiently, accurately, and inclusively. By leveraging AI alongside human expertise, research teams can streamline decision-making, foster consensus, and enhance the overall robustness of their evaluations.
This section explores strategies for engaging multiple reviewers and AI tools in joint analysis, organizing the sharing of AI-generated insights across teams, and establishing procedures for feedback incorporation to refine research assessments collaboratively. These approaches aim to build a cohesive, transparent, and dynamic review environment that maximizes the strengths of both human judgment and artificial intelligence.
Strategies for Involving Multiple Reviewers and AI Tools in Joint Analysis
Effective collaboration begins with clear strategies to integrate human reviewers and AI systems seamlessly into the research evaluation process. Engaging multiple reviewers ensures diverse perspectives and expertise, while AI tools provide consistent, data-driven insights that support each reviewer’s assessment.
- Establish roles for AI and human reviewers to clarify the scope of AI assistance versus human judgment, such as initial data screening by AI followed by detailed expert analysis.
- Encourage the use of AI to generate preliminary summaries, highlight key findings, or identify potential inconsistencies, which reviewers can then interpret and validate.
- Use collaborative platforms that allow simultaneous access to AI outputs and enable reviewers to annotate, comment, and discuss findings in real-time, fostering interactive review sessions.
- Integrate AI feedback mechanisms that adapt based on reviewer inputs, ensuring the system’s outputs evolve to better support the team’s specific research domain and review criteria.
Organizing Steps for Sharing AI Review Outputs Across Teams for Consensus Building
Sharing AI-generated review results effectively across team members is vital for building consensus and ensuring transparency. Structured dissemination and collaborative interpretation of AI outputs help prevent misunderstandings and promote collective decision-making.
- Standardize the format of AI review reports, including summaries of findings, flagged issues, and confidence levels, to ensure clarity and consistency across teams.
- Implement centralized repositories or collaborative platforms where AI outputs are uploaded automatically, enabling easy access and version control.
- Schedule regular review meetings or discussion sessions focused on AI outputs, encouraging team members to discuss discrepancies, validate insights, and share interpretations.
- Use visualizations such as heatmaps, dashboards, or annotated reports to facilitate understanding of complex AI analyses and highlight areas requiring further scrutiny.
- Maintain detailed logs of review decisions and AI input adjustments to track consensus evolution and support accountability.
Procedures to Incorporate Feedback and Refine Research Evaluation Collaboratively
Continuous improvement of the review process relies on effective procedures for collecting feedback, implementing modifications, and refining AI-assisted evaluations. Collaborative feedback loops help align AI outputs with human expectations and research standards.
- Establish formal channels for reviewers to submit feedback on AI recommendations, including usability, accuracy, and relevance concerns.
- Integrate iterative review cycles where AI outputs are refined based on collective reviewer input, enabling the system to learn from diverse perspectives.
- Hold debrief sessions to analyze discrepancies between AI suggestions and human judgments, identifying potential biases or gaps in the AI model.
- Maintain documentation of feedback and subsequent adjustments to AI algorithms or review protocols to support transparency and continuous learning.
- Encourage a culture of open communication, where reviewers feel empowered to challenge AI outputs and contribute to the enhancement of collaborative review processes.
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, adopting AI-driven methods for reviewing research findings significantly enhances the accuracy, efficiency, and transparency of the evaluation process. By carefully preparing data, applying robust analysis techniques, and maintaining ethical standards, researchers and reviewers can unlock deeper insights and ensure trustworthy conclusions. Embracing these innovative approaches paves the way for more rigorous and collaborative research endeavors in the future.